Johanniskräuter
| Johanniskräuter | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
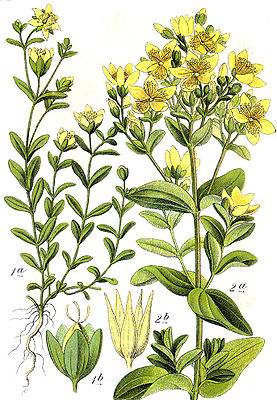
Illustration aus Sturm: links Niederliegendes Johanniskraut (Hypericum humifusum) | ||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||
| Hypericum | ||||||||||||
| L. |
Johanniskräuter (Hypericum) ist eine Pflanzengattung innerhalb der Familie der Johanniskrautgewächse (Hypericaceae).[1] Die etwa 500 Arten sind fast weltweit verbreitet.[2] Bekannt ist vor allem das als Antidepressivum medizinisch genutzte Echte Johanniskraut (Hypericum perforatum).
Beschreibung
Vegetative Merkmale
Die Hypericum-Arten gedeihen sowohl als einjährige, mehrjährige und ausdauernde krautige Pflanzen mit Wuchshöhen ab 5 Zentimetern wie auch als Sträucher und kleine Bäume mit Wuchshöhen von bis zu 12 Metern.
Die gegenständig angeordneten Laubblätter sind einfach und bei einer Länge von 1 bis 8 Zentimetern eiförmig.

Generative Merkmale
Die zwittrigen Blüten sind bei Durchmessern von 0,5 bis 6 Zentimetern radiärsymmetrisch mit doppelter Blütenhülle. Es sind je fünf (selten vier) Kelch- und Kronblätter vorhanden. Die vielen, meist 70, selten bis zu 120 Staubblätter sind meist zu drei bis fünf Bündeln zusammengefasst. Es sind selten zwei, meist drei bis fünf freie Griffel vorhanden oder sie sind teilweise bis vollständig untereinander verwachsen.[3]
Es wird in der Regel eine scheidewandspaltige (septizide) Kapselfrucht gebildet, die sich nach ihrer Austrocknung öffnet und zahlreiche kleine Samen entlässt; bei einigen wenigen Arten ist die Frucht beerenähnlich fleischig.[3]
Systematik und Verbreitung
Die Gattung Hypericum wurde 1753 von Carl von Linné in Species Plantarum mit Diagnose in Genera Plantarum[4] aufgestellt.[5]
Die Gattung Hypericum ist fast weltweit verbreitet. Arten fehlen allein in Wüsten, arktischen Regionen und im tropischen Tiefland.
Innere Systematik
Die Gattung Hypericum ist seit 2012 in 36 Sektionen gegliedert:[6][7][8][9]
- Sektion Adenosepalum Spach
- Sektion Adenotrias (Jaub. & Spach) R.Keller
- Sektion Androsaemum (Duhamel) Godron
- Sektion Arthrophyllum Jaub. & Spach
- Sektion Ascyreia Choisy
- Sektion Brathys (Mutis ex L. f.) Choisy
- Sektion Bupleuroides Stef.
- Sektion Campylopus Boiss.
- Sektion Campylosporus (Spach) R.Keller
- Sektion Concinna N.Robson
- Sektion Coridium Spach
- Sektion Crossophyllum Spach
- Sektion Drosocarpium Spach
- Sektion Elodeoida N.Robson
- Sektion Graveolentia N.Robson
- Sektion Heterophylla N.Robson
- Sektion Hirtella Stef.
- Sektion Humifusoideum R.Keller
- Sektion Hypericum
- Sektion Inodora Stef.
- Sektion Monanthema N.Robson
- Sektion Myriandra (Spach) R.Keller
- Sektion Oligostema (Boiss.) Stef.
- Sektion Olympia (Spach) Nyman
- Sektion Origanifolia Stef.
- Sektion Psorophytum (Spach) Nyman
- Sektion Roscyna (Spach) R.Keller
- Sektion Sampsonia N.Robson
- Sektion Santomasia (N.Robson) N.Robson
- Sektion Taeniocarpium Jaub. & Spach
- Sektion Takasagoya (Y.Kimura) N.Robson
- Sektion Triadenioides Jaub. & Spach
- Sektion Trigynobrathys (Y.Kimura) N.Robson
- Sektion Tripentas (Casp.) N.Robson
- Sektion Umbraculoides N.Robson
- Sektion Webbia (Spach) R.Keller
Arten und ihre Verbreitung



































- Hypericum abilianum N.Robson: Sie kommt nur in Angola vor.[2]
- Hypericum aciculare Kunth: Sie kommt in Ecuador und Peru vor.[2]
- Hypericum aciferum (Greuter) N.Robson: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im südwestlichen Kreta vor.[2]
- Hypericum acmosepalum N.Robson: Sie gedeiht in Höhenlagen von 900 bis 2700 Metern in den chinesischen Provinzen nordwestliches bis westliches Guangxi, nordwestliches bis südwestliches Guizhou, südwestliches Sichuan sowie Yunnan.[1]
- Hypericum acostanum N.Robson: Sie kommt nur im südlichen Ecuador vor.[2]
- Hypericum addingtonii N.Robson: Sie kommt in Yunnan vor.[1]
- Hypericum adenotrichum Spach: Sie kommt in der westlichen und zentralen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum adpressum W.P.C. Barton: Sie kommt in den nördlichen, zentralen und östlichen Vereinigten Staaten vor.[2]
- Ägyptisches Johanniskraut (Hypericum aegypticum L.): Es kommt im Mittelmeerraum in drei Unterarten vor[10], darunter:
- Hypericum aegypticum subsp. webbii (Spach) N.Robson: Diese Unterart kommt auf Sizilien, Sardinien, Kreta und in Griechenland vor.[10]
- Hypericum aethiopicum Thunb.: Die zwei Unterarten sind vom südlichen tropischen Afrika bis ins Südliche Afrika verbreitet.[2]
- Hypericum afrum Lam.: Sie kommt vom nördliches Algerien bis nordwestlichen Tunesien vor.[2]
- Hypericum albiflorum (Hub.-Mor.) N.Robson: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in der südwestlichen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum amblycalyx Coust. & Gand.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im östlichen Kreta vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum amblysepalum Hochst.: Sie kommt im Gebiet von Israel, Jordanien, Syrien, dem Libanon, in Irak, im Iran und in der Türkei vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum anagalloides Cham. & Schltdl.: Sie ist vom südwestlichen Kanada bis Baja California verbreitet.[2]
- Hypericum andinum Gleason: Sie kommt in Bolivien und Peru vor.[2]
- Hypericum andjerinum Font Quer & Pau: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im nördlichen Marokko vor.[2]
- Blut-Johanniskraut, Mannsblut (Hypericum androsaemum L.)
