Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute
| Ecuadorian-Peruvian Wars | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the South American territorial disputes | |||||||
 Map of the disputed territories from 1916 onwards | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
In 1858-1860 Supported by: |
In 1858-1860 Supported by: | ||||||
|
Incidents of 1903 and 1904 Diplomatic incident of 1910 In 1941 |
Incidents of 1903 and 1904 Diplomatic incident of 1910 | ||||||
|
In 1995 Supported by: |
In 1995 | ||||||
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute was a territorial dispute between Ecuador and Peru, which, until 1928, also included Colombia.[Note 1] The dispute had its origins on each country's interpretation of what Real Cedulas Spain used to precisely define its colonial territories in the Americas. After independence, all of Spain's colonial territories signed and agreed to proclaim their limits in the basis of the principle of uti possidetis juris, which regarded the Spanish borders of 1810 as the borders of the new republics. However, conflicting claims and disagreements between the newly formed countries eventually escalated to the point of armed conflicts on several occasions.
The dispute de jure had come to an end in the aftermath of the Ecuadorian–Peruvian War with the signing of the Rio de Janeiro Protocol on January 29, 1942. However, this treaty was also questioned, and the two countries went to war on two more occasions: the Paquisha War in 1981, and the Cenepa War in 1995. Tensions subsided but persisted over the next three years. On October 26, 1998, Ecuador and Peru signed a comprehensive peace accord that established a framework for ending a border dispute. Formal demarcation of border regions started on May 13, 1999. The agreement was ratified without opposition by the congresses of both nations, finally bringing a definitive end to the dispute.
Spanish era
Spanish conquest and establishment of the Viceroyalty of Peru
Beginning with the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1492, the Spanish conquistadores expanded the range of the Spanish Crown's reach from early small settlements in the Caribbean to various continental territories, eventually including Central America and most of South America.
The Spaniards arrived at the borders of the Inca Empire in 1528, and on November 16, 1532, taking advantage of the Inca Civil War, the tiny army of Francisco Pizarro began the Spanish conquest of Peru. In the following decades, Spain consolidated its power over the entire Andean region, repressing successive indigenous rebellions.
To govern the new territories of Spain, in 1542 Holy Roman Emperor Charles V (King Charles I of Spain) created two Viceroyalties, the Viceroyalty of New Spain (in modern-day Mexico) and the Viceroyalty of Peru (a.k.a. the Viceroyalty of New Castile). In 1542, King Charles named Blasco Núñez Vela Peru's first viceroy, but the viceroyalty was not organized until the arrival of Viceroy Francisco de Toledo in 1572. Toledo promptly declared war on Vilcabamba, the last refuge of the Inca; soon afterwards, Tupac Amaru, the last Inca emperor, was captured and executed in Cuzco.
Territorial division of the Viceroyalty of Peru

Because the territory of the Viceroyalty of Peru was so large, and far away from centers of government in Lima and Santo Domingo, Peru (as well as New Spain) was divided into a number of real audiencias (royal audiences), a type of superior judicial tribunal that combined executive and judicial authority, and can be considered "major provinces". The audiences controlled the gobernaciones,[Note 2] alcaldias mayores,[Note 3] corregimientos,[Note 4] and alcaldias ordinarias.[Note 5] The territory was also divided ecclesiastically, into archbishoprics, religious provinces, suffragan bishopries, parishes and curateships. The archbishoprics and religious provinces corresponded with the audiences, the bishoprics with the gobernaciones and alcaldias mayores, and the parishes and curateships with the corregimientos and alcaldias ordinarias.[1]
These civil divisions were not uniform, with numerous exceptions being made based on the specific circumstances. The Viceroys were presidents of the audiences at the capitals of their Viceroyalties, with other audiences being presided over by captain-generals, or by persons known as gowned presidents. Power was devolved to the captain-general of an audience by the Viceroy, and the audience's territory was administered by the audience's president and the political, military, and religious officials underneath him.[1]
Between 1542 and 1717, the Viceroyalty controlled most of the territory of South America (save for a few non-Spanish colonies and the Commandancy General of Caracas, which was a dependency of the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo). The territory was divided among (noting dates of creation):
- Royal Audience of Tierra Firme (1564)
- Royal Audience of Santa Fe de Bogotá (1548)
- Royal Audience of San Francisco of Quito (1563)
- Royal Audience of the City of Kings Lima (1543)
- Royal Audience of La Plata de los Charcas (1559)
- Royal Audience of Chile (1563–1573; 1606)
The district of an audience was established in the royal decree by which it was created; the laws laid out in the myriad of Cédulas Reales issued by the Spanish Crown were compiled several times throughout the centuries-long history of Spanish presence in the region. These compilations were referred to as the Laws of the Indies; the 1680 compilation, organized under Charles II, known as the Recopilación de las Leyes de los Reynos de Indias (Compilation of the Laws of the Kingdoms of the Indies), set a template by which the laws were organized.
Under Title XV of Book II of the Recopilación, the limits of the audiences of Lima and Quito were defined as follows:
- The district of the Royal Audience of San Francisco of Quito was described in Law X, Title XV of Book II: "In the City of San Francisco of Quito, in Peru, shall reside another Royal Audience and Chancellery of ours, with a president; four judges of civil cases [oidores], who will also be judges of criminal cases [alcaldes del crimen]; a crown attorney [fiscal]; a bailiff [alguacil mayor]; a lieutenant of the Gran Chancellor; and the other necessary ministers and officials; and which shall have for district the Province of Quito, and along the coast towards the Ciudad de los Reyes [Lima] to the Port of Paita, exclusive; and inland towards Piura, Cajamarca, Chachapoyas, Moyobamba and Motilones, exclusive, including towards the aforesaid part the towns of Jaén, Valladolid, Loja, Zamora, Cuenca, La Zarza and Guayaquil, with the rest of the towns, which are in their districts or will be founded [in them]; and towards the towns of La Canela and Quijos, it should include said towns and the rest that shall be discovered; and along the coast towards Panama, until the Port of Buenaventura, inclusive; and inland to Pasto, Popayán, Cali, Buga, Chapanchinca and Guarchicona; because the rest of the places of the Government (Gobernación) of Popayán are of the Audience of the New Kingdom of Granada, with which, and with the one of Tierrafirme [Panama], it shall share a border on the north; and with the one of Los Reyes in the south; having for its western border the South Sea [Pacific Ocean] and eastern the provinces still not yet pacified nor discovered."[2][3][Note 6]
- The district of the Royal Audience and Chancellery of Lima was described in Law V, Title XV of Book II: "In the City of Kings Lima, the capital of the provinces of Peru, shall reside another Royal Audience and Chancellery of ours, with a viceroy, governor and captain general, and a lieutenant, who will be president; eight judges of civil cases [oidores]; four judges of criminal cases [alcaldes del crimen]; two crown attorneys [fiscal], one for civil, and the other for criminal cases; a bailiff [alguacil mayor]; a lieutenant of the Grand Chancellor; and the other necessary ministers and officials; and which shall have for district the coast from that city down to the Captaincy General of Chile exclusive, and up to the port of Paita inclusive, and, for inland, to San Miguel de Piura, Cajamarca, Cachapoyas, Moyabamba and the Motilones, inclusive, and as far as Collao, exclusive, along the boundaries outlining the Royal Audiencia of La Plata, and the city of Cuzco, with its boundaries, inclusive, sharing the boundaries on the north with the Royal Audiencia of Quito, on the south with the Audiencia of La Plata, on the west with the Southern sea, and on the east with the provinces yet undiscovered, accordingly as they may be established."[2][3][Note 7]
Creation of New Granada
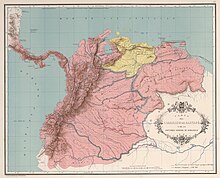
The two original Spanish viceroyalties of New Spain and Peru had existed intact up until 1717, when King Philip V of Spain issued the Real Cédula of May 27, 1717. The order split off the northwestern corner of Peru and created the Viceroyalty of New Granada. New Granada shared its capital with the Royal Audience of Santa Fé de Bogotá, and additionally had jurisdiction over the New Kingdom of Granada, as well as the audiences of Tierra Firme (now called Panama), Quito, and the Captaincy General of Venezuela. The territories of the Viceroyalty comprised the territories of, respectively, the modern Republics of Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela, as well as the northern regions of Peru, the Brazilian northwest, and the western part of Guyana.
The Royal Audience of Quito had been established by a royal decree in 1563, its territory including Pasto, Popayán, Cali, Buenaventura and Buga in what is currently Colombia, and extended as far south as Piura in what is now Peru.[4][5] The eastern limit was ill-defined at the time, due to a lack of geographical knowledge and the low importance given to unpopulated, hard-to-reach territories.[5] As the Jesuit Missionaries from Quito and other missionaries entered the Amazon Basin, the Amazon region with its tributaries were more clearly defined and by 1740, the Real Cedula of 1740 precisely defined the borders between the Viceroyalties of New Granada and Peru.
Having temporarily suppressed the Viceroyalty of New Granada, on November 5, 1723, Philip V emitted another Cédula, which returned control of the Royal Audience of Quito to the Viceroyalty of Peru. The Cédula of August 20, 1739 (also called the Cédula de Reerección Definitiva del Virreinato de Nueva Granada, "Definitive Decree of Re-erection of the Viceroyalty of New Granada") reinstated the viceroyalty with its 1717 territories, including the Royal Audience of Quito.[6] The border between Quito and the Viceroyalty of Peru was defined in 1740 by another Cédula:
Starting from the Tumbes on the Pacific Coast, the line follows by the ridges and other cordilleras of the Andes through the jurisdiction of Paita, and Piura to the Marañón, at 6 degrees, 30 minutes South Latitude, and on the interior, leaving to Peru the jurisdiction of Piura, Cajamarca, Moyobamba and Motilones; and by the cordillera of Jeveros, crossing the river Ucayali, at 6 degrees of South Latitude, up to the Javary River or Jauri River at its confluence with the Carpi; and on the waters of the latter to Solimões or the Amazonas and from thence down to the most westerly mouth of the Caquetá or Yapurá, where the boundaries with Brazil begin."[6]
This cedula greatly modified the original demarcation, but served only to fix the starting point of the line on the pacific coast at the river Tumbes. This document was the first mention of the Tumbes as the boundary between the two viceroyalties.[6]
Real Cédula of 1802
Don Francisco de Requena requested that control of the Government and Commandancy General of Maynas pass from the Viceroyalty of Santa Fe (New Granada) to the Viceroyalty of Peru. In response, on July 15, 1802, the Spanish crown under the rule of Charles IV of Spain issued the Real Cédula of 1802. The decree split the Government and Commandancy General of Maynas and the Governorate of Quijos from the Audience of Quito, and added them to the Viceroyalty of Peru.[7] The text of the decree, as reproduced in the Annals of the diplomatic and consular missions of Colombia (1901), reads:

I have resolved that the administration and General Command of Maynas with the towns of the administration of Quijos be separated from the province of Quito and added to the Viceroyalty of Santa Fe, except for Papallacta, for reason that they are all on the shores of the Napo River or its immediacies, extending the aforementioned General Command not only downstream of the Marañón River, to the borders of the Portuguese colonies, but also down all the other rivers entering the Marañón by its northern and southern margins as do the Morona, Huallaga, Paztaza, Ucayali, Napo, Javari, Putumayo, Japurá, and other less significant, until the place in which these cease to be navigable streams: the villages of Lamas and Moyobamba must also become part of the aforementioned General Command... To which end I order that you aid, added as is the administration of Maynas and Quijos to this Viceroyalty, with whatever steps you deem necessary, and I request of you, the Commander General, that you serve them not only for the advancement and conservation of the peoples in the custody of the missionaries, but also for the security of my dominions, by preventing them from being brought forward by the vassals of the Portuguese Crown, by naming the junior sergeants or Lieutenant Governor that you see fit, for the defense of these frontiers and the administration of justice... I have also resolved to erect a diocese in said missions... I THE KING[Note 8]
In a footnote, Dr. Antonio José Uribe, Minister of Foreign Affairs of Colombia from 1901 to 1902, wrote,
With respect to this Real Cédula of 1802, it is worth noting that there are three specimens available, all of them Peruvian in origin, and not one of them agrees with any of the others, they are: the one produced by Dr. [Enrique Vacas] Galindo; the one contained in the volume published in Brazil; and the one in the Peruvian brief presented before the Government of Spain in the matter of the limits with Ecuador.[Note 9][8]
thereby casting suspicion on the authenticity of one or more of the copies of the document, complicating the already difficult matter of interpreting its meaning.[Note 10]
According to Pedro Moncayo y Esparza, a 19th-century Ecuadorian writer, the Viceroy of Santa Fe and the President of Quito objected to the execution of the Real Cédula of 1802, as it had all the makings of an apocryphal document: it was not registered in the official cedulario, and its contents could not be found in the Recopilacion de Indias, nor had it been located in the Archive of the Indies in Spain.[9] However, during the Peruvian congressional committee hearings regarding the dismissal of the Treaty of Mapasingue, signed between Ecuador and Peru at the end of the war of 1857–1860, it was stated that the Real Cédula of 1802 and the documents proving its execution were found in the archives of the ancient government of Maynas.[10]
The lack of clarity within the document as to whether the transfer of administrative power was purely military and ecclesiasticcal in nature, or territorial as well, formed the basis for an imprecise territorial situation between Ecuador and Peru when the two nations obtained their independence from Spain.[5]
1803–1818
- 1803: A similar event occurred in 1803, when it was decided that the military affairs of the Province of Guayaquil (whose capital was the strategically situated port city of Guayaquil) would be run from Lima.
- 1810: all administrative and economic affairs of the province were turned over to the Viceroyalty of Peru, a state of affairs that would endure until 1819. Jaén de Bracamoros had no such cedula transferring it to Peru and would rightly belong to Ecuador. However, Jaén decided to join Peru after it took part in northern Peru's revolutionary wars of independence.
- September 28, 1812: the Council of Regency requested from Madrid the Expediente sobre la erección del Obispado de Maynas y las Cédulas que se expedieron en 1805 acerca de los limites ("File on the erection of the Diocese of Maynas and the Decrees that were issued in 1805 regarding the borders"). With no response forthcoming, a Decree of the Courts rendered the Decree of 1802 null and void on November 13, 1812.
- September 13, 1813: the Real Cédula de 1813 was issued to replace the 1802 decree, in its first article ordering "entregar al Ordinario las nuevas Reducciones y Doctrinas que tuviesen mas de 10 años de antiguedad, proveyéndose en eclesiásticos seculares, conforme a las Leyes del Patronato."
- September 26, 1813: the Bishop of Maynas, Friar Hipólito Sánchez Rangel, notifies the Overseas Minister that "solo assisten los Religiosos de Quito en Maynas y dice es fuerza, pues, si se tratan de hacer justicia que se me ponga en otro Obispado que sea menos penoso."
- May 1, 1814: the census carried out by Sanchez Rangel reads: in 58 towns of the 90 that make up said diocese there are no more than eight assistant priests, three of which are located at the extremes of the Bishopric: three in small rivers, one in the dilated course of the great rivers Guallaga and Marañón, and none in the Napo, Putumayo, Ucayale and Pastaza. This mean that 60 villages were without a parish and almost all the missions were abandoned. Sanchez Rangel had written in 1813: "Desde que salieron los jesuitas de estas tierras no ha habido quien se contraiga a su fomento espiritual ni temporal; todos se han buscado a sí mismos. De esta proposición que es absoluta y de una eterna verdad se ha seguido naturalmente lo que estamos viendo y tocando con dolor, que ya no ha quedado cosa alguna de lo que aquellos padres establecieron y solo hay lo que produce la madre naturaleza."
- September 27, 1814: Sanchez Rangle requests that the Bishopric of Maynas be suppressed, its erection null and void due to a lack of compliance with the Real Cédula de 1802.
- February 22, 1815: The Council of the Indies receives a letter from Sanchez Rangel dated January 28, 1814. Bishop Rangel proves that the Decree of 1802 has not been met by the government, the priests at the edges of the Bishopric, nor the "P.P. de Ocopa".
