Burgos Province
Burgos | |
|---|---|
 Provincial Palace (19th century) in Burgos, seat of the Diputación de Burgos, the province governing body | |
 Map of Spain with Burgos highlighted | |
| Coordinates: 42°23′N 3°40′W / 42.383°N 3.667°W | |
| Country | Spain |
| Autonomous community | Castile and León |
| Capital | Burgos |
| Government | |
| • President | César Rico Ruiz (PP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 14,292 km2 (5,518 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 11th |
| 2,78% of Spain | |
| Population ()[1] | |
| • Rank | Ranked 36th |
| 0,80% of Spain | |
| Demonym(s) | Spanish: burgalés/a English: burgalese |
| ISO 3166 code | ES-BU |
| Official language(s) | Spanish |
| Parliament | Cortes Generales |
| Website | www |
The Province of Burgos is a province of northern Spain, in the northeastern part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is bordered by the provinces of Palencia, Cantabria, Vizcaya, Álava, La Rioja, Soria, Segovia, and Valladolid. Burgos is the province of Spain that has borders with most provinces. Its capital is the city of Burgos.
The Cartularies of Valpuesta from the monastery Santa María de Valpuesta, in Burgos, are considered to be the oldest known documents containing words written in the Spanish language.[2]
Overview
Since 1964, archaeologists have been working at numerous areas of the Archaeological Site of Atapuerca, where they have found ancient hominid and human remains, the former dating to more than one million years ago, with artefacts from the Palaeolithic and Bronze Ages of man. The site has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The province has an area of 14,300 km2 (5,500 sq mi) and a population of approximately 375,000 of whom nearly half live in the capital. The other locations higher than 20,000 inhabitants apart from Burgos are Miranda de Ebro and Aranda de Duero, both very industrialized. The Sierra de la Demanda, the northwesternmost end of the Sistema Ibérico, is located in Burgos Province.[3]
The most important rivers in the province are the Ebro and the Duero. The river Duero is in the south of the province and leads to the Atlantic Ocean at Porto, Portugal. Planted near it is a notable vineyard, Ribera de Duero. The north and south-east of the province are mountainous. The Ebro flows to the Mediterranean Sea.
In Valpuesta the oldest texts in the Spanish language has been found, dating from the tenth century.[4]
Transportation is developed through a wide net of highways and roads. Besides, the province is served by the Burgos Airport, and was to have received High-speed rail AVE around 2016.
History

In the Atapuerca area, archaeologists have found evidence of occupation by hominids and humans for more than one million years. Discoveries have included the earliest hominid skull in Europe.
The Celtiberian region that became Burgos was inhabited by the Morgobos, Turmodigi, Berones and perhaps also the Pellendones, the last inhabitants of the northern part of the Celtiberian region. According to the Greek historian Ptolemy, the principal cities included: Brabum, Sisara, Deobrigula (nowadays Tardajos), Ambisna Segiasamon (Sasamón) and Verovesca (Briviesca). Under Roman colonization, it was part of Hispania Citerior ("Hither Spain") and then Hispania Tarraconensis.
In the fifth century, the Visigoths drove back the Suevi. In the eighth century, the Arabs occupied all of Castiles. Alfonso III the Great, king of León reconquered the area around the middle of the ninth century, and built many castles for the defence of Christendom. Gradually the area was reconquered. The region came to be known as Castile (Latin castella), i.e. "land of castles". In the eleventh century, Burgos became the capital of the Kingdom of Castile.
Population development
The historical population is given in the following chart:

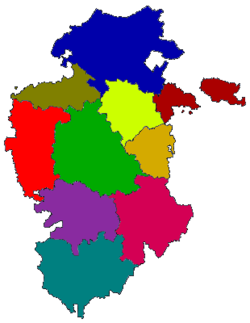
Comarcas
The province of Burgos is divided in 10 comarcas.
- Merindades
- Valle del Rudrón
- Ebro
- La Bureba
- Montes de Oca
- Alfoz de Burgos
- Sierra de la Demanda
- Odra y Pisuerga
- Arlanza
- Ribera del Duero
Administrative divisions
The province of Burgos is divided into 371 municipalities, being the Spanish province with the highest number, although many of them have fewer than 100 inhabitants.