- Hypericum annulatum Moris: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten auf der Balkan-Halbinsel, in Sardinien, im nordöstlichen und östlichen tropischen Afrika und auf der Arabischen Halbinsel vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum aphyllum Lundell: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Belize vor.[2]
- Hypericum apiculatum (N.Robson) Sennikov: Sie kommt auf der Krim, von der Türkei bis zum nordwestlichen Iran und bis Zentralasien vor.[2]
- Hypericum apocynifolium Small: Sie kommt in den zentralen und südöstlichen USA vor.[2]
- Hypericum apricum Kar. & Kir.: Sie kommt in Zentralasien vor.[2]
- Hypericum arbuscula Standley & Steyerm.: Sie kommt in Mexiko und Guatemala vor.[2]
- Hypericum arenarioides A.Rich.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur vom westlichen bis westlich-zentralen Kuba vor.[2]
- Hypericum armenum Jaub. & Spach: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von der östlichen Türkei bis zum nördlichen Iran vor.[2]
- Hypericum asahinae Makino: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf der japanischen Insel Honshu vor.[2]
- Hypericum ascyron L.: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten im gemäßigten Asien und vom östlichen Kanada bis zu den USA vor.[2]
- Hypericum asperuloides Czern. ex Turcz.: Sie kommt im nördlichen Kaukasusraum vor.[2]
- Hypericum asperulum Jaub. & Spach: Sie kommt vom nördlichen Irak bis nordwestlichen Iran vor.[2]
- Hypericum asplundii N.Robson: Sie kommt in Ecuador vor.[2]
- Hypericum assamicum S.N.Biswas: Dieser Endemit kommt nur Assam vor.[2]
- Hypericum athoum Boiss. & Orph.: Sie kommt nur im nordöstlichen Griechenland vor.[2]
- Hypericum atomarium Boiss.: Sie kommt vom südöstlichen Griechenland und von Inseln der Ägäis bis zur westlichen und südwestlichen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum attenuatum Fisch. ex Choisy: Sie kommt vom südlichen Sibirien bis China vor.[2]
- Hypericum aucheri Jaub. & Spach: Sie kommt in Bulgarien, Griechenland und in der Türkei vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum augustini N.Robson: Sie gedeiht in Höhenlagen von 1200 bis 1700 Metern in den chinesischen Provinzen südliches Yunnan (nur in Jinghong sowie Shiping) und südwestliches Guizhou (nur in Anlong) vor.[1]
- Hypericum auriculatum (N.Robson & Hub.-Mor.) N.Robson: Sie kommt nur in der südlichen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum australe Ten.: Sie kommt auf den Balearen, in Frankreich, Korsika, Italien, Sardinien, Sizilien, in Marokko, Algerien und Tunesien vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum austrobrasiliense Vog.Ely, Boldrini & Bordignon: Sie wurde 2015 aus dem südlichen Brasilien erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum austroyunnanicum L.H.Wu & D.P.Yang: Sie kommt im westlichen Yunnan vor.[2]
- Hypericum aviculariifolium Jaub. & Spach: Sie kommt nur in der Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum baccharoides Cuatrec.: Sie kommt vom nordöstlichen Kolumbien bis nordwestlichen Venezuela vor.[2]
- Balearen-Johanniskraut (Hypericum balearicum L.): Es kommt ursprünglich nur auf den Balearen vor.[2]
- Hypericum balfourii N.Robson: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im nordnordöstlichen Sokotra vor.[2]
- Hypericum barbatum Jacq.: Sie kommt nur in Süd-Italien, in Österreich und auf der Balkan-Halbinsel vor.[2]
- Hypericum beamanii N.Robson: Sie kommt in Guatemala vor.[2]
- Hypericum beanii N.Robson: Sie kommt in den chinesischen Provinzen Yunnan sowie Guizhou vor.[2]
- Hypericum beccarii N.Robson: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Sumatra bis zum westlichen Java vor.[2]
- Hypericum bellum H.L. Li: Sie kommt vom indischen Bundesstaat Arunachal Pradesh bis China vor.[2]
- Hypericum benghalense S.N. Biswas: Sie kommt im indischen Bundesstaat Westbengalen vor.[2]
- Hypericum bequaertii De Wild.: Sie kommt in Zaire, Kenia und Uganda vor.[2]
- Hypericum bifurcatum N.Robson:Sie kommt in Neuguinea vor.[2]
- Hypericum bilgehan-bilgilii Basköse & Savran: Sie wurde 2018 aus der Türkei erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum bithynicum Boiss.: Sie kommt in der Türkei und in Transkaukasien vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum boehlingraabei Kit Tan, Iatrou, Vold & Strid: Sie kommt in Griechenland vor.[2]
- Hypericum bolivaricum N.Robson: Sie kommt in Kolumbien vor.[2]
- Hypericum bordignonii Vog.Ely & Boldrini: Sie wurde 2015 aus Brasilien erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum boreale Britton: Sie kommt vom zentralen sowie östliches Kanada bis zur nördlich-zentralen und östlichen USA vor.[2]
- Hypericum bourgaei (Boiss.) N.Robson: Sie kommt von der westlich-zentralen bis in die zentrale Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum brachyphyllum (Spach) Steud.: Sie kommt in den südöstlichen USA vor.[2]
- Hypericum brasiliense Choisy (Syn.: Hypericum anceps Larranaga): Brasilien bis Bolivien und bis zum nördlichen Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum brevistylum Choisy: Westliches Südamerika bis nordwestliches Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum bryoides Gleason: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum buckleyi M.A.Curtis: Östliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum bupleuroides Stef.: Nordöstliche Türkei bis westliches Transkaukasien.[2]
- Hypericum caespitosum Cham. & Schltdl.: Zentrales und südlich-zentrales Chile.[2]
- Hypericum callacallanum N.Robson: Nördliches Peru.[2]
- Hypericum callithyrsum Coss.: Nördliches Marokko und südliches Spanien.[2]
- Großkelchiges Johanniskraut, Immergrünes Johanniskraut (Hypericum calycinum L.): Südöstliches Bulgarien bis zur Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum campestre Cham. & Schltdl.: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten vom südlichen Brasilien bis zum nordöstlichen Argentinien vor.[2]
- Hypericum canadense L.: Sie kommt in Kanada und in den USA vor.[11][2] Eingebürgert ist es auf Heideflächen in Irland und den Niederlanden.
