Cochlear nerve
| Cochlear nerve | |
|---|---|
 Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea. (Cochlear nerve is in center, shown as striped.) | |
 Part of the cochlear division of the acoustic nerve, highly magnified. | |
| Details | |
| From | Vestibulocochlear nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus cochlearis |
| MeSH | D003056 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.133 |
| TA2 | 6318 |
| FMA | 53431 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
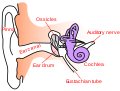
The cochlear nerve (also auditory nerve or acoustic nerve) is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory information from the cochlea of the inner ear directly to the brain. The other portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve is the vestibular nerve, which carries spatial orientation information to the brain from the semicircular canals, also known as semicircular ducts.[1]
Anatomy and connections
In terms of anatomy, an auditory nerve fiber is either bipolar or unipolar, with its distal projection being called the peripheral process, and its proximal projection being called the axon; these two projections are also known as the "peripheral axon" and the "central axon", respectively. The peripheral process is sometimes referred to as a dendrite, although that term is somewhat inaccurate. Unlike the typical dendrite, the peripheral process generates and conducts action potentials, which then "jump" across the cell body (or soma) and continue to propagate along the central axon. In this respect, auditory nerve fibers are somewhat unusual in that action potentials pass through the soma. Both the peripheral process and the axon are myelinated.
In humans, there are on average 30,000 nerve fibers within the cochlear nerve.[2] The number of fibers varies significantly across species; the domestic cat, for example, has an average of 50,000 fibers. The peripheral axons of auditory nerve fibers form synaptic connections with the hair cells of the cochlea via ribbon synapses using the neurotransmitter glutamate. The central axons form synaptic connections with cells in the cochlear nucleus of the brainstem.
The cell bodies of the cochlear nerve lie within the cochlea and collectively form the spiral ganglion, named for the spiral shape it shares with the cochlea. These central axons exit the cochlea at its base and form a nerve trunk, which, in humans, is approximately one inch long. This travels in parallel with the vestibular nerves through the internal auditory canal, through which it connects to the brainstem. There, its fibers synapse with the cell bodies of the cochlear nucleus.
Types of neurons
In mammals, cochlear nerve fibers are classified as either type I or type II.
- Type I neurons make up 90-95% of the neurons and innervate the inner hair cells. They have relatively large diameters, are bipolar, and are myelinated. Each type I axon innervates only a single inner hair cell, but each inner hair cell is innervated by up to 30 such nerve fibers, depending on species and location within the cochlea.
- Type II neurons make up the remaining 5-10% of the neurons and innervate the outer hair cells. They have relatively small diameters, are unipolar, and are unmyelinated.
Cochlear nuclear complex
In mammals, the axons from each cochlear nerve terminate in the cochlear nuclear complex that is ipsilaterally located in the medulla of the brainstem. The cochlear nucleus is the first 'relay station' of the central auditory system and receives mainly ipsilateral afferent input.
The three major components of the cochlear nuclear complex are (see figure below):
- the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN)
- the anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN)
- the posteroventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN)
Each of the three cochlear nuclei are organized to sort sound according to a specific spacial arrangement. As such, sound frequencies detected by the cochlea are transmitted electrically to specific positions in the cochlear nuclei. The axons from the low-frequency region of the cochlea project to the ventral portion of the dorsal cochlear nucleus and the ventrolateral portions of the anteroventral cochlear nucleus. The axons from the high-frequency region project to the dorsal portion of the anteroventral cochlear nucleus and the uppermost dorsal portions of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The axons from the intermediate frequency region project to intermediate targets. Through this process, a spatial representation of sound is created by electrical nerve impulses through the cochlear complex.
See also
References
- ^ Palmer, A R (1987). "Physiology of the cochlear nerve and cochlear nucleus". British Medical Bulletin. 43 (4): 838–855. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072221. ISSN 1471-8391. PMID 3329928.
- ^ Spoendlin H, Schrott A (1989). "Analysis of the human auditory nerve". Hear Res. 43 (1): 25–38. doi:10.1016/0378-5955(89)90056-7. PMID 2613564. S2CID 37038957.
Additional images
-
Ear anatomy
-
Cochlear nucleus innervated by a branching auditory nerve fibre
-
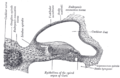
Terminal nuclei of the vestibular nerve, with their upper connections.
-
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat.
-
Floor of ductus cochlearis.
-
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea