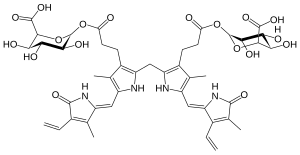
Bilirubin diglucuronide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2,17-Diethenyl-3,7,13,18-tetramethyl-1,19-dioxo-10,19,21,22,23,24-hexahydro-1H-biline-8,12-diyl)bis(1-oxopropane-3,1-diyl) di(β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(12S,13R,14S,15S,16S,132S,133R,134S,135S,136S)-65-[(Z)-(3-Ethenyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-ylidene)methyl]-85-[(Z)-(4-ethenyl-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-ylidene)methyl]-13,14,15,133,134,135-hexahydroxy-64,84-dimethyl-3,11-dioxo-61H,81H-2,12-dioxa-6(3,2),8(2,3)-dipyrrola-1,13(2)-bis(oxana)tridecaphane-16,136-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | bilirubin+diglucuronide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H52N4O18 | |
| Molar mass | 936.911 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Bilirubin di-glucuronide is a conjugated form of bilirubin formed in bilirubin metabolism.[1] The hydrophilic character of bilirubin diglucuronide enables it to be water-soluble. It is pumped across the hepatic canalicular membrane into the bile by the transporter MRP2.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Chowdhury, J. R.; Chowdhury, N. R.; Wu, G.; Shouval, R.; Arias, I. M. (1981). "Bilirubin mono- and diglucuronide formation by human liver in vitro: Assay by high-pressure liquid chromatography". Hepatology. 1 (6): 622–7. doi:10.1002/hep.1840010610. PMID 6796486.
- ^ Lengyel, G.; et al. (2007-08-29). "Modulation of sinusoidal and canalicular elimination of bilirubin-glucuronides by rifampicin and other cholestatic drugs in a sandwich culture of rat hepatocytes". Hepatology Research. 38 (3). Wiley: 300–309. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00255.x. PMID 17760873.