- Hypericum canariense L.: Sie kommt auf Madeira und auf den Kanarischen Inseln vor.[2]
- Hypericum capitatum Choisy: Sie kommt in zwei Varietäten in der südlichen und südöstlichen Türkei und im Gebiet von Libanon und Syrien vor.[2]
- Hypericum caprifoliatum Cham. & Schltdl.: Sie kommt vom südlichen Brasilien bis Argentinien vor.[2]
- Hypericum caprifolium Boiss.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Spanien vor.[2]
- Hypericum caracasanum Willd.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten im nordwestlichen und nördlichen Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum cardiophyllum Boiss.: Sie kommt von der südsüdöstlichen Türkei bis ins nordwestliche Syrien vor.[2]
- Hypericum cardonae Cuatrec.: Costa Rica bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum carinatum Griseb.: Südliches Brasilien bis nördliches Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum carinosum R.Keller: Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum cassiopiforme N.Robson: Sie kommt nur im nördlichen Peru vor.[2]
- Hypericum castellanoi N.Robson: Sie kommt von Kolumbien bis ins nordwestliche Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum cavernicola L.B.Sm.: Sie kommt nur in Uruguay vor.[2]
- Hypericum cerastoides (Spach) N.Robson: Sie kommt in Bulgarien, Nordmazedonien, Griechenland, der europäischen Türkei und Anatolien vor.[10]
- Hypericum chamaemyrtus Triana & Planchon: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Kolumbien bis ins nordwestliche Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum chapmanii W.P.Adams: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im nordwestlichen Florida vor.[2]
- Hypericum choisyanum Wallich ex N.Robson: Nördliches Pakistan bis China.[2]
- Hypericum cistifolium Lam.: Südöstliche USA bis östliches Texas.[2]
- Hypericum coadunatum C.Sm. ex Link: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf Gran Canaria vor.[2]
- Hypericum cohaerens N.Robson: Guizhou, Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum collenetteae N.Robson: Westliches Saudi-Arabien.[2]
- Hypericum collinum Schltdl. & Cham.: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum concinnum Benth.: Nördliches und zentrales Kalifornien.[2]
- Hypericum conjungens N.Robson: Südwestliches Tansania bis Sambia.[2]
- Hypericum connatum Lam.: Bolivien bis Brasilien und nördliches Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum cordifolium Choisy: Zentrales und östliches Nepal.[2]
- Hypericum cordiforme A.St.-Hil. (Syn.: Hypericum cordatum (Vell.) N.Robson): Brasilien.[2]
- Quirlblättriges Johanniskraut (Hypericum coris L.): Sie kommt nur in Südost-Frankreich, in Nord-Italien und in der Schweiz vor.[2]
- Hypericum costaricense N.Robson: Costa Rica bis Panama.[2]
- Hypericum crenulatum Boiss. (Syn.: Hypericum musadoganii Yild.): Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum crux-andreae (L.) Cr.: Östliche USA bis östliches Texas.[2]
- Hypericum cuatrecasii Gleason: Zentrales Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum cuisinii W.Barbey: Sie kommt nur in Griechenland, Kreta, auf Inseln der Ägäis und in der westlichen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum cumulicola (Small) W.R Adams: Küste von Florida.[2]
- Hypericum curvisepalum N.Robson: China.[2]
- Hypericum cycladicum Trigas: Sie wurde 2018 von der griechischen Insel Andros erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum cymbiferum Boiss. & Balansa: Westlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum cymobrathys N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum daliense N.Robson: Nördliches Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum davisii N.Robson: Östliche Türkei bis nordwestlicher Iran.[2]
- Hypericum decaisneanum Coss. & Daveau: Nordöstliches Libyen.[2]
- Hypericum decandrum Turcz.: Ecuador bis nördliches Peru.[2]
- Hypericum delphicum Boiss. & Heldr.: Sie kommt nur auf den griechischen Inseln Euböa und Andros vor.[2]
- Hypericum densiflorum Pursh: Sie kommt in zwei Varietäten und den östlichen Vereinigten Staaten vor.[2]
- Hypericum densifolium P.D.Sell: Sie wurde 2018 aus Großbritannien erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum denticulatum Walter: New York bis Tennessee und Alabama.[2]
- Hypericum denudatum A.St.Hil.: Südliches Brasilien bis Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum dichotomum Lam.: Hispaniola.[2]
- Hypericum diosmoides Griseb.: Kuba bis Puerto Rico.[2]
- Hypericum dogonbadanicum Assadi: Südwestlicher Iran.[2]
- Hypericum dolabriforme Vent.: Östlich-zentrale USA.[2]
- Hypericum drummondii (Grev. & Hook.) Torrey & A.Gray: Zentrale und östliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum dyeri Rehder: Nördliches Pakistan bis Nepal.[2]
- Hypericum eastwoodianum I.M.Johnston: Sie kommt in Mexiko vor.[2]
- Hypericum edisonianum (Small) W.P.Adams: Sie kommt nur in Florida vor.[2]
- Hypericum ekeri E.Yüce & Aytaç: Sie wurde 2017 aus der Türkei erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum ekmanii A.H.Lioger: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in der Dominikanischen Republik vor.[2]
- Hypericum elatoides R.Keller: China.[2]
- Zierliches Johanniskraut (Hypericum elegans Stephan ex Willd.): Mitteleuropa bis zur Türkei und Sibirien.[2]
- Hypericum eleonorae Jelen.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im südöstlichen Armenien vor.[2]
- Hypericum ellipticum Hook.: Östliches Kanada bis USA.[2]
- Hypericum elodeoides Choisy: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten vom Himalaja bis in das südliche China vor.[2]
- Sumpf-Johanniskraut (Hypericum elodes L.): Es kommt in West- und Südwesteuropa, von Portugal und Schottland bis Deutschland und Italien und auf den Azoren vor.[2]
- Hypericum elongatum Ledeb. ex Rchb.: Sie kommt in vier Varietäten von der Türkei bis ins nordwestliche China und auf der Krim vor.[2]
- Krähenbeerenblättriges Johanniskraut (Hypericum empetrifolium Willd.): Es kommt in drei Unterarten von Griechenland bis zur westlichen Türkei und dem nordöstlichen Libyen und im nördlichen Albanien vor.[2]
- Hypericum enshiense L.H.Wu & F.S.Wang: Hubei.[2]
- Hypericum epigeium R. Keller: Mexiko bis Guatemala.[2]
- Hypericum erectum Thunb. (Syn.: Hypericum chejuense S.-J.Park & K.J.Kim): Sie kommt in drei Varietäten und in mindestens sieben Formen vom südlichen China und südlichen Sachalin bis zum gemäßigten Ostasien vor.[2]
- Hypericum ericoides L.: Sie kommt nur im östlichen und südöstlichen Spanien vor.[2]
- Hypericum erythreae (Spach) Steud.: Sie kommt vom südöstlichen South Carolina bis zum südöstlichen Georgia vor.[2]
- Hypericum espinalii N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum faberi R.Keller: Zentrales und östliches China.[2]
- Hypericum fanjingense N.Robson: Guizhou und Hunan.[2]
- Hypericum fasciculatum Lam.: Südöstliche USA und Kuba.[2]