- February 7, 1815: The President of Quito, Toribio Montes reports regarding the Missions of Maynas, saying "He manifesto a V.E. en informes anteriores, que las Missiones del Marañón se hallan en un sensible atraso, faltándoles el número completamente Ministros evangélicos...Incluye a Maynas en los dominios de Quito"
- 1816: The King of Spain issues a Royal Order revoking and annulling the Real Cédula de 1802; on September 22, the President of Quito receives the files related to the revocation.
- 1818: The President of Quito names Don Juan Navas Governor of Quijos. On June 19, the Council of the Indies tells the story of the creation of the Bishopric and the General Command of Maynas, the lack of compliance with the Decree of 1802, and the impossibility of compliance with the former.
- July 22, 1818: The President of Quito asks the Viceroy of Peru for the revocation and annulment of the Real Cédula de 1802. On August 23, the Viceroy acknowledges the Royal Order of 1816, returning the province of Maynas to Quito.
Wars of Independence
The Republic of Gran Colombia was founded in 1819, with Simón Bolívar as president. On August 7 of that year, the independence of what is now Colombia was won in the Battle of Boyacá. The independence of Venezuela was won on June 24, 1821, in the Battle of Carabobo. One of Bolívar's generals, Venezuelan-born General Antonio José de Sucre won the Battle of Pichincha on May 24, 1822, and freed the territory that was then Ecuador.
Gran Colombia comprised what is now Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela and Panama. It was Simón Bolívar's dream to unite all of South America, a project which he would never achieve.
Even before the battles for the freedom of the South American colonies were over, Bolívar established the uti possidetis juris principle as the basis for the territorial demarcation of the new nation-states that were to be born out of the ancient colonial jurisdictions. In essence, the principle stated that the borders of the new countries should correspond to the Spanish administrative borders, as they were in 1809. By this principle, the territory of the Viceroyalty of Peru would become the Republic of Peru (modern Peru), and the territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada would become the Republic of Colombia (Greater Colombia, which included modern Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Panama). Border disputes arose when Peru began basing its borders on the Cedula Real of 1802 which gave them rights to claim territory in the Amazon region and the Cédula of 1803 which gave Peru the right to claim Guayaquil and the coast of Ecuador. Colombia claimed that both Cedulas do not change political borders because the Cedula of 1802 refers only to Ecclesiastical borders and the 1803 cedula deals with mercantile and military jurisdictions. Gran Colombia based its borders on the unmodified Cédula of 1740 to define its borders with Peru.
- July 6, 1822: Monteagudo-Mosquera Treaty
- Mosquera's mission to Lima had two objectives: (1) To come up with a treaty of alliance between Gran Colombia and Peru against Spain, and (2) To have Peru recognize that Guayaquil was to be part of Gran Colombia. Monteagudo initially refused to give up Guayaquil without first having the people of that city express their will voluntarily. The treaty was signed, nonetheless, but precise territorial demarcation was left for a later treaty. [1]
Gran Colombia–Peru conflict
Bolívar had aspirations to maintain the unity of Gran Colombia, a republic that would unite most of the former Spanish colonies of the Viceroyalty of New Granada (Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Panama) under his rule. Peruvian President José de la Mar, who had been a member of Bolívar's troops during the wars of independence and born in Cuenca, Ecuador, had his own political ambition. De La Mar wanted to establish himself as the formal ruler of Peru, which in precolonial times was called the Inca Empire which controlled parts of Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia. Because of De La Mars ambition of restoring the glory of the Inca Empire by annexing Ecuador and Bolivia to Peru, relations between Bolívar and De la Mar quickly boiled over and the two soon became rivals.
Deciding to free Peru (what is now Peru and Bolivia) from what he considered to be an authoritarian project, De la Mar promoted an anti-Bolivarian campaign which gained popular support and led to insurrections, both in Peru and in Bolivia (Upper Peru), where the Colombian Army was expelled. Finally, he decided to confront Bolívar more directly by launching an attack. On June 3, 1828, de la Mar invaded the southern region of Gran Colombia; he occupied Loja and tried to capture Guayas, and intended to annex those territories to Peru.
Furious upon hearing the news, Simón Bolívar resolved to declare war against Peru. Sucre was appointed Commander of the Colombian Army. In 1829, De la Mar and General Agustín Gamarra occupied Cuenca, but were defeated in what is known as the Battle of Portete de Tarqui (also known as the Battle of Tarqui) by Sucre on February 27, 1829. A coup supported by General Gamarra in the Peruvian Army against President De la Mar paved the way for a peace treaty. Subsequently, the Convenio de Girón between Peru and Gran Colombia recognizes the borders as the "same ones of the corresponding Viceroyalties before independence." On July 10, the Piura Armistice recognised the annexation of Guayaquil to Gran Colombia, and on September 22, the war between Peru and Gran Colombia formally ended. [2]
- February 28, 1829: La Mar-Sucre Convention
- This convention was signed the day after the Battle of Tarqui was won by Gran Colombia, ending Peru's attempt to forcefully annex the Department of Guayaquil and the Department of Azuay from Gran Colombia.
- September 22, 1829: Larrea-Gual Treaty
- Ecuador considers this a transitional treaty that resulted from the Battle of Tarqui and later developed into the disputed Pedemonte-Mosquera Protocol the next year. The uti possidetis principle was ratified, allowing for small concessions with the end of coming up with a more natural and precise border so as to avoid further conflict. The parties agreed to form a binational commission to establish a permanent border. [3]
The Gran Colombia federation dissolved in 1830 because of political struggles between regions which strengthened after Bolívar's resignation. Ecuador was born as a country on May 13, 1830, and began its separate existence with the adoption of a Constitution on September 23, 1830. According to this constitution, the Republic of Ecuador was composed of the provinces of Azuay, Guayas and Quito. These provinces later divided into the many provinces that exist today in Ecuador.
Confusion about Gran Colombia
The term Gran Colombia is used today to refer to the federation that was formed between the Republics of Ecuador, Colombia (with Panama) and Venezuela before 1830. However, Gran Colombia is an anachronistic term, as the country was simply referred to as Colombia, which is clear, for example, by looking at original documentation of the many treaties signed between Colombia and Peru before 1830.[original research?]
In Peru, the dissolution of Gran Colombia is seen as a country ceasing to exist, giving way to the formation of new nation states that had nothing to do with the original federation. The significant implication of this view is that the treaties Peru had signed with Gran Colombia were voided, as the country in question no longer existed, and was replaced with three new states, the Republic of New Granada (which subsequently changed its name to Republic of Colombia), the Republic of Venezuela and the Republic of Ecuador.
An alternative view is that Ecuador and Venezuela separated from the Gran Colombia Federation (from Colombia in actuality) and inherited any treaties that Gran Colombia had signed with Peru as they applied to their corresponding territories. There are indications that Colombia itself maintained this position.[original research?]
The Pedemonte-Mosquera Protocol
Ecuador and Colombia maintain that the Pedemonte-Mosquera Protocol was signed in Lima on August 11, 1830, by Peru and Gran Colombia as a result of the Battle of Portete de Tarqui. The protocol settled the eastern section of the disputed border from the Andes Mountains to Brazil by making the Marañón River and Amazon River the new border between the two republics. The protocol settled the western section of the border from the Andes Mountains to the Atlantic Ocean by making the Macará river and the Tumbes river the new boundary. However, it left the status of a small area in the Andes Mountains named Jaén de Bracamoros in dispute. It was decided by Pedemonte and Mosquera that on a later date, either the Chinchipe River or the Huancabamba River would be chosen as the new boundary.
Ecuador has used this protocol as primary legal support of its core claims throughout the history of the conflict. Peru has disputed the credibility and the existence of the Piedemonte-Mosquera protocol on several points:
- The original document has not been produced either by Colombia or Ecuador.
- Piedemonte and Mosquera were believed to be at different locations on the day in question.
- The protocol was never ratified by either country's congress.
- Even if the protocol took place, Ecuador had separated from the Gran Colombia Federation a month before the signing of the protocol – August 11, 1830.
- The copy produced by Colombia is not sufficient evidence for Peru.
Even though it seems unlikely that Ecuador would have concocted a historical treaty of this nature, the fact that the existence of the original document cannot be demonstrated conclusively is significant.
