Artiopoda
| Artiopoda Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
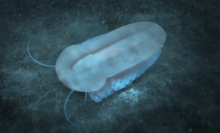
| Misszhouia, a nektaspid | |
| |
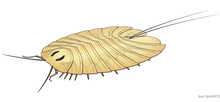
| Cheloniellon, a cheloniellid | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| (unranked): | †Artiopoda Hou and Bergstrom, 1997 |
| Subgroupings | |
| |
The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997[5] to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Trilobitomorpha. Trilobites, in part due to abundance of findings owing to their mineralized exoskeletons, are by far the best recorded, diverse, and long lived members of the clade. Other members, which lack mineralised exoskeletons, are known mostly from Cambrian deposits.[6]
Description

According to Stein and Selden (2012) artiopods are recognised by the possession of filiform antennulae, limbs with bilobate exopods, with the proximal lobe being elongate and bearing a lamella, while the distal lobe is paddle-shaped and setiforous (bearing hair-or bristle like structures). The limb endopod has seven podomeres/segments, with first four podomeres bearing inward facing (endite) structures, while podomeres five and six are stenopodous (cylindrical and stout). Common plesiomorphies also include the antennules and at least three sets of post-antennular limbs being incorporated into the head shield, the postantennular limbs having no or little differentiation into distinct morphologies, and broad paratergal folds which contribute to the dorsoventrally flattened look of artiopods.[7] The limbs of artiopods have also been suggested to bear exites, which were described as similar those of the megacheiran Leanchoilia and probably not homologous to those present in crustaceans.[8]
Taxonomy
Internal taxonomy
The Artiopoda have been considered by many studies to consist of two major clades; one reusing Trilobitomorpha to encompass trilobites, nektaspids, concilitergans and xandarellids, and the other called Vicissicaudata encompassing aglaspidids, xenopods and cheloniellids.[9] There are some taxa, such as Squamacula and the members of "Protosutura", which often are placed near the base of Artiopoda, outside the Vicissicaudata+Trilobitomorpha clade. These relationships are not always recovered.[10]
Relationships with other arthropods
The relationship of Artiopoda with the two major clades of modern arthropods, the Chelicerata and the Mandibulata, are unresolved, with some phylogenies recovering Artiopoda as more closely to chelicerates, forming the clade Arachnomorpha, while others recover Artiopoda as more closely related to mandibulates, forming the clade Antennulata.[11] Some studies place them as stem-group euarthropods, with mandibulates and chelicerates more closely related to each other than either is to Artiopoda.[10] Some studies have recovered a close relationship with Marrellomorpha, with the proposed clade including Artiopoda and Marrellomorpha dubbed Lamellipedia, though this relationship is not found in other analyses.[12][13] The enigmatic artiopodan-like arthropod Kiisortoqia, which bears large "frontal appendages" has been suggested to be closely related to Artiopoda in some analyses.[10]
Gallery
-
Restoration of the trilobite Triarthrus eatoni
-
Fossils of Naraoia compacta (Nektaspida)
-
Life restoration of Sidneyia (Vicissicaudata)
-
Diagram of Sinoburius (Xandarellida)
-
Life restoration of Aglaspis (Aglaspidida)
-
Life restoration of Tegopelte (Conciliterga)
-
Life restoration of Pleuroctenium (Agnostida)
Phylogeny
After Jiao et al. 2021.[14]
| Artiopoda |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ^ Liu, Cong; Fu, Dongjing; Wu, Yu; Zhang, Xingliang (July 2024). "Cambrian euarthropod Urokodia aequalis sheds light on the origin of Artiopoda body plan" (PDF). iScience: 110443. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.110443.
- ^ Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy (March 2015). "Notchia weugi gen. et sp. nov.: a new short-headed arthropod from the Weeks Formation Konservat-Lagerstätte (Cambrian; Utah)". Geological Magazine. 152 (2): 351–357. doi:10.1017/S0016756814000375.
- ^ a b Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F. (2023). "New artiopodan euarthropods from the Chengjiang fauna (Cambrian, Stage 3) at Malong, Yunnan, China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 68. doi:10.4202/app.01080.2023.
- ^ McCoy, Victoria E.; Herrera, Fabiany; Wittry, Jack; Mayer, Paul; Lamsdell, James C. (2025). "A possible vicissicaudatan arthropod from the Late Carboniferous Mazon Creek Lagerstätte". Geological Magazine. 162. doi:10.1017/S001675682400044X.
- ^ Hou, X. & Bergström, J. 1997. Arthropods of the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, southwest China. Fossils and Strata, No. 45. Scandinavian University Press, Oslo, 22 Dec 1997: 116 pp.[1]
- ^ Schmidt, Michel; Hou, Xianguang; Zhai, Dayou; Mai, Huijuan; Belojević, Jelena; Chen, Xiaohan; Melzer, Roland R.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Liu, Yu (2021-08-19). "Before trilobite legs: Pygmaclypeatus daziensis reconsidered and the ancestral appendicular organization of Cambrian artiopods". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.08.18.456779. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- ^ Stein, Martin; Selden, Paul A. (June 2012). "A restudy of the Burgess Shale (Cambrian) arthropod Emeraldella brocki and reassessment of its affinities". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 10 (2): 361–383. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.566634. ISSN 1477-2019. S2CID 55018927.
- ^ Liu, Yu; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Schmidt, Michel; Bond, Andrew D.; Melzer, Roland R.; Zhai, Dayou; Mai, Huijuan; Zhang, Maoyin; Hou, Xianguang (2021-07-30). "Exites in Cambrian arthropods and homology of arthropod limb branches". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 4619. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24918-8. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 8324779. PMID 34330912.
- ^ Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Legg, David A.; Braddy, Simon J. (February 2013). "The phylogeny of aglaspidid arthropods and the internal relationships within Artiopoda". Cladistics. 29 (1): 15–45. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2012.00413.x. PMID 34814371. S2CID 85744103.
- ^ a b c Berks, H. O.; Lunde Nielsen, M.; Flannery‐Sutherland, J.; Thorshøj Nielsen, A.; Park, T.‐Y. S.; Vinther, J. (2023). "A possibly deep branching artiopodan arthropod from the lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (North Greenland)". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (3). doi:10.1002/spp2.1495.
- ^ Aria, Cédric (2022-04-26). "The origin and early evolution of arthropods". Biological Reviews. 97 (5): 1786–1809. doi:10.1111/brv.12864. ISSN 1464-7931. PMID 35475316. S2CID 243269510.
- ^ Moysiuk, Joseph; Izquierdo-López, Alejandro; Kampouris, George E.; Caron, Jean-Bernard (July 2022). "A new marrellomorph arthropod from southern Ontario: a rare case of soft-tissue preservation on a Late Ordovician open marine shelf". Journal of Paleontology. 96 (4): 859–874. doi:10.1017/jpa.2022.11. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ Stein, Martin (November 2013). "Cephalic and appendage morphology of the Cambrian arthropod Sidneyia inexpectans". Zoologischer Anzeiger - A Journal of Comparative Zoology. 253 (2): 164–178. doi:10.1016/j.jcz.2013.05.001.
- ^ Jiao, De-Guang; Du, Kun-Sheng; Zhang, Xi-Guang; Yang, Jie; Eggink, Daniel (May 2022). "A new small soft-bodied non-trilobite artiopod from the Cambrian Stage 4 Guanshan Biota". Geological Magazine. 159 (5): 730–734. doi:10.1017/S0016756821001254. ISSN 0016-7568.











