मैकेनिकल इक्विलिब्रियम
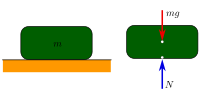
क्लासिकल मैकेनिक्स में, कौनों पार्टिकल मैकेनिकल इक्विलिब्रियम (अंग्रेजी: mechanical equilibrium) में होला अगर ओह पर नेट फोर्स जीरो होखे।[1]:39 एकरे एक्स्टेंशन के रूप में, कौनों कई पार्ट से बनल फिजिकल सिस्टम मैकेनिकल इक्विलिब्रियम में होला अगर ओकरे सगरी पार्ट सभ पर लागे वाला नेट फोर्स जीरो होखे[1]:45–46[2]
संदर्भ
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 John L Synge; Byron A Griffith (1949). Principles of Mechanics (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- ↑ Beer FP, Johnston ER, Mazurek DF, Cornell PJ, and Eisenberg, ER (2009). Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics (9th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 158.
{cite book}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)