Ecuador has managed to produce a copy made in 1870 that the Colombian embassy in Lima sent to Bogotá. The copy in question was obtained from someone's personal collection. However, it was not certified by Peru and remains disputed.
The Piedemonte-Mosquera protocol is mentioned in a Colombian document titled Legislative Act No. 3 published October 31, 1910. [4] The document explains how the borders between Colombia and its neighbors have been established; as to its border with Peru, it indicates they are those adopted by Mosquera-Piedemonte, in development of the treaty of September 22, 1829.
There are conflicting versions of what exactly took place. For an Ecuadorian view point, see [5] Archived 2008-06-07 at the Wayback Machine. For Peruvian points of view, see [6][7].
Treaties with Brazil and Colombia (1832–1856)
- February 10, 1832: The Separation of Ecuador from Gran Colombia legally recognized
- The Republic of Nueva Granada (Colombia) recognizes separation of the Departments of Quito, Guayaquil, and Azuay from the Gran Colombia union to form the New nation of Ecuador which declared its separation on May 12, 1830.
- July 12, 1832: Pando-Noboa Treaty
- Peru recognizes Ecuador as a new republic and signs a treaty of friendship, alliance and commerce. Article XIV mentions that until a convention, respecting the limits of the 2 states, shall have been concluded, the present limits shall be recognized and respected.
- 1841–1842 Period: León-Valdivieso and Daste-Charún negotiations
- In 1841 Ecuador demands return of the jurisdictions of Tumbes, Jaén and Maynas. After violent discussions, Ecuador gives an ultimatum to the effect that if there's no answer from Peru by a certain date, Ecuador would be forced to occupy territories considered Ecuadorian according to article 5 of the Larrea-Gual treaty of 1829. [8] Peru considered it absurd to return provinces that were de facto, and that it also considered de jure, Peruvian. Peru considered Maynas annexed to the Viceroyalty of Peru by the Cedula (Royal Decree) of 1802. Ecuador's claim to Tumbes and Jaén is from the Cedula of 1563 and Cedula of 1740 unmodified in the eastern regions of Ecuador. [9] Territorial negotiations failed in 1842 as the Ecuadorian envoy insisted on the return of Jaén and Maynas.
- October 23, 1851: Peru-Brazil Treaty
- Peru fixes its eastern border with Brazil; however, Ecuador and Colombia protested that the border fixed with Brazil north of the Amazon called the Apoparis-Tabatinga line is within disputed Amazon Territories. The disputed territories (triangular in shape) at that time was disputed between Ecuador, Colombia and Peru and covered everything east of the Andes mountains and everything in between the Caquetá-Japurá river and Marañón-Amazon river.
- March 10, 1853: Creation of the Peruvian Government of Loreto
- To justify its claims to the disputed amazonian territory Peru decides to create a separate amazonian political military government naming it the Government of Loreto, after Peru successfully takes over a small amazonian port called Nauta. The policy of the Loreto Government is to concentrate on exploring, taking over, and settling these vacant areas with Peruvian citizens before Ecuador and Colombia, thus having a good de facto position if the dispute goes to arbitration. Before 1890, the fluvial armada concentrated in taking over the small river ports along the Marañón river like Nauta, Omaguas, Iquitos, Regis, Parinari, Antonio, Santander, Barrabca, Borja, Mazan, and Destacamento. Most of the exploration of the tributary rivers north of the Marañón river was conducted by a Peruvian military commander named Coronel Pedro Portillo in the early 20th century. The Peruvian fluvial armada at that time consisted of lightly armed rafts and boats with its main base in Iquitos, the capital of Loreto. In this way most of the northern tributary rivers which drained into the Marañón – Amazon river and its adjacent disputed territories were occupied by Peruvians.
Ecuadorian–Peruvian War (1857–1860)
This was an expensive war fought over disputed territory bordering the Amazon. On September 21, 1857, Ecuador decided to adjudicate to Britain territories in the Canelos region as payment for international debt it had incurred during the war of independence. Peru immediately protested the Ecuadorian action citing the uti possidetis juris principle by which the Canelos region would belong to Peru, based on the territorial concession of 1802 to the Viceroyalty of Peru. Despite Peruvian complaints, Ecuador proceeded in its negotiations with the British. This led to an 1859 occupation and blockade of Guayaquil by President Castilla. (Ecuador at the time was undergoing a civil struggle.) On February 25, 1860, Peruvian minister Manuel Morales and his Ecuadorian counterpart, Nicolás Estrada, signed the Treaty of Mapasingue in order to end the dispute. (Mapasingue is a location near Guayaquil where Peruvian troops had been stationed.) Ecuador voided the concession of territories claimed by Peru to the British, and Peru withdrew its forces. However, the territorial situation remained unclear and was left to be resolved at a later time.
Boundary negotiations and treaties (1860–1941)

- 1864: Peruvian Navy establishes presence in Iquitos
- Steamships of the Peruvian Navy arrived at Iquitos, first the Morona and Pastaza of 500 and 300 tons, and then two smaller steamboats of 50 tons, the Napo and the Putumayo. Shortly afterwards a dockyard and a navy factory arrive from England and are installed, thus establishing the Factoria Naval de Iquitos.
- August 1, 1887: Espinoza-Bonifaz Convention
- In the Espinoza-Bonifaz convention Ecuador and Peru submitted their dispute to arbitration by the King of Spain. Ecuador announced its withdrawal from the process months before a decision was issued, which was expected to be in 1910. Ecuador alleged that the King was not impartial because the officially undisclosed decision was not favorable. Additionally, there were popular protests in Ecuador against Peru. The King subsequently abstained from issuing a decision. Arbitration documents confirmed Peru's right to Maynas and other lands in dispute. [10] Ecuador's position was that arbitration did not arrive at a satisfactory conclusion because even Peru's representative had expressed that the King did not have the capacity to consolidate peace, as both countries were parting from absolutely opposing principles. [11]
- May 2, 1890: Herrera-García Treaty
- Because of the many disagreements during the arbitration by the King of Spain, Ecuador and Peru decided to enter direct negotiations. This was in part accepted by Peru due to the recent Peru-Chile (1879–1883) war, which resulted in its defeat and loss of territory to Chile. The treaty signed by Pablo Herrera and Arturo García gave dominion and access to the Amazon river, the Napo and Putumayo rivers, and control over parts of the provinces of Tumbes and Maynas, and the Canelos [12]. This treaty was quickly ratified by Ecuador's congress. Since the Peruvian Congress thought the treaty unfavourable, they ratified it in October 1891, provided they were allowed to introduce modifications, which reduced Ecuadorian sovereignty over the Marañón – Amazon rivers. Ecuador's congress subsequently disapproved the Herrera-García treaty due to the modifications introduced by Peru. Ecuador also requested meetings to further discuss its validity thesis on the Guayaquil (Gual-Larrea) Treaty of 1829. [13]
- 1903–1904 incidents
- In both 1903 and 1904 there were military confrontations in the Napo River basin. The first one is known as the Battle of Angostero and the second one occurred at a location known as Battle of Torres Causana. Less numerous but better equipped Peruvian forces were able to cause the retreat of Ecuadorian troops to locations around the Tena and Archidona rivers. [14]
- May 6, 1904: Tobar – Rio Branco Treaty between Brazil and Ecuador
- In 1904 Ecuador decides to sign a treaty of friendship, alliance, and free navigation with Brazil. With this treaty Ecuador relinquishes its ancient Spanish colonial rights to present-day Brazilian territory that exactly covers an area between the Caqueta and Amazon rivers.
- July 15, 1916: Muñoz-Suarez Treaty between Colombia and Ecuador
- This treaty put an end to a long-lasting border dispute, that arose after Ecuador's separation from the Gran Colombia on May 13, 1830. Under the terms of the treaty, the new boundary was a somewhat straight imaginary line that started in the Pacific Ocean and ended in the Amazon River. In the Andes region the boundary followed the present borders between Ecuador and Colombia. Then starting around 75°W Longitude the border followed a somewhat straight line midway between the Putumayo and Napo rivers until it reaches the Ampiyacu River, which was picked as a natural border in the jungle region between Ecuador and Colombia. The border then followed the Ambiyacu River and ended when it reached 72°W Longitude on the Amazon River. With this treaty Ecuador gave up a portion of its ancient colonial claims to a territory that reached north to the Caqueta River and east to the Brazilian border.