- Hypericum fieriense N.Robson: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf Sokotra vor.[2]
- Hypericum fissurale Woron.: Nordöstliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum foliosum Aiton: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf den Azoren vor.[2]
- Hypericum formosanum Maxim.: Nördliches Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum formosissimum Takht.: Südöstliche Türkei bis Transkaukasien.[2]
- Hypericum formosum Kunth: Nördliches und zentrales Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum forrestii (Chittenden) N.Robson: China bis nordöstliches Myanmar.[2]
- Hypericum fosteri N.Robson: Nordöstliches Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum fragile Heldr. & Sart. ex Boiss.: Sie kommt nur in Ost-Griechenland vor.[2]
- Hypericum frondosum Michx.: Südöstliche USA bis Texas.[2]
- Hypericum fuertesii Urban: Zentrales und südwestliches Hispaniola.[2]
- Hypericum fursei N.Robson: Nördlicher Iran.[2]
- Hypericum furusei N.Robson: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf der japanischen Insel Hokkaido vor.[2]
- Hypericum gaitii Haines: Östliches und südliches Indien.[2]
- Hypericum galinum S.F.Blake: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum galioides Lam.: Südöstliche USA bis östliches Texas.[2]
- Hypericum garcieae Pierce: Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum geminiflorum Hemsley: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Taiwan bis Luzon vor.[2]
- Hypericum gentianoides (L.) Britton: Sie kommt ursprünglich im östlichen Kanada und in der zentralen und östlichen USA vor und ist in Frankreich und in Südamerika ein Neophyt.[11]
- Hypericum gladiatum N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum glandulosum Aiton: Madeira, Kanarische Inseln.[2]
- Hypericum gleasonii N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum globuliferum R.Keller: Madagaskar.[2]
- Hypericum gnidiifolium A. Rich.: Äthiopien.[2]
- Hypericum gnidioides Seemann: Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama.[2]
- Hypericum goyanesii Cuatrec.: Zentrales Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum gracilipes Stapf ex C.Fischer: Assam bis südöstliches Bangladesch.[2]
- Hypericum graciliramum R.Ortiz: Sie wurde 2018 aus Großbritannien erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum gracillimum Koidz.: Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum gramineum G. Forster: Assam bis Taiwan, Neuguinea, Neukaledonien und Australien bis Neuseeland.[2]
- Hypericum grandifolium Choisy: Madeira, Kanarische Inseln.[2]
- Hypericum graveolens Bucklcy: Tennessee und North Carolina.[2]
- Hypericum griffithii Hook. f. & Thoms, ex Dyer: Östlicher Himalaja bis südöstliches Tibet.[2]
- Hypericum gymnanthum Engelm. & A.Gray: Sie ist in dem USA, in Guatemala bis Honduras und auf den Azoren beheimatet und kommt als Neophyt in Polen vor.[2]
- Hypericum hachijyoense Nakai: Japan.[2]
- Hypericum hakonense Franch. & Savat.: Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum haplophylloides Halácsy & Bald.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten im südlichen Albanien vor.[2]
- Hypericum harperi R. Keller: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum hartwegii Benth.: Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum havvae Güner: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum hedgei N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum helianthemoides (Spach) Boiss.: Südöstliche Türkei bis Turkmenistan und Iran.[2]
- Hypericum hengshanense W.T.Wang: Südöstliches China.[2]
- Hypericum henryi H. Léveillé & Vaniot: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten von China bis Indochina und auf Sumatra vor.[2]
- Hypericum heterophyllum Vent.: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum himalaicum N.Robson: Nördliches Pakistan bis China.[2]
- Bocks-Johanniskraut (Hypericum hircinum L.): Es kommt in fünf Unterarten vom Mittelmeerraum bis zur Arabischen Halbinsel vor.[2]
- Behaartes Johanniskraut (Hypericum hirsutum L.): Es kommt im nördlichen Algerien und von Europa bis China und zum Iran vor.[2]
- Hypericum hirtellum (Spach) Boiss.: Irak und Iran.[2] Es gibt zwei Varietäten.[2]
- Hypericum hispanicum (Pau) M.A.Alonso, Agulló, J.L.Villar, Juan & M.B.Crespo: Südöstliches Spanien.[2]
- Hypericum hookerianum Wight & Am.: Südliches Indien, Nepal bis Indochina.[2]
- Hypericum horizontale N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum hubeiense L.H.Wu & D.P.Yang: Hubei.[2]
- Hypericum huber-morathii N.Robson: Südwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum humbertii Staner: Südwestliches Uganda bis Burundi.[2]
- Hypericum humboldtianum Steud.: Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Niederliegendes Johanniskraut (Hypericum humifusum L.): Europa bis Nordwestafrika und Makaronesien.[2]
- Hypericum hypericoides (L.) Cr.: USA bis Honduras, Karibik.[2] Es gibt drei Unterarten.[2]
- Hypericum hyssopifolium Chaix: Sie kommt in Spanien, Frankreich, Italien, auf der Balkan-Halbinsel, in Armenien und in der Ukraine vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum icaricum Kit Tan: Sie wurde 2018 von der östägäischen Insel Ikaria erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Hypericum ichelense N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum imbricatum Poulter: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum irazuense Kuntze ex N.Robson: Costa Rica und Panama.[2]
- Hypericum iwate-littorale H.Koidz.: Nordöstliches Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum japonicum Thunb. (Syn.: Hypericum jeongjocksanense S.-J.Park & K.-J.Kim): Indischer Subkontinent bis zu den Kurilen und Australasien.[2]
- Hypericum jaramilloi N.Robson: Costa Rica und Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum jovis Greuter: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Kreta vor.[10]
- Hypericum juniperinum Kunth: Sie kommt in Kolumbien und Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum kalmianum L.: Östliches Kanada bis nordöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum kamtschaticum Ledeb.: Russlands Ferner Osten bis Japan.[2]
- Hypericum karjaginii Rzazade: Türkei bis nordwestlicher Iran.[2]
- Hypericum kawaranum N.Robson: Nördliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum kelleri Bald.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Kreta vor.[10]
- Hypericum kiboense Oliv.: Gebirge des östlichen tropischen Afrika.[2]
- Hypericum killipii N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum kimurae N.Robson: Westliches Hokkaido.[2]
- Hypericum kinashianum Koidz.: Honshu und Kyushu.[2]
- Hypericum kingdonii N.Robson: Arunachal Pradesh bis Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum kitamense (Y.Kimura) N.Robson: Nordwestliches Hokkaido.[2]
- Hypericum kiusianum Koidz.: Südliches und südlich-zentrales Japan.[2] Es gibt zwei Varietäten.
