List of equipment of the Armed Forces of Ukraine
The list of equipment of the Armed Forces of Ukraine can be subdivided into: infantry weapons, vehicles, aircraft, watercraft, and clothing. Due to the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine, quantities of operational equipment are highly uncertain.
Infantry weapons
Handguns
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokarev TT-33 | 
|
Semi-automatic | 7.62x25mm Tokarev | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[1] | |
| Margolin MCM | 
|
.22 Long Rifle | Used for training.[2] | ||
| Makarov PM | 
|
9×18mm Makarov | Standard-issue handgun of the Ukrainian Ground Forces.[3] | ||
| Stechkin APS | 
|
Automatic | [4][5] | ||
| SPP-1 | 
|
Underwater |
4.5x40 mmR | Still used by Maritime Special Forces[4] | |
| PSM | 
|
Semi-automatic | 5.45x18mm | Used by high-ranking officers and government officials.[6][7] | |
| CZ 75 | 
|
9x19mm Parabellum | Donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[8] | ||
| CZ 82 | 
|
9×18mm Makarov | 30,150 donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[9] | ||
| Fort-12 | 
|
Standard pistol of the Omega Group.[10] | |||
| Fort-14TP | 
|
Replacing the Makarov PM.[3] | |||
| Fort-17 | 
|
Used by special forces.[11] | |||
| Fort-21 | 
|
9×19mm Parabellum | Produced since 2009, it is a Ukrainian version of the Israeli IWI Jericho 941, which itself is a clone of the Czech CZ 75. Has been used and tested by Ukrainian special forces.[12] In use with the UAF.[13] | ||
| Glock 17 | 
|
Used by special forces.[14] 600 donated by Canada.[15] | |||
| Beretta M9 | 
|
Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Probably donated by the United States[16][better source needed] | |||
| Kimber R7 Mako | 
|
200 donated by Kimber to Ukraine in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[17] | |||
| SIG Sauer M18 | 
|
[18][better source needed] | |||
| Heckler & Koch SFP9 | 
|
500 donated by Germany in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[19] |
Shotguns
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KS-23 | 
|
Pump action shotgun | 23×75mmR (Barrikada slug) | Use by anti-terrorist units[20] | |
| Mossberg 500 | 
|
12 gauge | Donated by the United States during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[21][22] | ||
| Saiga-12 | 
|
Semi-automatic shotgun | 12 gauge | "Saiga-12K - Tactical" carbine adopted by the Ukrainian Navy and National Guard in 2009[23] |
Rifles
Semi-automatic rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Savage MSR-15 | Semi-automatic carbine | 5.56×45mm NATO | Used by the Territorial Defense Forces[24] | ||
| Adams Arms P1 | M4 AR-15 based semi-automatic rifles donated to Ukraine by Adams Arms[25][26] | ||||
| Kel-Tec SUB-2000 | 9x19mm Parabellum | 400 donated by Kel-Tec in 2022.[27] |
Assault rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKM | 
|
Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Used by National Guard and Territorial Defense units.[28][29] | |
| AKMS | 
|
Limited use.[30] Some were donated by Poland.[31] | |||
| AK-74 (AKS74/AKS74u) | 
|
5.45×39mm | Standard issue for the Ukrainian Ground Forces.[3] | ||
| Seen in use with suppressors attached.[32] | |||||

|
Assault carbine | Shortened variant of the AKS-74[3] | |||
| APS | 
|
Underwater assault rifle | 5.66x39mm MPS | Used by Maritime Special Forces[4] | |
| IPI Malyuk | 
|
Bullpup assault rifle | 7.62×39mm 5.45×39mm 5.56×45mm NATO |
Bullpup Kalashnikov variant. Used by special forces units. Some regular units were also issued Malyuks.[33] | |
| Fort-221 | 
|
Bullpup assault rifle | 5.45×39mm 5.56×45mm NATO |
Used by special forces[3] | |
| Fort-224 | Shortened version of the Fort-221[3] | ||||
| UAR-15 | 
|
Assault carbine | 5.56×45mm NATO | Based on the AR-15 platform[34] | |
| M4-WAC-47 | 
|
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO 7.62×39mm |
Based on the M4 carbine.[3] | |
| Samopal vz. 58 | 
|
Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | 5,000 donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[9] | |
| Zastava M70 | 20,000+ sent by Croatia in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[35] Seen in use by Ukrainians being trained by the British Army[36] | ||||
| Type 56-1 | 
|
Confiscated Iranian rifles supplied to Ukraine.[37][38] | |||
| FN FNC | 5.56×45mm NATO | 5,000 rifles sent by Belgium in March 2022 in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[39] | |||
| FN SCAR-L | 
|
Bullpup assault rifle | Sent by Belgium in May 2022 in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[39] | ||
| FN F2000 | 
|
An unknown quantity, sent by Belgium in May 2022 in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[40][39] | |||
| CZ BREN 2 | 
|
Modular assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Unknown number delivered by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion.[9] | |
| FS MSBS Grot C16A2 | 10,000 Grot C16A2 rifles delivered during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[41] | ||||
| FB wz. 88 Tantal | Assault rifle | 5.45×39mm | Donated by Poland.[31] | ||
| AK-74M | 
|