- June 21, 1924: Ponce-Castro Oyangurin Protocol
- This is a protocol signed between Ecuador and Peru, wherein both parties agreed to send their representatives to Washington so that they could try to resolve their border disputes in an amicable manner through a direct negotiation compromise method followed by a partial arbitration by the President of the United States. The meetings commenced on September 30, 1935, and lasted two years. From the start the President of the United States was asked not to interfere with the direct negotiations by the Peruvian delegation, since his duty would be to arbitrate a final solution based on these direct negotiations if said negotiations failed. During that time period neither party seemed to agree on defining the boundaries of the disputed area to be arbitrated by the President of the United States. In essence, Ecuador considered all of Tumbez, Jaén, and Maynas to be Ecuadorian because of its numerous de jure colonial titles, but was willing to divide them up through a compromise negotiation method for the sake of peace. In contrast, Peru considered Tumbez, Jaén, and Maynas to be all Peruvian because of their de facto occupation and the real cedula of 1802 title, and showed up in Washington to only negotiate what the borders of these provinces were in relation to Ecuador. Because of the failure to agree on what lands were disputed, the conference in Washington was doomed to failure. Finally, on February 6, 1937 Ecuador proposed a transactional line similar to the Herrera-Garcia Treaty for arbitration and asked for complete arbitration by the President of the United States if this is rejected. Peru promptly rejected this the next day and later the Peruvian Delegation passed a note to the Ecuadorian Delegation, which informed them that they had just received instructions from their government in Peru to abandon the negotiations. Because of this the President of the United States, Franklin D. Roosevelt, was not able to put a final solution to the border dispute through a peaceful arbitration.
- July 6, 1936: Ulloa-Viteri Accord
- This agreement established a status quo border line based on the effective possession of territory that each country had in the Amazon region at the time. This border was very similar to that established by the Rio de Janeiro Protocol 5 years later. To Ecuador, the status quo line simply demonstrated how much territory Peru had taken from Ecuador in the preceding century. Ecuador never considered this agreement a final treaty of borders, and continued its aspirations which were based on Gual-Larrea and Pedemonte-Mosquera.
Ecuadorian–Peruvian War (1941)
In 1941, the two countries went to war. As with all other such incidents, there are conflicting accounts to this day as to which side fired the first shot. Peru's version of events (notably well documented in Peruvian sources [15][16][dead link]) is that Ecuador had been making incursions into its territory since 1937 and occupied several border locations by 1940.
Given these circumstances, the President of Peru, Manuel Prado Ugarteche, ordered the formation of the North Grouping, a military unit in charge of the Northern Operational Theater, on January 11, 1941, consisting of two light divisions with three battalions each, plus four other independent battalions and three artillery batteries (one with six 105 mm guns) (Delgado).
In front of these forces, the Ecuadorian Border Security command had under its orders two Army battalions, the "Montecristi" and the "Cayambe", each one consisting of around 250 troops, armed with 7.92 mm Mauser rifles and a couple of Czech 7,92 mm ZB-26 light machine-guns, plus two Vickers-Maxim machine-guns. There was also a "Córdova" battalion, made up of around 100 troops, and a so-called "Mariscal Sucre" artillery battery, with 71 troops and no artillery pieces. In fact, the only artillery in the whole province of El Oro consisted of six Italian 65 mm mountain guns, sold to Ecuador as leftovers from the Great War, and almost without shells. These guns were never put into action. (Rodríguez, 1943).
As for anti-aircraft defenses, the Ecuadorians had only a pair of 20 mm Breda guns deployed on Puerto Bolívar, which was the only port of entry for supplies, reinforcements, and weapons to arrive to the province, by sea, from the port-city of Guayaquil. The Ecuadorian Army of 1941 had not a single warplane. (Rodríguez, 1943).
It is claimed that on Saturday, July 5, 1941, the Huaquillas unit of the Ecuadorian army invaded Peruvian territory, an action which originated a combat that extended across the entire Zarumilla front, up to a region known as Quebrada Seca.
Ecuador's version of events is that Peru's invasion was an unprovoked act of aggression carried out with the explicit purpose of forcing Ecuador to sign an unfavorable treaty that would impose the status quo border line.
A communiqué by Ecuador's Foreign Ministry indicated that Peruvian forces had been seen advancing north towards the border; all of the Peruvian troops stationed in Tumbes had left Zarumilla and those in Piura and other nearby sites were in turn advancing towards Zarumilla.
According to the Ministry, the actions of the Ecuadorian army were limited to repelling the invasion which was occurring across much of the border. [17] As support for its arguments, Ecuador has repeatedly cited the obvious difference in military might between the two countries, and the lack of preparedness of its forces. It has been speculated that Peru prepared to carry out an all-out invasion and could have been simply waiting for the slightest provocation.
Ecuador has also cited Peru's history of conflict with its other neighbors as evidence of its belligerence. It has been pointed out, however, that these circumstances did not preclude Ecuador from attempting to lay claim to territories it still considered its own. Also, during the War of the Pacific, the Ecuadorian military occupied a portion of the disputed territories.
The much larger and better equipped Peruvian force of 13,000 men quickly overwhelmed the 1,800 Ecuadorian troops guarding the province of El Oro. The Peruvian army had at its disposal a battalion of armor made up of Czech LTP tanks, with artillery and air support. (Beginning in the second third of the 20th century, Peru allegedly had one of the strongest military forces in South America, even as recently as 2005 it ranked second after Brazil and stronger than Argentina [18]).
The Ecuadorian president, Carlos Arroyo del Río, kept Ecuador's best forces in Quito, for fear of his political opponents (Arroyo would later resign on May 31, 1944, after much unrest in the country). Peru carried out the first use of paratroops in combat in the Western Hemisphere, dropping three paratroopers over the port-city of Puerto Bolívar (Delgado), one of them having been rescued by Ecuadorian fishermen when he landed on the waters of the Jambelí channel.
This attempt was largely successful in allowing a relatively easy takeover of El Oro towns, devoid by then of any Ecuadorian military presence after the short-lived ceasefire of July 26, brokered by the mediator countries (USA, Brazil and Argentina). After the ceasefire, most of the Ecuadorian troops, by now exhausted and without ammunition, left the field of battle and made their way out of El Oro, towards the city of Cuenca.
Thus, when Peru reopened the advance on July 29, which began with simultaneous bombings on the Ecuadorian towns of Machala, Puerto Bolívar, Pasaje, Santa Rosa, and Arenillas, plus a mission to the city of Guayaquil to drop leaflets, the Peruvian forces easily occupied the deserted towns of the province. A new ceasefire having been decreed to enter in effect on July 31 at 18:00 forced the Peruvian command to step up its efforts to occupy Machala and Puerto Bolívar, which they did with troops disembarked directly on Puerto Bolívar from the sea in the afternoon of July 31. (Delgado)
Even then, hostilities didn't cease, as Peruvian forces began operations against the Ecuadorian posts on the Amazonian jungle, most of which were easily overrun.
With Peru occupying El Oro and menacing Guayaquil, plus pressure from the United States and Latin America to stop the hostilities as a sign of hemispheric unity against the Axis powers (in World War II), Peru and Ecuador signed the Rio de Janeiro Protocol.
Rio de Janeiro Protocol

In May 1941, as tensions at the Ecuadorian–Peruvian border mounted and war was imminent, the governments of the United States of America, Brazil, and Argentina offered their services in aiding in the mediation of the dispute. Their efforts failed to prevent the outbreak of hostilities on July 23, 1941, but the diplomatic intervention led to a definitive cease-fire being put into place on July 31. Despite this, limited skirmishes continued to occur through the months of August and September in the Ecuadorian provinces of El Oro and Loja, as well as in the Amazonian lands. Ecuador accused Peru of continuing its advances into the highland province of Azuay.
On October 2, with military observers from the three mediating countries serving as witnesses, Ecuador and Peru signed the Talara Accord, which created a demilitarized zone inside the provinces of El Oro and Loja, pending the signing of a definitive peace treaty. Diplomatic efforts continued, with the mediating countries being joined by Chile.