- Hypericum kotschyanum Boiss.: Südliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum kouytchense H.Léveillé: Guizhou und Guangxi.[2]
- Hypericum kurodakeanum N.Robson: Nördliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum lacei N.Robson: Myanmar.[2]
- Hypericum lagarocaule N.Robson: Sichuan.[2]
- Hypericum lalandii Choisy: Nigeria, südlicher Sudan bis südliches Afrika, Madagaskar.[2]
- Hypericum lancasteri N.Robson: China.[2]
- Hypericum lanceolatum Lam.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten auf den Komoren und auf Réunion vor.[2]
- Hypericum lancifolium Gleason: Nordöstliches Kolumbien und nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum lancioides Cuatrec.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten vom nordwestlichen Venezuela bis Ecuador vor.[2]
- Hypericum lanuginosum Lam.: Südliche Türkei bis zur Sinai-Halbinsel, Zypern.[2]
- Hypericum laricifolium Juss.: Nordwestliches Venezuela bis Peru.[2]
- Hypericum latisepalum (N.Robson) N.Robson: Sichuan und Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum laxiflorum N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum legrandii L.B.Sm.: Uruguay.[2]
- Hypericum leprosum Boiss.: Südwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum leschenaultii Choisy: Sumatra bis Sulawesi.[2]
- Hypericum libanoticum N.Robson: Libanon bis zum südwestlichen Syrien.[2]
- Hypericum limosum Griseb.: Westliches Kuba.[2]
- Hypericum linariifolium Vahl: Sie kommt in Madeira, Spanien, Portugal, Frankreich und Großbritannien vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum linarioides Bosse: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten auf der Balkan-Halbinsel, in der Türkei, Armenien und der Ukraine vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum linoides A. St. Hil.: Brasilien bis nordöstliches Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum lissophloeus W.P.Adams: Nordwestliches Florida.[2]
- Hypericum llanganaticum N.Robson: Zentrales Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum lloydii (Svenson) W.P.Adams: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum lobbii N.Robson: Assam.[2]
- Hypericum lobocarpum Gatt.: Zentrale USA bis westliches Alabama.[2]
- Hypericum longistylum Oliv.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten im zentralen und südlichen China vor.[2]
- Hypericum lorentzianum Gilg ex R.Keller: Südliches Brasilien bis nordöstliches Argentinien.[2]
- Hypericum loxense Benth.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Ecuador bis Peru vor.[2]
- Hypericum ludlowii N.Robson: Bhutan bis nordwestliches Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum lycium (N.Robson & Hub.-Mor.) N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum lycopodioides Triana & Planchon: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum lydium Boiss.: Türkei bis Libanon und westlicher Iran, Krim.[2]
- Hypericum lysimachioides Boiss. & Noe: Sie kommt in zwei Varietäten von der Türkei bis zum westlichen Iran vor.[2]
- Hypericum macgregorii F. Mull.: Neuguinea.[2]
- Hypericum maclarenii N.Robson: Westliches Sichuan.[2]
- Geflecktes Johanniskraut (Hypericum maculatum Crantz, Syn.: Hypericum dubium Leers): Es kommt in drei Unterarten von Europa bis Sibirien vor.[2]
- Hypericum macvaughii N.Robson: Nordöstliches Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum madagascariense (Spach) Steudel: Nördliches und zentrales Madagaskar.[2]
- Hypericum magdalenicum N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum magniflorum Cuatrec.: Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum maguirei N.Robson: Südliches Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum majus (A.Gray) Britton: Sie ist in Kanada und in den USA beheimatet und kommt in Mitteleuropa in Frankreich und Japan als Neophyt vor.[2]
- Hypericum malatyanum Peşmen: Zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum marahuacanum N.Robson: Sie kommt in vier Unterarten von Kolumbien bis Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum marginatum Woron.: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum martense N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum matangense N.Robson: Südöstliches Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum mexicanum L.: Kolumbien und Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum microcalycinum Boiss. & Heldr.: Südwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum microlicioides L.B.Sm.: Südliches Brasilien.[2]
- Hypericum microsepalum (Torrey & Gray) A.Gray ex S.Watson: Alabama bis nördliches Florida.[2]
- Hypericum millefolium Urban & Ekman: Haiti.[2]
- Hypericum minutiflorum Heenan: Nordinsel Neuseelands.[2]
- Hypericum minutum Davis & Poulter: Südwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum momoseanum Makino: Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum monadenum N.Robson: Südliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum monanthemum Hook. f. & Thomson ex Dyer: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Nepal bis China vor.[2]
- Hypericum monogynum L.: Zentrales und südliches China, Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum monroi N.Robson: Costa Rica bis Panama.[2]
- Berg-Johanniskraut (Hypericum montanum L.): Europa bis zum Kaukasusraum, Nordwestafrika.[2]
- Hypericum montbretii Spach: Sie kommt auf der Balkan-Halbinsel, in Vorderasien und in der Ukraine vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum moranense Kunth: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum mutilum L.: Sie kommt in Kanada, in den USA und im östlichen Mexiko vor.[2]
- Hypericum myrianthum Cham. & Schltdl.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Brasilien bis zum nordöstlichen Argentinien vor.[2]
- Hypericum myricariifolium Hieron.: Zentrales Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum myrtifolium Lam.: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum mysurense Wall. ex Wight & Am.: Südliches Indien, Sri Lanka.[2]
- Hypericum nagasawae Hayata: Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum nakaii H. Koidz.: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten auf Hokkaido vor.[2]
- Hypericum nakamurae (Masamune) N.Robson: Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum nanum Poir.: Libanon bis südwestliches Syrien. Es gibt zwei Varietäten.[2]
- Hypericum natalense J.M.Wood & M.S.Evans: Südliches Afrika.[2]
- Hypericum naudinianum Coss. & Durieu: Algerien und Marokko.[2]
- Hypericum neurocalycinum Boiss. & Heldr.: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum nikkoense Makino: Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum nitidum Lam.: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten in der südöstlichen USA, in Belize und in Kuba vor.[2]
- Hypericum nokoense Ohwi: Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum nudiflorum Michx. ex Willd.: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum nummularioides Trautv.: Nordöstliche Türkei bis zum westlichen Kaukasus.[2]