Unknown quantity, seen in use after being captured during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[42] | |||
| AK-12 | Unknown quantity, seen in use after being captured during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[42] | ||||
| Colt Canada C7 | 5.56×45mm NATO | C7A1s delivered to Ukraine by the Netherlands before September 2022.[43][44] C8 carbines delivered by Canada in February or March 2022[15] | |||
| Robinson Armament XCR | 
|
An unknown quantity, seen in the hands of Ukrainian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[45] | |||
| M4 carbine | 
|
Carbine assault rifle | Used by special forces.[14] | ||
| M16A4 | 
|
Assault rifle | [46] | ||
| Remington ACR | 
|
Modular assault rifle | An unknown quantity, seen in the hands of Ukrainian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[45] | ||
| SIG MCX | 
|
5.56×45mm NATO .300 AAC Blackout |
An unknown quantity, seen in the hands of Ukrainian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[45] | ||
| Steyr AUG | 
|
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Australian-made version used.[47][48] | |
| CETME Model L | 
|
Donated by Spain in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[49] | |||
| Australian Combat Assault Rifle | Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO 7.62×51mm NATO |
Unknown small quantity delivered in July 2023.[50] |
Battle rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIG SG 510 | Battle rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Used by special forces[51][page needed][47] | ||
| Heckler & Koch G3 | 
|
At least 1,000 G3A3/4s sent by Portugal as part of military aid in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[52] | |||
| FN FAL | Unknown quantity delivered by Belgium in 2022.[39] Seen in the hands of Ukrainian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[53][54] | ||||
| M14 | 35,000 sent by Estonia.[55] |
Sniper rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVD | 
|
Semi-automatic | 7.62×54mmR | Standard issue rifle for the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[56] 12 rifles sent by the Czech Republic.[9] | |
| Stiletto-Systeme STL-016 | Bolt-action | .300 Winchester | Based on the Mosin-Nagant M1891/30[57] | ||
| Zbroyar Z-008 | 
|
7.62×51mm NATO | [58] | ||
| Zbroyar VPR-308 | Military sniper version of the Zbroyar Z-008[59] | ||||
| Zbroyar UAR-10 | 
|
Semi-automatic | Replacing the SVD rifle in the sniping role.[56] | ||
| Fort-301 | 
|
Locally produced version of the Galatz rifle.[60] | |||
| Sako TRG-22 | Bolt-action | Used by the Omega special force unit of the National Guard.[61] Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[62] | |||
| M110 | 
|
Semi-automatic | An unknown quantity, seen in the hands of Ukrainian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[63] | ||
| Desert Tech SRS | Bolt-action | Introduced by the National Guard in 2016[64] | |||
| Savage Model 110 | 125 were bought in 2018 for the Ukrainian Air Assault Forces.[24] | ||||
| M24 SWS | 
|
Part of United States military aid.[65] | |||
| Barrett MRAD | .338 Lapua Magnum | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[62] | |||
| Remington Model 700 | 
|
.308 Winchester | Used by the Ukrainian Ground Forces[24] | ||
| Kimber Advanced Tactical | 10 donated by Kimber [66] | ||||
| SIG Sauer SSG 3000 | 
|
7.62×51mm NATO | Used by Alpha Group and Guard Special Forces[11] | ||
| Cadex Defense CDX-TAC | .338 Lapua Magnum | Supplied by Canada[62] | |||
| Accuracy International AWM | Donated by the Netherlands in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[67] | ||||
| Accuracy International AX308 | 
|
Donated by the Netherlands in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[68] | |||
| Haenel HRL 338 | [19] |
Submachine guns
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fort-224 | 
|
Bullpup submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Used by special forces[69] | |
| Škorpion vz. 61 | 
|
Submachine gun | 9×18mm Makarov | 2,085 donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[9] | |
| CZ Scorpion Evo 3 | 
|
9×19mm Parabellum | Unknown quantities delivered from the Czech Republic, deployed in combat during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[70] | ||
| Uzi | 
|
Surplus FN-licensed Uzis supplied to Ukraine[71][72] | |||
| SIG MPX |  |
[73][better source needed] |
Machine guns
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM M1910/30 | 
|
Heavy | 7.62×54mmR | Prior to 2014, Ukraine had more than 30,000 units stored in strategic reserve.[74] Widely used in the Russo-Ukrainian war, some were modified with modern optics and supressors.[75][76] | |
| DPM | 
|
Light | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian War.[77] | ||
| RPD | 
|
7.62×39mm | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[77] | ||
| RPK | 
|
Used by the National Guard.[78] | |||
| RPK-74 | 
|
5.45×39mm | Standard issue light machine gun[56] | ||
| PK | 
|
General-purpose | 7.62×54mmR | PKM standard issue general-purpose machine gun.[56] The Bulgarian MG-1M variant is also used.[79] | |
| KPV | 
|
Heavy | 14.5x114mmR | 60 KPVT transferred by Lithuania in 2015.[80] Base for anti-aircraft guns.[81] | |
