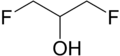
1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Difluoropropan-2-ol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.561 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6F2O | |||
| Molar mass | 96.077 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 (at 25 °C) [1] | ||
| Boiling point | 54 to 55 °C (129 to 131 °F; 327 to 328 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol is a metabolic poison which disrupts the citric acid cycle and is used as a rodenticide, similar to sodium fluoroacetate. It is the main ingredient (along with 1-chloro-3-fluoro-2-propanol) in the rodenticide product Gliftor which was widely used in the former USSR[2][3][4] and still approved in China.[5]
References
- ^ Sigma Aldrich
- ^ Buklan AI, Kravets AF (1986). "[Gliftor poisoning]". Sudebno-Meditsinskaia Ekspertiza (in Russian). 29 (1): 55–6. PMID 3961873.
- ^ Feldwick MG, Noakes PS, Prause U, Mead RJ, Kostyniak PJ (1998). "The biochemical toxicology of 1,3-difluoro-2-propanol, the major ingredient of the pesticide gliftor: the potential of 4-methylpyrazole as an antidote". Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 12 (1): 41–52. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0461(1998)12:1<41::AID-JBT6>3.0.CO;2-P. PMID 9414486. S2CID 29455648.
- ^ Menon KI, Feldwick MG, Noakes PS, Mead RJ (2001). "The mode of toxic action of the pesticide gliftor: the metabolism of 1,3-difluoroacetone to (-)-erythro-fluorocitrate". Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 15 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1002/1099-0461(2001)15:1<47::AID-JBT6>3.0.CO;2-E. PMID 11170315. S2CID 9064673.
- ^ Wood, Alan. "Gliftor". Compendium of Pesticide Common Names. Retrieved 14 June 2021.