- Pfennigblättriges Johanniskraut (Hypericum nummularium L.): Es kommt nur in den Pyrenäen, in Nordspanien, in den französischen Alpen und kam früher auch in Italien vor.[2]
- Hypericum nuporoense N.Robson: Nördliches Hokkaido.[2]
- Hypericum oaxacanum R. Keller ex N. Robson: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum oblongifolium Choisy: Nördliches Pakistan bis zentrales Nepal.[2]
- Hypericum oligandrum Milne-Redh.: Von der Demokratischen Republik Kongo bis zum Caprivi-Streifen.[2]
- Hypericum oliganthum Franch. & Savat.: Südliches Korea, zentrales und südliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum olivieri (Spach) Boiss.: Südöstliche Türkei bis zum nördlichen Irak und dem nordwestlichen Jordanien.[2]
- Olymp-Johanniskraut (Hypericum olympicum L.): Es kommt in zwei Varietäten und zwei Formen auf der Balkan-Halbinsel und in der Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum orientale L.: Türkei bis zum Kaukasusraum.[2]
- Hypericum origanifolium Willd.: Sie kommt in zwei Varietäten von der Türkei bis zum Kaukasusraum und zum nordwestlichen Syrien vor.[2]
- Hypericum ovalifolium Koidz.: Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum oxyphyllum N.Robson: Westliches Sichuan.[2]
- Hypericum pachyphyllum Collett & Hemsley: Nördliches Myanmar.[2]
- Hypericum pallens Banks & Solander: Südliche Türkei bis Libanon.[2]
- Hypericum pamphylicum N.Robson & P.Davis: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum papillare Boiss. & Balansa: Östlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum papillosum N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum papuanum Ridl.: Neuguinea.[2]
- Hypericum parallelum N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum paramitanum N.Robson: Nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum parvulum Greene: Nördliches Mexiko.[2]
- Großblumiges Johanniskraut (Hypericum patulum Thunb.): Die Heimat ist Sichuan und Guizhou.[11][2]
- Hypericum pauciflorum Kunth: Texas bis Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum paucifolium S. Watson: Texas bis Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum pedersenii N.Robson: Brasilien.[2]
- Hypericum peninsulare Eastw.: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum peplidifolium A.Rich.: Von Bioko bis Eritrea und zum südlichen tropischen Afrika.[2]
- Durchwachsenblättriges Johanniskraut (Hypericum perfoliatum L.): Makaronesien bis zur südwestlichen Türkei.[2]
- Echtes Johanniskraut (Hypericum perforatum L.): Es wird vielfach medizinisch genutzt. Es kommt in vier Unterarten von Europa bis China, in Makaronesien, Nordwestafrika und im südwestlichen Sudan vor.[2]
- Hypericum peshmenii Yildirmli: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum petiolulatum Hook. f. & Thomson ex Dyer: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Nepal bis zum südlichen China und nördlichen Vietnam vor.[2]
- Hypericum phellos Gleason: Sie kommt in vier Unterarten vom nordöstlichen Kolumbien bis zum nordwestlichen Venezuela vor.[2]
- Hypericum philonotis Schltdl. & Cham.: Mexiko bis Honduras.[2]
- Hypericum pibairense (Miyabe & Y.Kimura) N.Robson: Nördliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum pimeleoides Planchon & Linden ex Triana & Planchon: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum piriai Arechav.: Brasilien bis Uruguay.[2]
- Hypericum pleiostylum C. Rodr. Jim.: Südöstliches Brasilien.[2]
- Hypericum podocarpoides N.Robson: Himalaja.[2]
- Hypericum polyanthemum Klotsch ex Reichardt: Südliches Brasilien bis Uruguay.[2]
- Hypericum polyphyllum Boiss. & Balansa: Südliche Türkei bis nordwestliches Syrien.[2]
- Hypericum pratense Schltdl. & Cham.: Südliches Mexiko bis Nicaragua.[2]
- Hypericum prattii Hemsley: China.[2]
- Hypericum prietoi N.Robson: Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum pringlei S. Watson: Nordöstliches und zentrales Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum prolificum L.: Südöstliches Kanada und zentrale und östliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum prostratum Cuatrec.: Nordöstliches und zentrales Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum pruinatum Boiss. & Balansa: Nordöstliche Türkei bis südwestliches Georgien.[2]
- Hypericum przewalskii Maxim.: Nördliches und zentrales China.[2]
- Hypericum pseudoerectum N.Robson: Nördliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum pseudohenryi N.Robson: Sichuan und Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum pseudolaeve N.Robson: Türkei bis Transkaukasien.[2]
- Hypericum pseudomaculatum Bush: Zentrale und südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum pseudopetiolatum R.Keller: Japan.[2]
- Hypericum pseudorepens N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum psilophytum (Diels) Maire: Südliches Marokko bis Tunesien.[2]
- Hypericum pubescens Boiss.: Sie kommt in Portugal, Spanien, Sardinien, Sizilien, Marokko, Algerien, Tunesien und Libyen vor.[10][2]
- Schönes Johanniskraut (Hypericum pulchrum L.): Nordwestliches und westliches Europa bis zum nordwestlichen Kroatien.[2]
- Hypericum pulogense Merr.: Nördliches Luzon.[2]
- Hypericum pumilio Bornm.: Zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum pumilum Sessé & Mocino: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten im nordöstlichen und zentralen Mexiko vor.[2]
- Hypericum punctatum Lam.: Östliches Kanada bis zentrale und östliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum pycnophyllum Urb.: Sie kommt in der Dominikanischen Republik vor.[2]
- Hypericum qinlingense X.C.Du & Y.Ren: Shaanxi.[2]
- Hypericum quartinianum A. Rich.: Äthiopien bis zum südlichen tropischen Afrika, südwestliche Arabische Halbinsel.[2]
- Hypericum quitense R. Keller: Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum radfordiorum Weakley ex Allison: North Carolina.[2]
- Hypericum radicans N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum recurvum N.Robson: Peru.[2]
- Hypericum reflexum L. f.: Kanarische Inseln.[2]
- Hypericum relictum N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum repens L.: Zypern.[2]
- Hypericum reptans Hook. f. & Thoms. ex Dyer: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Nepal bis ins nordwestliche Yunnan vor.[2]
- Hypericum retusum Aucher: Südöstliche Türkei bis nördlicher Irak und nördliches Syrien.[2]
- Hypericum revolutum Vahl: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten vom südöstlichen Nigeria, Bioko und Eritrea bis Südafrika und der Arabische Halbinsel vor.[2]
- Richers Johanniskraut (Hypericum richeri Vill.): Es kommt in drei Unterarten in den Gebirgen von Südeuropa und Mitteleuropa bis zur Balkan-Halbinsel und den Karpaten vor.[2]
- Hypericum rigidum A. St. Hil.: Sie kommt in vier Unterarten im südöstlichen und südlichen Brasilien vor.[2]
- Hypericum roberti Coss. ex Batt.: Sie kommt vom nordöstlichen Algerien bis zum nordwestlichen Tunesien vor.[2]
- Hypericum robsonii H.A.Keller & S.Crockett: Die 2015 erstbeschriebene Art kommt in Argentinien vor.[2]
