Alpha GPC
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.496 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
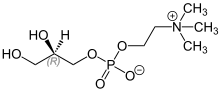
| Formula | C8H20NO6P |
| Molar mass | 257.223 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
L-α-Glycerophosphorylcholine (alpha-GPC, choline alfoscerate, sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) is a natural choline compound found in the brain. It is also a parasympathomimetic acetylcholine precursor[1] which has been investigated for its potential for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[2] and other dementias.[3]
Alpha-GPC rapidly delivers choline to the brain across the blood–brain barrier and is a biosynthetic precursor of acetylcholine.[2] It is a non-prescription drug in most countries. The FDA determined that intake of no more than 196.2 mg/person/day is considered generally recognized as safe (GRAS).[4]
Production
Industrially, alpha-GPC is produced by the chemical or enzymatic deacylation of phosphatidylcholine enriched soya phospholipids followed by chromatographic purification. Alpha-GPC may also be derived in small amounts from highly purified soy lecithin as well as from purified sunflower lecithin.[5][6]
Safety
Alpha-GPC metabolizes to trimethylamine n-oxide in the gastrointestinal tract, which has implications for cardiovascular health. In one study, risk of stroke over a ten-year period was increased by about 40% in users of alpha-GPC.[7]
References
- ^ De Jesus Moreno Moreno M (January 2003). "Cognitive improvement in mild to moderate Alzheimer's dementia after treatment with the acetylcholine precursor choline alfoscerate: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial". Clinical Therapeutics. 25 (1): 178–93. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(03)90023-3. PMID 12637119.
- ^ a b Parnetti L, Mignini F, Tomassoni D, Traini E, Amenta F (June 2007). "Cholinergic precursors in the treatment of cognitive impairment of vascular origin: ineffective approaches or need for re-evaluation?". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 257 (1–2): 264–9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2007.01.043. PMID 17331541. S2CID 34661218.
- ^ Doggrell SA, Evans S (October 2003). "Treatment of dementia with neurotransmission modulation". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 12 (10): 1633–54. doi:10.1517/13543784.12.10.1633. PMID 14519085. S2CID 46175609.
- ^ "Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) Determination for the Use of AlphaSize® Alpha-Glycerylphosphoryl Choline" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. 25 January 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2013.
- ^ E. Traini, V. Bramanti, F. Amenta (2013), "Choline alphoscerate (alpha-glyceryl-phosphoryl-choline) an old choline- containing phospholipid with a still interesting profile as cognition enhancing agent", Current Alzheimer Research, vol. 10, no. 10, pp. 1070–1079, doi:10.2174/15672050113106660173, PMID 24156263
{citation}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ P. L. Scapicchio (2013), "Revisiting choline alphoscerate profile: a new, perspective, role in dementia?", The International Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 123, no. 7, pp. 444–449, doi:10.3109/00207454.2013.765870, PMID 23387341, S2CID 39888580
- ^ Lee G, Choi S, Chang J, Choi D, Son JS, Kim K, Kim SM, Jeong S, Park SM (1 November 2021). "Association of L-α Glycerylphosphorylcholine With Subsequent Stroke Risk After 10 Years". JAMA Network Open. 4 (11): e2136008. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36008. PMC 8613599. PMID 34817582.