| NSV | 
|
12.7×108mm | Standard issue heavy machine gun.[77] | ||
| DShK | 86 guns transferred from Lithuania in 2015.[80] Domestically modified variants and Romanian-made DShKMs also seen in use.[82][83] | ||||
| UKM-2000 | 
|
General-purpose | 7.62×51mm NATO | Donated by Poland starting in June 2022[31] | |
| Fort-401 | 
|
Light | 5.56×45mm NATO | Used by special forces. Highly modified Israeli IWI Negev[56] | |
| UK vz. 59 | 
|
General-purpose | 7.62×54mmR | 3,200 donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[9] | |
| Beretta MG 42/59 | 
|
7.62×51mm NATO | Italian version of the German MG 3, donated by Italy in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[84] | ||
| Rheinmetall MG 3 | 
|
238 were donated by Germany in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[19] | |||
| Heckler & Koch MG5 | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[19][85] | ||||
| Ksp 58B | Donated by Sweden in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[86] | ||||
| AAT-52 | 
|
Mounted on the donated VAB APCs[87] | |||
| FN Minimi | 
|
Light | 5.56×45mm NATO | Delivered by Belgium and Canada (domestically made version) in 2022[39][15] | |
| FN MAG |  |
General-purpose | 7.62×51mm NATO | Donated by Belgium and Canada (domestically made version) in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[39][15] | |
| Zastava M53 | 
|
7.92×57mm Mauser | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[77][88] | ||
| CETME Ameli | Light | 5.56×45mm NATO | Donated by Spain in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[89][90] | ||
| M249 | 
|
Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[88] | |||
| M240 | 
|
General-purpose | 7.62×51mm NATO | Donated by the US.[88] | |
| M2 Browning | 
|
Heavy | 12.7×99mm NATO | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[91] The Turkish Canik M2 is also used.[92] |
Grenades and launchers
Smoke grenades
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-18 | 
|
Smoke grenade | N/A | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[93] | |
| Merkkisavuheite 80-16 | N/A | Donated by Finland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[94] | |||
| RDG-M | 
|
58mm | Captured from Russian forces.[95] | ||
| RGR | 
|
Tear gas | N/A | Captured from Russian forces.[95] |
Hand grenades
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sirpalekäsikranaatti M50 | Hand grenade | 50mm | Donated by Finland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[94] | ||
| RGD-5 | 
|
58mm | Standard issue grenade of the Ukrainian Army.[96] Bulgarian-made grenades are also used.[95] | ||
| F-1 | 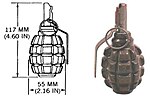
|
55mm | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[1] | ||
| RGN |  |
60mm | Standard issue grenade of the Ukrainian Army.[96] | ||
| RGO |  |
Limited use.[1] | |||
| DM51 |  |
57mm | 100,000 DM51A2 donated by Germany.[19][95] | ||
| L109 |  |
65mm | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[97][better source needed] | ||
| m/963 |  |
57mm | Donated by Portugal.[52] | ||
| M67 |  |
64mm | American and Canadian grenades used by the UAF.[95][15] | ||
| OF 37 HE | Delivered by France in May 2022[98] | ||||
| GHO-2 HE | 56mm | [99] | |||
| RG-60TB | 
|
60mm | Thermobaric grenade, captured from Russian forces.[95] |
Anti-tank grenades
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RKG-3 | 
|
Anti-tank |
362mm | Mostly used in domestically modified RKG-1600 variant[100] with 3D printed stabilisation fins and modified fuzing for dropping from commercial drones[101] |
Grenade launchers
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP-25 Kostyor | 
|
Grenade launcher | 40 mm caseless grenade | Underbarrel grenade launcher.[102] Some used standalone with the Black Storm Defender stock[103] | |
| AGS-17 | 
|
Automatic |
30×29mm | [91] | |
| UAG-40 | 
|
Automatic |
40×53mm | 500 units purchased in 2016 for the Ukrainian Armed Forces[104] | |
| RGSh-30 | Grenade launcher | 30mm | Primarily used by Ukrainian special forces since 2014.[105] | ||
| Fort-600 | 
|
Grenade launcher | 40×46mm SR | Used by the Ukrainian Air Assault Forces.[106] | |
| RGP-40 |  |
Multi-shot grenade launcher | Used by special forces.[14] | ||
| M32 Grenade Launcher | 
|
Multiple-shot grenade launcher | Donated to the Ukrainian Ground Forces by the United States in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[107] | ||
| M320 Grenade Launcher Module | 
|
Grenade launcher | Used by special forces.[14] | ||
| Mk 19 |  |
Automatic |
40×53 mm | Donated by the US.[91] | |
| GM-94 | 
|
Pump-action Grenade launcher | 43×30mm | [108] |
Anti-materiel and anti-tank weapons
Anti-materiel rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TASKO 7ET3 | Semi-automatic | .50 BMG 12.7×108mm |
Adopted by special forces and anti-terrorist units.[109] | ||
| SGM-12.7 | Bolt action | 12.7x108mm | Domestically made anti-materiel rifle[110] | ||
| Snipex M100 | [111] | ||||
| PGW LRT-3 SWS | .50 BMG | Donated by Canada[112] | |||
| ZVI Falcon OP-99 | 19 given by the Czech Republic as part of a military package in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[9] | ||||