- Hypericum rochelii Griseb. & Schenk: Sie kommt nur in Rumänien, Bulgarien, Griechenland und im ehemaligen Jugoslawien vor.[2]
- Hypericum roeperianum W.G.Schimper ex A.Rich.: Guinea, Nigeria bis Kamerun, Äthiopien bis Mpumalanga.[2]
- Hypericum roraimense Gleason: Südliches Venezuela bis Guayana.[2]
- Hypericum rotundifolium N.Robson: Südwestliches Guizhou.[2]
- Hypericum rubicundulum Heenan: Neuseeland.[2]
- Hypericum rubritinctum N.Robson: Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum rumeliacum Boiss.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten nur auf der Balkan-Halbinsel und in Süd-Rumänien vor.[2]
- Hypericum rupestre Jaub. & Spach: Südliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum ruscoides Cuatrec.: Kolumbien bis Ecuador.[2]
- Hypericum russeggeri (Fenzl) R.Keller: Türkei bis nordwestliches Syrien.[2]
- Hypericum sabiniforme Trevir.: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum salsolifolium Hand.-Mazz.: Südliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum salsugineum N.Robson & Hub.-Mor.: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum salvadorense N.Robson: Brasilien.[2]
- Hypericum sampsonii Hance: China, Vietnam, Myanmar, Japan und Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum saruwagedicum Diels: Neuguinea.[2]
- Hypericum saturejifolium Jaub. & Spach (Syn.: Hypericum confertum Choisy nom. illeg.): Westlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum saxifragum Robson & Hub.-Mor.: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum scabroides N.Robson & Poulter: Östliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum scabrum L.: Türkei bis zum Libanon und bis China.[2]
- Hypericum scioanum Chiov.: Äthiopien bis nordwestliches Sambia.[2]
- Hypericum scopulorum Balf.f.: Sokotra.[2]
- Hypericum scouleri Hook.: Westliches Kanada bis Mexiko.[2]
- Hypericum scruglii Bacch., Brullo & Salmeri: Sardinien.[2]
- Hypericum sechmenii Ocak & Koyuncu: Nordwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum selaginella N.Robson: Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum senanense Maxim.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten auf Honshu vor.[2]
- Hypericum seniawinii Maxim.: Südliches China bis nördliches Vietnam.[2]
- Hypericum senkakuinsulare Hatusima: Nansei-Inseln.[2]
- Hypericum setosum L.: Südöstliche USA bis östliches Texas.[2]
- Hypericum sewense N.Robson: Neuguinea.[2]
- Hypericum sherriffii N.Robson: Südöstliches Bhutan.[2]
- Hypericum siamense N.Robson: Nördliches Thailand.[2]
- Hypericum sikokumontanum Makino: Südliches Japan.[2]
- Hypericum silenoides Juss.: Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten von Mexiko bis Honduras und vom westlichen Südamerika bis zum nordwestlichen Argentinien vor.[2]
- Hypericum simonsii N.Robson: Nordöstliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum sinaicum Hochst. ex Boiss.: Südwestliches Jordanien bis nordwestliches Saudi-Arabien.[2]
- Hypericum smithii (N.Robson) N.Robson: Zentrales und östliches Sokotra.[2]
- Hypericum socotranum Good: Nordwestliches Sokotra.[2]
- Hypericum somaliense N.Robson: Nordöstliches Somalia.[2]
- Hypericum sorgerae N.Robson: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum spectabile Jaub. & Spach: Südöstliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum sphaerocarpum Michx.: Südöstliches Kanada bis zentrale und östliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum sprucei N.Robson: Ecuador bis nördliches Peru.[2]
- Hypericum spruneri Boiss.: Sie kommt nur in Italien und auf der westlichen Balkan-Halbinsel vor.[2]
- Hypericum stellatum N.Robson: Chongqing.[2]
- Hypericum stenobotrys Boiss.: Südliche Türkei bis Libanon.[2]
- Hypericum stenopetalum : Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum steyermarkii Standley: Mexiko und Guatemala.[2]
- Hypericum strictum Kunth (inkl. Hypericum graciliforme N.Robson): Sie kommt in zwei Unterarten in Kolumbien vor.[2]
- Hypericum struthiolifolium Juss.: Nördliches und zentrales Peru.[2]
- Hypericum stuebelii Hieron.: Nördliches Peru.[2]
- Hypericum styphelioides A.Rich.: Sie kommt in drei Unterarten auf Kuba vor.[2]
- Hypericum subalatum Hayata: Nördliches und nordöstliches Taiwan.[2]
- Hypericum subcordatum (R.Keller) N.Robson: Shaanxi und Sichuan.[2]
- Hypericum subsessile N.Robson: Sichuan und Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum suffruticosum W.P.Adams & N.Robson: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum swinkianum G.Wilh. & Rericha: Die 2016 erstbeschriebene Art kommt in den nördlichen Vereinigten Staaten vor.[2]
- Hypericum synstylum N.Robson: Östliches Äthiopien bis nördliches Somalia.[2]
- Hypericum taihezanense Sasaki ex S. Suzuki; Guangdong bis nördliches Borneo, westliches Sumatra.[2]
- Hypericum taygeteum Quézel & Contandr.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im Taygetos-Gebirge in Südgriechenland vor.[2]
- Hypericum tenuicaule Hook. f. & Thoms. ex Dyer: Östliches Nepal bis Bhutan.[2]
- Hypericum tenuifolium Pursh: Südöstliche USA.[2]
- Hypericum teretiusculum A. St. Hil.: Südliches Brasilien bis Paraguay.[2]
- Hypericum ternatum Poulter: Südwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum ternum A. St. Hil.: Brasilien.[2]
- Hypericum terrae-firmae Sprague & Riley: Belize.[2]
- Hypericum tetrapetalum Lam.: Alabama bis Florida, Kuba.[2]
- Geflügeltes Johanniskraut (Hypericum tetrapterum Fries): Es kommt in drei Varietäten von Europa bis zum Kaukasus und vom Mittelmeergebiet bis zum Iran vor.[2]
- Hypericum tetrastichum Cuatrec.: Nordöstliches Kolumbien bis nordwestliches Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum thasium Griseb.: Sie kommt nur auf der südöstlichen Balkan-Halbinsel vor.[2]
- Hypericum theodori Woron.: Östliches Aserbaidschan.[2]
- Hypericum thesiifolium Kunth: Costa Rica bis Venezuela.[2]
- Hypericum thuyoides Kunth: Sie kommt in Kolumbien vor.[2]
- Hypericum thymbrifolium Boiss. & Noe: Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum thymifolium Banks & Solander: Südliche Türkei bis Israel.[2]
- Hypericum thymopsis Boiss.: Östlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Filziges Johanniskraut[12] (Hypericum tomentosum L.): Es kommt in Portugal, Spanien, den Balearen, Frankreich, Italien, Sardinien, Marokko, Algerien und Tunesien und früher auch auf Korsika vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum tortuosum Balf. f.: Sokotra.[2]
- Hypericum tosaense Makino: Japan.[2]
- Hypericum trachyphyllum Griseb.: Europäische Türkei bis zur nordwestlichen Türkei und Inseln der Ägäis.[2]
- Hypericum trichocaulon Boiss. & Heldr.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Kreta vor.[2]
- Krausblättriges Johanniskraut (Hypericum triquetrifolium Turra): Mittelmeergebiet bis westlicher Iran.[2]
- Hypericum tymphresteum Boiss. & Spruner: Griechenland.[2]
- Hypericum umbellatum A.Kern.: Sie kommt in Griechenland, Bulgarien, Rumänien und im früheren Jugoslawien vor.[2]
- Hypericum umbraculoides N.Robson: Sie kommt in Mexiko vor.[13]
- Hypericum undulatum Schousboe ex Willd.: Sie kommt in zwei Varietäten auf den Azoren, Madeira, Portugal, Spanien, Frankreich, Großbritannien, Irland, Algerien und Marokko vor.[10][2]
- Hypericum uniflorum Boiss. & Balansa: Südsüdwestliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum uniglandulosum Hausskn. ex Bomm.: Östlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum uralum Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don: Nördliches Pakistan bis nordwestliches Yunnan.[2]
- Hypericum vacciniifolium Hayek: Südliche Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum vaccinioides N.Robson: Südlich-zentrale Türkei.[2]
- Hypericum valleanum N.Robson: Südwestliches Kolumbien.[2]
- Hypericum venustum Fenzl: Türkei bis Transkaukasien.[2]
- Hypericum vermiculare Boiss. & Hausskn.: Nördlicher Irak bis zum Iran.[2]
- Hypericum vesiculosum Griseb.: Sie kommt nur in Griechenland und in der nordwestlichen Türkei vor.[2]
- Hypericum virgatum Lam.: USA.[2]
- Hypericum vulcanicum Koidz.: Hokkaido und Honshu.[2]
- Hypericum wardianum N.Robson: Nordwestliches Yunnan bis zum nordöstlichen Myanmar.[2]
- Hypericum watanabei N.Robson: Westliches Hokkaido.[2]
- Hypericum wightianum Wall.: Östlicher Himalaja bis südliches China, südliches Indien und Sri Lanka.[2]
- Hypericum williamsii N.Robson: Nepal bis Sikkim.[2]
- Hypericum wilmsii R.Keller: Sie kommt von Simbabwe bis ins südliche Afrika und auf Madagaskar vor.[2]
- Hypericum wilsonii N.Robson: Sie kommt im westlichen Hubei und vielleicht auch in Hunan vor.[2]
- Hypericum woodianum N.Robson: Sie kommt in Kolumbien vor.[2]
- Hypericum wurdackii N.Robson: Sie kommt im nördlichen Peru vor.[2]
- Hypericum xylosteifolium (Spach) N.Robson (Syn.: Hypericum inodorum Mill.): Sie kommt von der nordöstlichen Türkei bis ins westliche Transkaukasien vor.[2]
- Hypericum yamamotoanum H. Koidz.: Dieser Endemit kommt nur im südwestlichen Hokkaido vor.[2]
- Hypericum yamamotoi Miyabe & Y.Kimura: Sie kommt im nördlichen Japan vor.[2]
- Hypericum yezoense Maxim.: Sie kommt vom südlichen Sachalin und den Kurilen bis ins nördliche Japan vor.[2]
- Hypericum yojiroanum Tatewaki & K.Ito: Dieser Endemit kommt nur auf der japanischen Insel Hokkaido vor.[2]
Inhaltsstoffe und Anwendungen
Literatur
- Norman K. B. Robson, Mark Carine, David Pattinson, Nicolai Nürk, Sara Crockett, Jacek Waier, Alison Eyres: Hypericum online. A site dedicated to Hypericum – The St John's Worts. Zuletzt eingesehen am 9. Februar 2015.
- Xi-wen Li, Norman K. B. Robson: Hypericum. In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Hrsg.): Flora of China, Volume 13: Clusiaceae through Araliaceae. Science Press und Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Peking und St. Louis, 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7. Hypericum Linnaeus. - textgleich online wie gedrucktes Werk.
- Norman K. B. Robson: Hypericum L. In: T. G. Tutin, V. H. Heywood, N. A. Burges, D. M. Moore, D. H. Valentine, S. M. Walters, D. A. Webb (Hrsg.): Flora Europaea. Volume 2: Rosaceae to Umbelliferae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1968, ISBN 0-521-06662-X, S. 261–269 (englisch, eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Norman K. B. Robson: Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Guttiferae): 1. Infrageneric classification. In: Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History). Botany, Volume 5, Issue 6, 1977, S. 291–355.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d Xi-wen Li, Norman K. B. Robson: Hypericum. In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Hrsg.): Flora of China, Volume 13: Clusiaceae through Araliaceae. Science Press und Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Peking und St. Louis, 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7. Hypericum Linnaeus. - textgleich online wie gedrucktes Werk.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh gi gj gk gl gm gn go gp gq gr gs gt gu gv gw gx gy gz ha hb hc hd he hf hg hh hi hj hk hl hm hn ho hp hq hr hs ht hu hv hw hx hy hz ia ib ic id ie if ig ih ii ij ik il im in io ip iq ir is it iu iv iw ix iy iz ja jb jc jd je jf jg jh ji jj jk jl jm jn jo jp jq jr js jt ju jv jw jx jy jz ka kb kc kd ke kf kg kh ki kj kk kl km kn ko kp kq kr ks kt ku kv kw kx ky kz la lb lc ld le lf lg lh li lj lk ll lm ln lo lp lq lr ls lt lu lv lw lx ly lz ma mb mc md me mf mg mh mi mj mk ml mm mn mo mp mq mr ms mt mu mv mw mx my mz na nb nc nd ne nf ng nh ni nj nk nl nm nn no np nq nr ns nt nu nv nw nx ny nz oa ob oc od oe of og oh oi oj ok ol om on oo op oq or os ot ou ov ow ox oy oz pa pb pc pd pe pf pg ph pi pj pk pl pm pn po pp pq pr ps pt pu pv pw px py pz qa qb qc qd qe qf qg qh qi qj qk ql qm qn qo qp qq qr qs qt qu qv qw qx qy qz ra rb rc rd re rf rg rh ri rj rk rl rm rn ro rp rq rr rs rt ru Hypericum. In: POWO = Plants of the World Online von Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Kew Science, abgerufen am 15. März 2020.
- ↑ a b Norman K. B. Robson: Hypericum L. In: T. G. Tutin, V. H. Heywood, N. A. Burges, D. M. Moore, D. H. Valentine, S. M. Walters, D. A. Webb (Hrsg.): Flora Europaea. Volume 2: Rosaceae to Umbelliferae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1968, ISBN 0-521-06662-X, S. 261–269 (englisch, eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- ↑ Carl von Linné: Genera Plantarum. Eorumque characteres naturales secundum numerum, figuram, situm, et proportionem omnium fructificationis partium. 5. Auflage. Lars Salvius, Stockholm 1754, S. 341, Digitalisat.
- ↑ Carl von Linné: Species Plantarum. Band 2, Lars Salvius, Stockholm 1753, S. 783 (Digitalisat).
- ↑ Norman K. B. Robson: A review of Hypericum sect. Hirtella. In: Notes from the Royal Botanic Garden, Edinburgh, Volume 43, 1986, S. 255–265.
- ↑ Norman K. B. Robson: Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Guttiferae) 6. sections 20. Myriandra to 28. Elodes. In: Bulleton of the Natural History Museum. Botany, Series 26, 1996, S. 75–217.
- ↑ Norman K. B. Robson: Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Hypericaceae) 5(1). Sections 10. Olympia to 15/16 Crossophyllum. In: Phytotaxa, Volume 4, 2010, S. 5–126.
- ↑ Norman K. B. Robson: Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Hypericaceae) 9. Addenda, corrigenda, keys, lists and general discussion. In: Phytotaxa, Volume 72, 2012, S. 1–111 (Artenliste: S. 62–68) (Abstract als PDF-Datei).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Karol Marhold: Clusiaceae.: Hypericum In: Euro+Med Plantbase - the information resource for Euro-Mediterranean plant diversity. Berlin 2011.
- ↑ a b c Hypericum im Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Abgerufen am 20. September 2018.
- ↑ https://www.worldplants.de/world-plants-complete-list/complete-plant-list/?name=Hypericum-tomentosum#plantUid-156121
- ↑ Norman K. B. Robson: Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Guttiferae) 3. Sections Campylosorus to 6a. Umbraculoides. In: Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History). Botany. Volume 12, Nr. 4, 1985, S. 163–325 (hier: S. 317–320) (Digitalisat).