Capture of Malta (218 BC)
| Capture of Malta | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Second Punic War | |||||||||
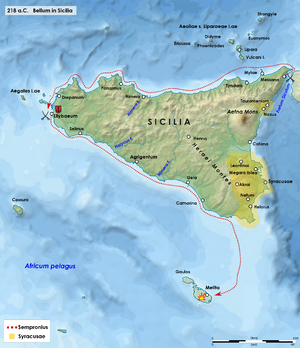 Naval operations around Sicily in 218 BC | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Roman Republic | Carthage | ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Tiberius Sempronius Longus | Hamilcar, son of Gisco (POW) | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| c. 26,000 | c. 2,000 | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Light | c. 2,000 captured and enslaved | ||||||||
The capture of Malta was the successful invasion of the Carthaginian island of Malta (then known as Maleth, Melite or Melita) by forces of the Roman Republic led by Tiberius Sempronius Longus in the early stages of the Second Punic War in 218 BC.
Background
Malta had been Carthaginian territory since 480 BC.[1] During the First Punic War, the island suffered a devastating raid by a Roman army under Gaius Atilius Regulus in 257 BC, but it remained under Carthaginian rule.[2]
When the Second Punic War broke out in 218 BC, a Carthaginian force of around 2,000 men under the command of Hamilcar, son of Gisco[a] garrisoned the Maltese Islands.[4] Despite the Carthaginian defeat at the Battle of Lilybaeum, the Romans were concerned that a Carthaginian-led revolt might break out in Sicily.[5] In order to prevent this, Malta – Carthage's nearest base to Sicily – had to be captured.[5]
Capture
Roman Consul Tiberius Sempronius Longus had over 26,000 men under his command,[5] and he sailed his fleet from Lilybaeum in order to capture Malta. Vastly outnumbered, Hamilcar surrendered the main city Maleth and his garrison to the Romans, without much of a fight. The fleet returned to Lilybaeum after a few days, where those who had been captured (with the exception of the nobles) were sold as slaves.[6]
Analysis
The main source about the invasion is an account by Livy.[6] The role of the Maltese inhabitants during the invasion is unclear, and some historians suggest that they might have turned over the Carthaginian garrison to the Romans.[6] The islands were in no position to resist the invasion, and surrendering without a fight was beneficial for the population since it spared the islands from destruction whilst also increasing the possibility for future economic gain.[7]
Archaeological evidence suggests a significant demographic continuity between the periods of Carthaginian and Roman rule of Malta.[8] The Maltese Islands were given some degree of autonomy under Roman rule, possibly as a reward for the islanders' shift of allegiance.[9]
Notes
References
- ^ Castillo 2006, p. 20
- ^ Castillo 2006, p. 22
- ^ Hoyos 2015, p. 222
- ^ Castillo 2006, p. 23
- ^ a b c Castillo 2006, p. 24
- ^ a b c Castillo 2006, p. 25
- ^ Sagona 2015, p. 264
- ^ Sagona 2015, p. 265
- ^ Sagona 2015, p. 266
Bibliography
- Castillo, Dennis Angelo (2006). The Maltese Cross: A Strategic History of Malta. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313323294.
- Hoyos, Dexter, ed. (2015). A Companion to the Punic Wars. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781119025504.
- Sagona, Claudia (2015). The Archaeology of Malta. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107006690.