On January 29, 1942, on the final day of the third Pan-American Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro, the foreign ministers of Ecuador and Peru, Julio Tobar Donoso and Alfredo Solf y Muro, signed a "Protocol of Peace, Friendship, and Boundaries", known as the Rio de Janeiro Protocol. The observers from the United States, Brazil, Argentina, and Chile co-signed the document, becoming "Guarantors of the Protocol".[11] The Rio Protocol was subsequently ratified by each country's congress on February 26, 1942.
By the terms of the Protocol, Ecuador agreed to withdraw its long-standing claim for rights to direct land access to the Marañón and Amazon rivers; Peru agreed to withdraw Peruvian military forces from Ecuadorian territory. An area of 200,000 km2 (77,000 sq mi) of hitherto disputed territory in the Maynas region of the Amazonian basin was awarded to Peru, which had been established to be the de facto possessor of the land since the end of the 19th century. The "status quo" line defined in the 1936 Lima Accord was used as the basis for the definitive border line; the previous border recognized current possessions, but not sovereignty. Relative to the 1936 line, Ecuador ceded 18,552 km2 of previously possessed territory to Peru, while Peru ceded 5,072 km2 of previously possessed territory to Ecuador.[12]
Ecuador's objections to the Protocol and thesis of Nullity
Six times during the demarcation technical problems were found and referred to the Guarantors, with Brazil acting as lead. One of them, which involved the then contested Cordillera del Cóndor, was submitted to arbitration by Captain Braz Dias de Aguiar. Both countries initially accepted the arbiter's award, issued July 1945, and demarcation began in the area according to that ruling.
During 1943 and 1946 the United States Air Force performed several aerial reconnaissance missions over the Cordillera del Cóndor region (losing 2 aircraft and 14 men in accidents.) to help in the demarcation efforts. They found that the Cenepa river was much longer than previously thought and that it runs between the Zamora and the Santiago. This finding conflicted with article VIII, point B-1 of the Rio Protocol, which laid out delineation of the border for that area as follows:
- From the Quebrada de San Francisco, the watershed between the Zamora and Santiago Rivers, to the confluence of the Santiago River with the Yaupi;
The difficulty was that there is not one watershed between the Zamora and the Santiago, but two, as interpreted by Ecuador. This resulted in Ecuadorian president Galo Plaza halting demarcation in 1949. About 78 kilometers of border were left unmarked. In 1953 Ecuador withdrew from the Demarcation Commissions, claiming the Protocol "impossible to implement" in that area.
On September 29, 1960, Ecuadorian president José María Velasco Ibarra declared the Rio Protocol null and void. (Peruvian analysts have speculated that this was a politically motivated move by Velasco Ibarra, who was considered a populist, but evidence to support this assertion is totally circumstantial).
With the sole exception of Cuba, the American community did not approve of Ecuador's diplomatic move, with the United States sending a letter of protest to Ecuador.
The arguments for what is called Ecuador's thesis of nullity varied, but they were generally the following:
- It was imposed by military force.
- It was signed while Ecuadorian towns were under occupation; invasion and occupation of nation states are prohibited by international law.
- International law does not accept the conquest of territory by force or violence. Even considering de facto possession (1936 status quo border line) Peru took about 14,000 km2 of territory.
- There was lack of compliance by Peru in denying Ecuador free navigation in Amazonian rivers as stipulated.
- It was a blow to the economic development of a South American country, which is contrary to existing pacts of cooperation.
Peru's counter-arguments included the following:
- Ecuador cannot unilaterally invalidate a protocol
- The core argument on implementability is a demarcation issue, not a justification to invalidate the entire protocol
- Peru disputes the notion that the protocol was imposed by premeditated military force
- Even though the protocol was signed while Peruvian troops were still occupying El Oro for tactical reasons, the Ecuadorian congress ratified it long after Peruvian troops had left
- Several Peruvian governments restricted the navigation clause in response to Ecuador's position on the treaty
- On the issue of conquest of territory by force, Peru has pointed out that the disputed territories (Tumbes, Jaén and Maynas) were not under de jure Ecuadorian administration, and that the province of El Oro was not annexed to Peru
Ecuador argued its thesis extensively for 30 years, but did not find support in the international community. Peru's position, on the other hand, was that a dispute did not exist at all after 1941, a position which lasted until 1995, when it was recognized as a problematic diplomatic issue.
Maps published in Ecuador since the 1960s up to the end of the 20th century officially had to exclude the unmarked 78 kilometers of border, that is, the Rio Protocol line was drawn as unresolved, and to include what Ecuador considered as its own by right, according to the Pedemonte-Mosquera protocol (1830) line, which puts the Marañón (Amazon) river as the border between Peru and Ecuador.
Such controversial maps of Ecuador, known in Ecuador as "Tufiño's map", were referred in Peru as "mapa recortado del Peru" (cut-off map of Peru).
Paquisha War (1981)
The Paquisha War was a brief military clash that took place between January and February 1981 between Ecuador and Peru over the control of three watchposts. While Peru felt that the matter had already been decided in the Ecuadorian–Peruvian War of 1941, Ecuador did not agree with the Rio de Janeiro Protocol. Later in 1998 the Guarantors of the Rio Protocol ruled that the border of the undelimited zone was indeed the line of the Cordillera del Cóndor, as Peru had been claiming since the 1940s.
In the aftermath of the incident, both sides increased their military presence along the Cordillera del Cóndor area and Cenepa Valley, starting an escalating spiral of tension and provocation that finally resulted in another military confrontation in 1995, the Cenepa War.
Cenepa War (1995)
The Cenepa War was a brief (January 26 – February 28, 1995) and localized military conflict between Ecuador and Peru, fought over control of a disputed area on the border between the two countries. The two nations had signed a border treaty following the Ecuadorian–Peruvian War of 1941, but Ecuador later disagreed with the treaty as it applied to the Cenepa and Paquisha areas, and in 1996 Ecuador declared the treaty null and void.
The indecisive outcome of the Cenepa War—both sides claimed victory—along with the mediation efforts of Argentina, Brazil, Chile and the United States, paved the way for the opening of diplomatic negotiations that ultimately led to the signing of a definitive peace agreement (the Brasilia Presidential Act) on 26 October 1998.[13] The peace agreement was followed by the formal demarcation of the border on 13 May 1999 and the end of the multi-national MOMEP (Military Observer Mission for Ecuador and Peru) troop deployment on 17 June 1999 which effectively put an end to one of the oldest territorial disputes in the Western Hemisphere.[13]
Arbitration and final resolution (1995–1998)
A cease fire was brokered by the four guarantor countries, and subsequently the Itamaraty Peace Declaration was signed on February 17, 1995. One of the declaration's clauses included the creation of the Military Observer Mission Ecuador-Peru (MOMEP) in order to verify ceasefire agreements, as well as observe and report infractions through diplomatic channels.
The MOMEP contingent was made up of observers, logistics, and aviation support from the United States, Argentina, Brazil, and Chile as part of Operation Safe Border. The mission, unique in its scope, was fully funded by Peru and Ecuador. MOMEP was largely successful despite several tragic accidents due to land mines left in the area.
At a critical moment during late July and early August 1998 it appeared that Peruvian forces were preparing a preemptive assault on Ecuadorian forces (this is partially believed due to the Peruvian Air Force buying 19 Soviet-built MiG-29 fighter planes and 18 Su-25 attack aircraft from Belarus to counter the abysmal state the airforce was in at the beginning of the conflict, with 80% of the fleet grounded due to lack of spare parts), but the presence of the MOMEP contingent was instrumental in defusing the situation. [19][permanent dead link]
The guarantors assisted the parties in ministerial level discussions aimed at identifying the significant claims and disagreements of each side. Both countries agreed to a guarantor-sponsored technical commission composed of boundary experts in order to resolve the matter.
Before a critical meeting planned in Brazil for early 1997, both countries entered a period of unforeseen political events. In Peru, there was a hostage crisis in its Japanese embassy involving guerrillas of the Túpac Amaru Revolutionary Movement. Ecuador was going through a period of political instability as President Abdalá Bucaram, a strong supporter of an agreement on the border issue, was removed by congress due to alleged mental incapacity. (President Bucaram, who is known for his unusual antics, had visited Peru and was seen on TV eating ceviche and wearing alpaca hoods—a traditional indigenous outfit—along with President Alberto Fujimori.)
These delays nevertheless gave the guarantors more time to come up with a solution to the dispute. Eventually they concluded that a resolution would not be possible without granting something to each party.
The commission recognized Ecuador's position on one small already demarcated section of the border, and Peru's position on the larger issue of the single watershed between the Zamora and Santiago rivers. The latter was a blow to Ecuador's historic position, and left Tiwintza in Peruvian territory.
The solution that the commission reached was that an area of one square kilometer in the place of the fiercest struggle, Tiwinza, on the Peruvian side of the border, would be granted to Ecuador as a non-sovereign private property. The site could be used by Ecuador for commemorative and non-military events. Everyone born in Tiwinza will be considered Peruvian. Although none of the countries was completely satisfied with the solution, both accepted it, which was a significant diplomatic success.
The resolution also called for the creation of two national parks contiguous to one another (also referred to as a binational park) in the Cordillera del Condor region.
Ambassador Luigi Einaudi, the US guarantor representative, is credited with coming up with the idea of a private property concession in Tiwintza, working almost full-time on the problem, and coming up with ways to express issues in a manner not offensive to either party. [20]
On October 26, 1998, these two nations signed a comprehensive peace accord establishing the framework for ending a border dispute. Formal demarcation of border regions started on May 13, 1999. The agreement was ratified without opposition by both nations' congress. U.S. President Bill Clinton said: "This signing marks the end of the last and longest running source of armed international conflict in the Western hemisphere".[14]
Aftermath
This dispute is unique and significant in the study of causes and resolution of international conflict. Ecuador and Peru are populated by people who share a language, a culture, a religious preference, have basically the same social and ethnic diversity, and comparable economic difficulties. They are also both democracies (for the most part in modern times) which puts in doubt the common contention that democracies never go to war with each other.
Education and public perception
A 2000 study carried out as part of the educational ASA Program found teaching curriculum relating to the dispute to be extremely one-sided in both countries:[15]
- Notably, in Ecuador the dispute is a central issue in the study of Ecuador's borders. (Traditionally there has been a course named "History of Borders.")
- In Peru, the educational system does not give as much importance to the dispute with Ecuador, and is part of the course "Peruvian History". In contrast, the only topic related to the territorial dispute that is normally taught is the Rio Protocol, and its importance in the settlement of this dispute.
Many examples of bias are cited, which can typically be characterized as removal of critical information about the other side's position. Emotional and nationalistic coloring of the material also appears to be routine. Although expected under the circumstances, this has likely fed the cycle of conflict in the past.
Citizens of Ecuador and Peru feel both their countries have lost territory over time. The issue is one of overlapping maximalist territorial claims and aspirations.
High Peruvian military spending is seen by Ecuador as evidence of belligerence and expansionism. Peru also considers Ecuador belligerent and expansionist.
At the end of the 20th century things appear to have improved considerably. The Cenepa War of 1995 allowed an honorable resolution of the conflict without a clear winner. To many Ecuadorians this was viewed as restoring the honor of the country, which was at least as important as their claims to the disputed territory. Unfortunately, not everyone is completely satisfied.
Today, the entire Ecuadorian–Peruvian border is clearly delimited and demarcated, and the maps of both countries agree on the location of the common frontier. Bilateral work is being done by both countries Foreign Affairs officers to consolidate the economic and social integration. We can see part of this done by the Peruvian government with their Consulate in Machala, El Oro, where Minister Efrain Saavedra is the Consul General.
Economic impact
One of the concerns both countries have had is the impact of the dispute on foreign investment. Thomas McLarty, US envoy at the resolution talks and former aid to President Bill Clinton, has said peace is essential to South America's economic recovery. He added: "You clearly cannot have long-term growth and prosperity involving foreign investment without stability".[16] While there are still political instability issues in the region, resolution of the territorial conflict is helpful.
Trade between both countries has benefited considerably. Before signing the peace treaty, annual trade between Peru and Ecuador was about 100 million dollars. But as early as 1998, it had increased 5-fold.[17]
There was also a broad agreement of integration between both countries.[18][19] It included a binational fund for peace and development, national plans for productive, social and environmental development, and so on.
Political implications
According to Gabriel Marcella (US Department of National Security and Strategy), as a result of the Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute "a number of emerging views about international affairs, U.S. foreign policy, and modern inter-American affairs were either shattered or seriously challenged".[20] Some of the global and regional political implications of the dispute which have been noted are the following:
- It was a blow to the idea that democracies do not go to war with one another. An armed conflict between these two nations has existed well before then, nevertheless, on and off with major confrontations occurring in 1941, 1981 and 1995. Ecuador and Peru have both been full-fledged democracies for the most part in modern times, although of course not perfect or politically stable.
- It was a blow to the idea that Latin America is a model for peaceful international relations. It is a reminder that there are other territorial disputes and conflicting claims among other Latin American countries which could potentially threaten peace in the region.
- Civil-military relations in both countries have been impacted and need to be re-examined. If in fact the conflict was allowed to escalate after accidental encounters between patrols, it has been suggested that the civilian authority should perhaps assume more solid leadership and control.
- The principle that territorial treaties in Latin America are not the result of force or violence needs to be re-examined as a result.
See also
- Bolivian–Peruvian territorial dispute
- Chilean–Peruvian territorial dispute
- Colombian–Peruvian territorial dispute
- Ecuador–Peru relations
- Dispute resolution
- Territorial dispute
- Paquisha Incident
- General Richelieu Levoyer
Footnotes
- ^ Ecuador and Colombia signed the Muñoz Vernaza-Suárez Treaty in 1916, ending their dispute, while Peru and Colombia's Salomon-Lozano Treaty became effective in 1928
- ^ Defined as "the civil, as distinguished from the military, branch of the colonial governmental entities lesser in extent than the audiencias." (1910)
- ^ Defined as "the jurisdiction of the Alcalde mayor, who, as mayor, governed a town of lesser importance than the capital of a province." (1910)
- ^ Defined as "the district governed by a Corregidor, a correctional magistrate, who, in colonial times, exercised administrative functions over a district. (1910)
- ^ Defined as "jurisdiction of the Alcalde ordinario, who was similar to the alcaldia mayor, but of lesser extent. (1910)
- ^ This extract of Law X of Title XV of Book II of the Recopilación de las Leyes de los Reynos de Indias, made available in electronic form by the Congress of the Republic of Peru, reads in its original text: En La Ciudad de San Franciſco del Quito, en el Peru, reſida otra nueſtra Audiencia y Chancilleria Real, con vn Preſidente: quatro Oidores, que tambien ſean Alcaldes de el Crimen: vn Fiſcal: vn Alguazil mayor: vn Teniente de Gran Chanciller: y los demas Miniſtros y Oficiales neceſarios: y tenga por diſtrito la Provincia de el Quito, y por la Coſta azia la parte de la Ciudad de los Reyes, haſta el Puerto de Payta, excluſive: y por la tierra adentro, haſta Piura, Caxamarca, Chachapoyas, Moyabamba y Motilones, excluſive, incluyendo azia la parte ſuſodicha los Pueblos de Iaen, Valladolid, Loja, Zamora, Cuenca, la Zarca y Guayaquil, con todos los demas Pueblos, que eſtuvieren en ſus comarcas, y ſe poblaren: y azia la parte de los Pueblos de la Canela y Quixos, tenga los dichos Pueblos, con los demas que ſe deſcubrieren: y por la Coſta, azia Panama, haſta el Puerto de la Buenaventura, incluſive: y la tierra adentro a Paſto, Popayán, Cali, Buga, Chapanchica y Guarchicona; porque los demas lugares de la governacion de Popayán, ſon de la Audiencia del Nuevo Reyno de Granada, con la qual, y con la Tierrafirme parte terminos por el Septentrion: y con la de los Reyes por el Mediodia, teniendo al Poniente la Mar del Sur, y al Levante Provincias aun no pacificas, ni deſcubiertas.
- ^ This extract of Law V of Title XV of Book II of the Recopilación de las Leyes de los Reynos de Indias, made available in electronic form by the Congress of the Republic of Peru, reads in its original text: EN la Ciudad de los Reyes Lima, Cabeca de las Provincias del Peru, resida otra nuestra Audiencia y Chancilleria Real, con un Virrey, Governador y Capitan General, y Lugar-Teniente nuestro, que sea Presidente: ocho Oidores: quatro Alcaldes del Crimen, y dos Fiscales: uno de lo Civil, y otro de lo Criminal: un Alguazil mayor, y vn Teniente de Gran Chanicller: y los demas Ministros y Oficiales necessarios: y tenga por distrito la Costa, que hay desde la dicha Ciudad, hasta el Reyno Chile esclusive, y hasta el Puerto de Payta inclusive: y por la tierra adentro a San Miguel de Piura, Caxamarca, Chachapoyas, Moyobamba, y los Motilones, inclusive, y hasta el Collao, exclusive, por los terminos, que se senalan a la Real Audiencia de la Plata, y la Ciudad del Cuzco con los suyos, inclusive, partiendo terminos por el Septentrion con la Real Audiencia de Quito: por el Mediodia con la de la Plata: por el Poniente con la Mar del Sur: y por el Levane con Provincias no descubiertas, segun les estan senalados, y con la declaracion, que se contiene en la ley 14 de este titulo.
- ^ Uribe p.649: He resuelto que tenga por segregado del Virreynato de Santa Fe y de la provincia de Quito y agregado a ese Virreynato el Gobierno y Comandancia General de Mainas con los pueblos del Gobierno de Quijos, excepto el de Papallacta por estar todos ellos a las orillas del río Napo o en sus inmediaciones, extendiéndose aquella Comandancia General no sólo por el río Marañón abajo, hasta las fronteras de las colonias portugueses, sino también por todos los demás ríos que entran al Marañón por sus margines septentrional y meridional como son Morona, Huallaga, Paztaza, Ucayali, Napo, Yavari, Putumayo, Yapurá y otros menos considerables, hasta el paraje en que éstos mismos por sus altos y raudales dejan de ser navegables: debiendo quedar también a la misma Comandancia General los pueblos de Lamas y Moyobamba... A cuyo fin os mando que quedando como quedan agregados los gobiernos de Mainas y Quijos a es Virreynato auxiliés con cuantas providencias juzguéis necesarias y os pidiere el Comandante General y que sirvan en ellos no sólo para el adelantamiento y conservación de los pueblos, custodia de los misioneros sino también para la seguridad de mis dominios impidiendo se adelanten por ellos los vasallos de Corona de Portugal nombrando los cabos subalternos o Teniente de Gobernador que os pareciere necesarios, para la defensa de esas fronteras y administración de justicia...Así mismo he resuelto poner todos esos pueblos y misiones reunidos a cargo del Colegio Apostolico de Santa Rosa de Ocopa de ese Arzobispado...Igualmente he resuelto erigir un Obispado en dichas misiones...YO EL REY
- ^ Uribe p.651: Respecto de esta Real Cédula de 1802 conviene observar que hemos tenido a la vista tres ejemplares impresos, todas de fuente peruana y ninguno de ellos concuerda con los otros, a saber: el que reproduce el doctor Galindo, el que se contiene en el volumen publicado en Brasil y el presentado en el alegato de Perú ante el gobierno de España en 1889 en la cuestión de límites con Ecuador.
- ^ Bowman, p.759: "A royal cedula, dated 1802, complicated matters ... [there] was considerable uncertainty as to the validity of the cedula as well as its meaning..." (This paper was published in 1942, and establishes uncertainty of the Cedula's authenticity at least up until that date.)
References
- ^ a b Paredes-Van Dyke p.8.
- ^ a b p.56 (1910)
- ^ a b Spain (1680). Recopilación de las Leyes de Indias. Titulo Quince. De las Audiencias y Chancillerias Reales de las Indias [Digest of the Laws of India. Title Quince. Of Hearings and Real chancillerias Indies]. Madrid. Spanish-language facsimile of the original Archived June 29, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Historia del Ecuador - Ministerio de Turismo - Ecuador". Archived from the original on 2005-10-24. Retrieved 2005-10-25.
- ^ a b c "2 Sinopsis histórica". Archived from the original on 2005-11-21. Retrieved 2005-10-25.
- ^ a b c Ponce, p. 13
- ^ Luciano p.6
- ^ The latter of these is available at Wikisource.
- ^ Luciano p.7
- ^ Paredes & Van Dyke, p.259
- ^ "Territorial Disputes and Their Resolution: Peaceworks: Publications: U.S. Institute of Peace". Archived from the original on 2005-11-22. Retrieved 2005-10-28.
- ^ Julio Tobar Donoso, La Invasión Peruana y el Protocolo de Rio. Antecedentes y Explicación Histórica. Quito, Banco Central del Ecuador, 1982 (1st Ed. 1945). P. 462.
- ^ a b "Conflict name: Ecuador - Peru, In depth, Background to the 1995 fighting and Ecuador and Peru engage in armed conflict". Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, General Conflict Information. Archived from the original on 2013-09-27. Retrieved 2013-07-15.
- ^ "Peru and Ecuador sign border treaty". BBC News. October 27, 1998. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-09-01. Retrieved 2005-10-28.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Peru and Ecuador sign border treaty". BBC News. October 27, 1998.
- ^ Fujimori F., Alberto (2003-11-09). "PERÚ-ECUADOR: AVANCE EN COMERCIO BILATERAL". Alberto Fujimori. Archived from the original on 2004-11-23.
- ^ "Seminario Desarme - Eduardo Cabezas". Archived from the original on 2005-04-27. Retrieved 2005-11-03.
- ^ "Plan Binacional de Desarrollo de la Región Fronteriza Perú-Ecuador". Plan Binacional de Desarrollo de la Región Fronteriza Perú-Ecuador.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-02-19. Retrieved 2005-11-04.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
Further reading
- Santamaría de Paredes, Vicente; Weston Van Dyke, Harry (1910). A study of the question of boundaries between the republics of Peru and Ecuador. Press of B.S. Adams.
- Means, Philip A. (1932). Fall of the Inca Empire and the Spanish Rule in Peru, 1530–1780. New York: Scribner.
- Vacas Galindo, Enrique (1905). La integridad territorial de la República del Ecuador (in Spanish). Tip. Salesiana.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Colombia (1901). Antonio José Uribe (ed.). Anales diplomáticos y consulares de Colombia (in Spanish). Vol. 2. Bogotá: Imprenta Nacional.
- Isaiah, Bowman (July 1942). "The Ecuador-Peru Boundary Dispute". Foreign Affairs. 20 (4). Council on Foreign Relations: 757–761. doi:10.2307/20029191. JSTOR 20029191.
- Coral, Luciano (1894). Conflicto internacional: Ecuador y Perú (in Spanish). Guayaquil: Imprenta de "El Tiempo". Retrieved 2010-02-24.
- Eguiguren, Luis A. Apuntes sobre la cuestión internacional entre Perú y Ecuador: Maynas. Lima: Imprenta de Torres Aguirre, 1941.
- Eguiguren, Luis A. Notes on the territorial question between Peru and Ecuador: Invincible Jaén", Lima:Imprenta de Torres Aguirre, 1943.
- Zook, David H., Jr. Zarumilla-Marañón: The Ecuador-Peru Dispute. New York: Bookman Associates, 1964.
- Marcella, Grabriel. Downes, Richard. Security Cooperation in the Western Hemisphere: Resolving the Ecuador-Peru Conflict. University of Miami Iberian Studies Institute, 1999.
- Lyman, Eric J., "War of the Map: The territorial dispute between Peru and Ecuador has its roots in the Inca Empire", Mercator's World Magazine, 2000.
- Peirce, Holly. Security cooperation in the western hemisphere: Lessons from the 1995 Ecuador-Peru conflict (North-South Center conference reports). North-South Center at the University of Miami, 1997.
- Delgado, Luis Humberto. Las Guerras del Perú. Tomo I. Lima, 1971.
- Rodríguez, Luis. La Agresión Peruana de 1941. Quito, 1943.
- Herz, Monica and Nogueira, João. Ecuador vs. Peru: Peacemaking amid Rivalry. Boulder: Lynne Rienner Publishers, 2002.