| WKW Wilk | 
|
Donated by Poland.[31] | |||
| McMillan TAC-50 | Used by the Ukrainian Ground Forces[113] | ||||
| Desert Tech HTI | Bullpup semi-automatic | Introduced by the National Guard in 2020[114] | |||
| Barrett M99 | 
|
Single-shot | Seen in use with the Georgian Legion during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[115] | ||
| Barrett M82 | 
|
Semi-automatic | Donated to Ukraine by the Netherlands in February 2022[68] | ||
| Barrett M107 | 
|
Supplements the SVD rifle in the sniping role.[56] | |||
| AG 90 C | 
|
Donated by Sweden in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[86] | |||
| Snipex Rhino Hunter | 
|
Bolt-action | [116][117] | ||
| Snipex Alligator | 
|
14.5×114mm | [65][118] | ||
| Snipex T-Rex | 
|
Single-shot | Similar to the Snipex Alligator, but has no magazine. Used by special forces.[119] |
Anti-tank rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTRD-41 |  |
Single-shot anti-tank rifle | 14.5×114mm | Unknown quantity, seen in combat during the Russo-Ukrainian War[120] |
Recoilless rifles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPG-9 Kopyo | 
|
Reusable Recoilless rifle | 73mm | Used by the AFU, National Guard, and State Border Service. Bulgarian-made rifles seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[121] | |
| RGW 90 MATADOR | 
|
Disposable recoilless rifle | 90mm | 7,944 RGW 90 Matador donated by Germany,[19] plus 1,260 provided by Belgium.[39] | |
| RPG-75 |  |
68mm | 10,000 donated by the Czech Republic.[9] | ||
| Pansarvärnspjäs 1110 | 
|
Reusable recoilless rifle | 90mm | Donated by Estonia.[55] | |
| Carl Gustaf M2 | 
|
84mm | Hundreds donated by Canada and Estonia.[15][55] | ||
| FFV AT4 | 
|
Disposable |
Used by special forces.[14] | ||
| APILAS | 
|
112mm | Donated by Finland.[94] |
Anti-fortification
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panzerfaust 3 Bunkerfaust | Semi-disposable rocket-propelled grenade | 110mm | [19] | ||
| M141 BDM | 
|
Disposable rocket launcher | 83.5mm | Used by special forces.[14] | |
| M1A3 Bangalore torpedo | 
|
Demolition charge | 54mm | [122] |
Rocket-propelled grenades
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPG-7 | 
|
Reusable rocket-propelled grenade | 40mm | [123] | |
| RPG-16 | 58.3mm | In airborne forces only.[124] | |||
| RPG-18 |  |
Disposable rocket-propelled grenade | 64mm | 1,100 donated by Greece in 2022.[125] | |
| RPG-22 |  |
72.5mm | [123] | ||
| RPG-26 |  |
[123] | |||
| RPG-32 | Reusable rocket-propelled grenade | 105mm | [124][126] | ||
| Bulspike-AT | Disposable rocket-propelled grenade | 72.5mm | Bulgarian modified version of RPG-22, used by special forces.[14] | ||
| M80 Zolja | 
|
64mm | Supplied by North Macedonia.[127] | ||
| RPG-76 Komar | 40mm | Donated by Poland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[31] | |||
| Panzerfaust 3 |  |
Semi-disposable rocket-propelled grenade | 60mm | More than 3,000 rockets donated by Germany and the Netherlands[19][43] | |
| C90-CR |  |
Disposable rocket-propelled grenade | 90mm | More than 1,370 rockets donated by Spain and Estonia.[55][49] | |
| M72 LAW |  |
66mm | Used by special forces.[14] | ||
| PSRL-1 | Reusable rocket-propelled grenade | 40mm | [56] | ||
| Mk153 SMAW |  |
83.5mm | [128] |
Anti-tank guided missiles
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9K115 Metis | 
|
Wire-guided | 94mm | 9K115-2 Metis-M variant seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[129] | |
| 9K111 Fagot |  |
120mm | [130] | ||
| 9M113 Konkurs |  |
135mm | [130] | ||
| Barrier | Laser beam riding | 130mm | Fitted to BTR-3s, BTR-4s, and BMP-1s.[131] | ||
| Kombat |  |
125mm | Used on T-64, T-72, T-80, and T-84 tanks.[132] | ||
| Stugna-P |  |
152mm | The "Skif" export version has also been seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[133][134] | ||
| RK-3 Corsar |  |
105mm | [130] | ||
| MILAN |  |
Wire-guided | 103/115mm | More than 400 missiles donated by France, Belgium, and Estonia in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[135][39][55] | |
| NLAW | 
|
Predicted line of sight | 150mm | Used by special forces.[14] | |
| FGM-148 Javelin |  |
Infrared homing | 127mm | In service since 2018[56] | |
| BGM-71 TOW |  |
Wire-guided | 152mm | More than 7,000 missiles delivered by the US since 2022.[136] | |
| Akeron MP | 
|
Infrared homing television guidance | 140mm | Supplied by France.[137] |
Flamethrowers
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPO-A Shmel | 
|
Flamethrower | 93mm | [123] | |
| RPV-16 | 
|
In service since 2018.[138] Hundreds received in 2020.[139] |
Man-portable air-defense systems
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9K32 Strela-2 | Infrared homing | 72mm | More than 2,700 missiles donated by Germany and the Czech Republic.[19][9] | ||
| 9K34 Strela-3 | [140] | ||||
| 9K38 Igla |  |
Widely available weapon.[141] [142] | |||
| 9K310 Igla-1 | 
|
Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[143] | |||
| PPZR Piorun | Supplied by Poland.[135][31] | ||||
| Mistral |  |
90mm | 100 missiles were donated by France in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[135] 100 missiles and unspecified number of launchers were donated by Norway.[144] | ||
| Martlet | 
|
Laser-guided | 76mm | UK military aid in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[145] | |
| Starstreak |  |
Laser-guided high-velocity submunition | 130mm | 1,700 missiles donated by the United Kingdom in 2022.[135] | |
| FIM-92 Stinger |  |
Infrared homing medium-velocity | 70mm | More than 2,000 missiles donated by Latvia, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Germany, and the United States in 2022.[135][146] | |
| RBS-70 |  |
Laser beam-riding | 106mm | Donated by Sweden.[86] |
Mortars
Light mortars
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KBA-118 |  |
60 mm | [147] | |
| M60A Kamerton |  |
[91] | ||
| LMP-2017 |  |
Donated by Poland.[91] | ||
| M224 |  |
Seen in hands of Ukrainian soldiers.[91] | ||
| M60CMA |  |
Seen in hands of Ukrainian soldiers.[91] | ||
| M84 | Seen in hands of Ukrainain soliders.[91] | |||
| FBP Morteirete | Donated by Portugal in 2023.[148] | |||
| 82-BM-37 | 
|
82mm | [149] | |
| 2B14 Podnos | 
|
Reportedly used in the Donbas war.[150] | ||
| KBA-48M |  |
[147] | ||
| UPIK-82 |  |
More than 300 delivered in 2020.[151] | ||
| HM-19 | 
|
It is unclear how they arrived in Ukraine, but the most likely scenario is that they were seized from Iranian shipments to the Houthis and donated during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[37] | ||
| M69A | 
|
Seen in use with the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[152] | ||
| 20N5 | 
|
Seen in use with the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[153] |
Heavy mortars
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120-PM-38 | 
|
120mm | 30 units in service prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[130] | |
| 2B11 | 
|
10 donated by Lithuania in 2022.[135] | ||
| 2S12 Sani |  |
214 units prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[130] | ||
| M120-15 Molot |  |
120 units in service prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[130] | ||
| MP-120 | Adopted in January 2022, it's gradually replacing the M120-15 Molot.[154] | |||
| EM-120[155] | 140 in service in 2023.[156] | |||
| 120 Krh 85 92 | 
|
[156] | ||
| HM-16 | 
|
It is unclear how they arrived in Ukraine, but the most likely scenario is that they were seized from Iranian shipments to the Houthis and donated during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[37] | ||
| MO-120 RT 61 |  |
10 total provided by the Netherlands and Belgium in November 2022.[43][39][157] | ||
| 120mm mortar vz. 1982 | 
|
Unknown number provided by the Czech Republic in 2022.[9] | ||
| M120 Mortar System | 
|
30 donated by the United States in 2022.[135] |
Land mines
Anti-personnel mines
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MON-50 |  |
Command/Tripwire | 700 g RDX | [158] | |
| MON-90 | 
|
6.2 kg RDX | [158] | ||
| MON-100 | 
|
2 kg TNT | [158] | ||
| MON-200 | 
|
12 kg TNT | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[159] | ||
| OZM-72 |  |
660 g TNT | [158] | ||
| PFM-1 |  |
Pressure | 40 g liquid explosive | Reportedly used in 2022 against Russian forces in Izium.[160] | |
| M18 Claymore |  |
Command/Tripwire | 680 g C4 | Donated by the United States in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[161] |
Anti-tank mines
| Name | Image | Country of origin | Type | Caliber | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM-62M | 
|
Pressure | 7.5 kg TNT | [162] | |
| TM-72 | 
|
Magnetic | 2.5 kg TNT + RDX | [162] | |
| AT2 | 
|
Pressure | 907 g RDX + TNT | Donated by the German government in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[163] | |
| DM 31 | 
|
Magnetic | 5 kg RDX | 3,000 were donated by the German government in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[164] | |
| DM-12 PARM 2 | 
|
Off-route | 1.4 kg | Donated by the German government in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[165] | |
| RAAM | Pressure | USA supplied 9,000 155mm rounds of Remote Anti-Armor Mine (RAAM) Systems.[166] | |||
| HP2A2 | 
|
Seismic/Magnetic | First spotted in Ukraine during July 2022.[167] | ||
| PK-14 | Off-route | Donated by Estonia, first spotted in Ukraine in September 2022.[55] |
Combat vehicles
Tanks
Main battle tanks
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | |||||
| T-55 | 
|
M-55S | 28 | Prior to the Russian invasion, the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) estimated that Ukraine had 20 T-55 tanks in storage.[130] 28 M-55S donated by Slovenia in 2022.[168] | |
| T-62 | 
|
Captured: T-62M[169] T-62MV[169] |
30[169] | Some captured Russian tanks assigned to Territorial Defense units,[170] while others have been converted into armoured recovery vehicles[171] or heavy infantry fighting vehicles.[172] | |
| T-64 | T-64BV[130] T-64BV mod. 2017[130] T-64BM "Bulat"[130] T-64BM2 "Bulat"[130] |
426[130] 235[130] 100[130] |
Prior to the Russian invasion, the IISS estimated that Ukraine had 578 T-64 tanks in storage.[130] An undisclosed number of tanks will be repaired and modernized in the Czech Republic by VOP CZ.[173] | ||
| T-72 |   |
T-72AV[169] T-72AV mod. 2021[169] T-72B1[169] T-72B3[169] T-72M1[169] T-72MR[169] T-72 Avenger[168] |
500+[169] | 500 tanks in storage prior to the Russian invasion.[130] Afterwards hundreds of donated and captured tanks were put into Ukrainian service.[168][174][175] | |
| T-80 |  
|
T-80BV[130] T-80BVM[169] T-80U[169] T-80UK[169] |
88[130] | Prior to the Russian invasion, the IISS estimated that Ukraine had 34 T-80 tanks in storage.[130] After the invasion, some captured T-80BVMs and T-80UKs were pressed into service.[176][177][178] | |
| T-84 Oplot | 
|
5[130] | |||
| T-90 |  |
Captured: T-90A[179] T-90AK[179] T-90S[179] T-90M[179] |
10[169] | One T-90A tank was sent to the United States for testing at the Aberdeen Proving Ground, while others have been pressed into Ukrainian service.[180][181] | |
| PT-91 Twardy | 
|
60 | Donated by Poland.[168] | ||
| Leopard 1 | 
|
Leopard 1A5 Leopard 1A5BE |
135+ 30 |
Donated by the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark.[168] | |
| Leopard 2 | 
|
Leopard 2A4 Leopard 2A6 Strv 122 |
54 21 10 |
Donated by several countries.[168][182] | |
| Challenger 2 | 
|
14 | Donated by the United Kingdom.[168] | ||
| M1 Abrams | 
|
M1A1SA[183] | 31+ | Donated by the United States.[184] | |
Tank destroyers
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9P149 | 
|
Tracked tank destroyer | N/A | [130] | ||
| MT-LB | 
|
MT-LB-12 | Improvised self-propelled 100mm MT-12 "Rapira" anti-tank gun.[185] | |||
| 9P148 | 
|
Wheeled tank destroyer | 9P148 Konkurs 9P148 Amulet |
4+[186] | Some upgraded with Stugna-P launchers.[169][186] | |
| AMX-10 RC | 
|
AMX-10 RCR | 40 | [168] |
Armored fighting vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armored fighting vehicles | ||||||
| BRM-1(K) | 
|
Tracked reconnaissance vehicle | 115[130] | |||
| BPzV Svatava | 
|
N/A | Donated by the Czech Republic.[9] | |||
| FV107 Scimitar | 
|
Scimitar Mk 2 | 23 | 23 to be provided by the United Kingdom.[168] | ||
| BRDM-2 | 
|
Wheeled reconnaissance vehicle | BRDM-2[130] BRDM-2L1[130] BRDM-2T[130] |
327[130] 80[130] 25[130] |
Repaired and modernized by the Mykolaiv Armoured Plant.[187][188] | |
| Fennek | 
|
N/A | Donated by the Netherlands to the AFU.[168] | |||
| Ferret | 
|
Ferret Mk 1 | 1 | [189] | ||
| Infantry fighting vehicles (wheeled and tracked) | ||||||
| BMP-1 |  
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | BMP-1[130] BMP-1AK[130] BMP-1TS[190] BMP-1U "Shkval"[190] BMP-1A[168] BVP-1[168] BWP-1[168] Pbv 501A[168] |
213[130] 318[168] |
Several hundred donated by Germany, Czech Republic, Poland, and Greece.[168] Some captured Russian vehicles are also used.[191][192] | |
| BMP-2 | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | BMP-2[130] BVP-2[193] |
890[130] N/A |
Unknown number of BVP-2 to be donated by the Czech Republic.[193] Some captured Russian vehicles are also used.[194] | |
| BMP-3 | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | 40[169] | Prior to the Russian invasion, Ukraine had 4 BMP-3 in service.[130] After the invasion, several were captured and pressed into service.[195] | ||
| BMD-1 | 
|
Tracked airborne infantry fighting vehicle | 45[130] | Possibly non-operational.[169] | ||
| BMD-2 | 
|
Tracked airborne infantry fighting vehicle | 60[130] | Some captured Russian vehicles are used by the National Guard.[196] | ||
| YPR-765 | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | 196 | Donated to the UGF by the Netherlands.[168] | ||
| BVP M-80 | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | BVP M-80A | 35 | Donated by Slovenia.[168] | |
| Marder | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | 100 | Donated by Germany.[168] | ||
| Bradley | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | M2A2 ODS M7 Bradley FiST |
186 | Donated by the US.[184][168] | |
| CV90 | 
|
Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | CV9040 | 50 | Donated by Sweden.[86] 1000 more to be built during a joint venture between Sweden and Ukraine.[197][198] | |
| BTR-3 | 
|
Wheeled armored personnel carrier/Infantry fighting vehicle | BTR-3DA[130] BTR-3E1[130] |
54+[130] 6+[130] |
||
| BTR-4 | 
|
Wheeled infantry fighting vehicle | BTR-4[190] BTR-4EP[190] BTR-4MV1[190] |
45[130] | ||
| BTR-80 | 
|
Wheeled infantry fighting vehicle | Captured: BTR-82A BTR-82AM |
80[169] | Some captured BTR-82s are used by Ukrainian marines.[195] | |
| KTO Rosomak | 
|
Wheeled infantry fighting vehicle | KTO Rosomak | 200 | Delivered by Poland in July 2023.[31] | |
| Armoured personnel carriers (wheeled and tracked) | ||||||
| MT-LB |  
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | MT-LB[190] MT-LBu[190] MT-LBVM[190] MT-LBVMK[190] |
45[130] | ||
| GT-MU | 
|
Airborne tracked armoured personnel carrier | N/A | [190] | ||
| BTR-D | 
|
Airborne tracked armoured personnel carrier | 40[130] | Some captured Russian vehicles are used.[199] | ||
| BTR-MDM | 
|
Airborne tracked armoured personnel carrier | At least one captured BTR-MD was converted into an armored ambulance.[200] | |||
| M113 | 
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | M113[190] M113AS4[190] M113G3DK[190] |
778 (Including 200 Armoured Medical Treatment Vehicles). | Donated by several countries, used by both UGF and Marine Corps.[168] | |
| FV103 Spartan | 
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | ~114 | Donated by the UK and private donors.[135] | ||
| FV105 Sultan | 
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | N/A | Multiple were purchased for the Ukrainian Ground Forces by former President Petro Poroshenko.[201] | ||
| FV430 Bulldog | 
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | FV432 Mk 3 | N/A | Donated by the United Kingdom.[202][203] | |
| Bandvagn | 
|
Tracked armoured personnel carrier | Bandvagn BvS 10 Bandvagn BV-206S' |
92+ | Donated by the Netherlands, Italy, and Germany.[168] | |
| BTR-60 | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | BTR-60PB[190] BTR-60М[190] TAB-71M[168] |
6[130] N/A |
Ukraine was supplied with an unknown amount of TAB-71s around November 2022.[168] In August 2023, Bulgaria pledged to send 100 BTR-60s as military aid.[204] | |
| BTR-70 | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | BTR-70[190] BTR-70M[190] BTR-7[190] |
217[130] | ||
| BTR-80 | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | BTR-80[190] BTR-80M[190] |
224[130] | Some captured Russian vehicles are used.[205] | |
| VAB | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 56+ | Used by the Air Assault Forces.[206] | ||
| Patria Pasi | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | Sisu XA-185 | 20+[168] | [156] | |
| LAV 6 | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | ACSV | 39 | Donated by Canada.[168] | |
| Stryker | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 189 | Donated by the US.[184] | ||
| M1117 | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 250 | Donated by the United States.[168] | ||
| OT-64 SKOT | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 1+? | Purchased by the Ukrainian scout organization Plast for the 103rd Separate Territorial Defense Brigade.[207] | ||
| Valuk | 
|
Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 20[168] | Donated by Slovenia under a secret deal with Ukraine.[208] | ||
| Fuchs Evolution | 
|
? | Improved version of Tpz Fuchs to be donated by Germany.[209][210] | |||
Infantry mobility vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varta | 
|
Protected car | MAZ-5434 | 80+ | Used by the UGF, Marines, and National Guard.[211] | |
| Kozak-2 | 
|
Kozak-2M1 | 240+[212] | Used by the UGF and National Guard.[211] | ||
| Kozak-5 | 
|
Ford F-550 | Unknown | Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | ||
| KrAZ Cobra | 
|
Toyota Land Cruiser 200 | 10 | Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | ||
| KrAZ Cougar | 
|
Toyota Land Cruiser 79 | ? | Used by the National Guard.[206] | ||
| KrAZ Shrek | 
|
Shrek One | 2[citation needed] | [190] | ||
| KrAZ Spartan | 
|
Ford F-550 | ? | Used by Air Assault Forces and the National Guard.[213] | ||
| Bogdan Bars-6 | 
|
Kia KM450 | ? | [214] | ||
| Bogdan Bars-8 | 
|
Dodge Ram | 90 | [214] | ||
| Novator | 
|
Ford F-550 | 40 | Delivered in 2019.[215] | ||
| Ovid | 
|
GAZ-66 | 1 | Prototype. Used by the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[216] | ||
| Dozor-B |  |
Protected mobility vehicle | Dozor-B Oncilla |
10 27+ |
Used by the Air Assault Forces[206] | |
| Bushmaster | 
|
90 | 90 donated by Australia in 2022.[135] | |||
| Roshel Senator | 
|
100 + 300 | 400 pledged by Canada. As of December 2022, 100 were delivered to Ukraine.[135] | |||
| Iveco LMV | 
|
LMV LAV III |
90 14 |
At least 24 supplied by Italy and Norway in 2022.[135] 80 donated by Belgium in 2023.[168] | ||
| Iveco VM 90P | 
|
40.12 WM/P VM 90P |
4 45 |
Donated by Portugal and Italy.[52][84] | ||
| AMZ Dzik | 
|
Dzik-2 | N/A | Supplied by Poland.[31] | ||
| Snatch Land Rover |  
|
Light armoured mobility vehicle | +14 7 |
Some instances of units that are privately owned that have been donated to Ukraine.[217] Seven were delivered by Latvia in February 2021, as armored medical vehicles.[218][219] | ||
| Saxon | 
|
MRAP | 200[220] | Acquired from 2014 onwards.[221] Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[222] | ||
| Alvis 4 | 
|
7 | Donated by Estonia.[55] | |||
| Cougar |  
|
Mastiff Wolfhound |
97 | 60 donated by the United Kingdom and 37 by the United States in 2022.[135] | ||
| International M1224 MaxxPro | 
|
Unknown | 440 | 440 donated by the United States.[135] | ||
| Husky TSV | 
|
International MXT-MV based | 20 | 20 donated as part of a batch of 120 armoured personnel carriers sent by the United Kingdom.[135][223] | ||
| Light Tactical Vehicles | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | Unknown | 200+ | Donated by the US.[184] | |
| Oshkosh M-ATV | ||||||
| Humvee | 
|
Light infantry mobility vehicle | Unknown | 2,000+[168] | Supplied before and after the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[135][184] | |
| LC-79 APC-SH Fighter-2 | 11 | Bought by Come Back Alive Foundation for Ukrainian Forces. LC-79 APC-SH Fighter-2 vehicles are based on the Toyota Land Cruiser 79.[224] | ||||
| GAZ-2975 Tigr | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | Tigr Tigr-M |
7 32[179] |
At least 1 captured vehicle in service with the UAF.[225] | |
| Linza | 
|
KamAZ-53949-Linza | 4+ | As of 1 October 2022, at least four had been captured from the Russian Armed Forces during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[179] | ||
| MLS Shield | 
|
11 | 11 bought from Italy during the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine.[135] | |||
| BMC Kirpi | 
|
MRAP | 200 | 50 have been delivered, with 150 more to be delivered.[226] | ||
| ATF Dingo | 
|
50 | 50 donated by Germany.[135][19] | |||
| BATT UMG | 100[168] | Possibly purchased by Ukraine. Reportedly 66 vehicles were pledged by Germany.[227][228] | ||||
| Gaia Amir | 
|
Unknown | First seen in November 2022 during the Southern Ukraine campaign.[229][230] | |||
| MSPV Panthera T6 | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | Unknown | Delivered in December 2022.[168] | ||
| INKAS Titan-S | Unknown | Delivered in December 2022.[168] | ||||
| Toyota Land Cruiser | 
|
Land Cruiser 200 AT42M
|
7 | Lithuania bought 12 for international missions, with protection from small arms and IEDs. From Arctic Truck company.[231] Now, all 7 vehicles are with special trailers, donated to Ukraine army.[232] | ||
| BPM-97 | 
|
MRAP | 3 | three seen captured from Russian forces.[233][234][better source needed] | ||
| KamAZ-63968 Typhoon-K | 
|
1 | At least 1 captured vehicle used by the Ukrainian army.[235] | |||
| VPK-Ural | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | 3 | 3 captured from Russian forces [179][236] | ||
| GAZ-3937 'Vodnik' | 
|
1 | 1 seen captured from Russian forces[237] | |||
| Remdiesel Z-STS Akhmat | 1 | 1 captured from Russian forces [179] | ||||
| K-53949 Typhoon-K | 
|
1 | 1 captured from Russian forces [179] | |||
| Mowag Eagle I | 
|
11[238] | Delivered to Ukraine by an undisclosed German private company without Swiss approval.[239] | |||
| Otokar Cobra II | 
|
Cobra II | Unknown | Delivered in May 2023.[240] |
Field artillery
Towed mortars and anti-tank guns
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2B9 Vasilek | 
|
82 mm gun-mortar | ? | [96] | ||
| D-44 |  |
85 mm field gun | ? | Seen mounted on MT-LBs in the indirect fire support role.[241] | ||
| D-48 |  |
85 mm anti-tank gun | ? | An unknown number of guns were reactivated beginning 2015 due the Donbas war.[242] | ||
| BS-3 | 
|
100 mm field gun/anti-tank gun | ? | Reactivated during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[243] | ||
| T-12 |  |
MT-12 Rapira | 500+[130] | Pressed into service during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[242][244] Has been seen mounted on MT-LBs.[185][245] | ||
| 2B16 Nona-K | 
|
120 mm | 2[130] | 2 guns were in active service before 24 February 2022.[130] Some captured Russian guns are used as well.[246] | ||
| M240 | 
|
240mm mortar | ? | Brought back into service due to 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[247] |
Self-propelled mortars
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2S9 Nona |  
|
120 mm | 2S9 Nona-S[130] Captured: 2S23 Nona-SVK[179] |
40[130] | Some captured Nona-SVKs were pressed into service.[246] | |
| Bars-8MMK | 
|
Dodge Ram | 12+ | Alakran mortar carrier can be used on multiple chassis.[248][249] | ||
| Panzermörser M113 | 
|
10 | Delivered by Lithuania in November 2022.[250] | |||
| M120 Rak | 
|
24 | To be supplied by Poland.[168] | |||
| Alakran 120 | Unknown | Bought from Spain using EU/US funding.[251] |
Towed artillery
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Quantity | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mod 56 | 
|
105 mm | Mod 56 | 6 | One battery with six guns donated by Spain in 2022.[135] | |
| M101 | 
|
M101 M101A1 |
70 | As of January 2023, Lithuania donated 54 M101A1s.[135] 16 guns were donated by Slovenia.[168] | ||
| L118 |  |
L119 M119A3[252] |
132 | As of January 2023, the United Kingdom donated 60 L119s,[135] while the United States donated 72 M119s.[253] 9 L119s to be delivered from Portugal.[254] To be produced in Ukraine in the future and to gradually replace heavily worn-out D-30 howitzers.[255] | ||
| D-30 | 
|
122 mm | D-30 | 75[130] | 36 donated by Estonia[55] | |
| M-46 | 
|
130 mm | M-46 | 24+ | Donated by Croatia and Finland.[256][257][94] | |
| D-20 | 
|
152 mm | D-20 | 184+[130] | Some captured Russian guns seen in use.[258] | |
| 2A36 Giatsint-B | 
|
2A36 Giatsint-B | 180+[130] | In April 2023, Finland delivered an undisclosed amount of 152 K89s to Ukraine.[168] | ||
| 2A65 Msta-B | 
|
2A65 Msta-B | 130[130] | |||
| M1981 | 
|
Model 1981 | Unknown | An unspecified number of M1981 howitzers were given by Romania. First seen in May 2023.[259] | ||
| TRF1 | 
|
155 mm | TRF1 | 15 | Supplied by France.[135] | |
| FH-70 | 
|
FH-70 | 34 | 24 donated by Estonia and 10 by Italy.[55][135] | ||
| M777 | 
|
M777 | 152 | Donated by the US, Canada, and Australia.[135] |
Self-propelled artillery
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2S1 Gvozdika | 
|
122 mm | 2S1 Gvozdika 2S1 Goździks |
292+[130] 20[31] |
More than 20 guns donated by Poland, Czech Republic, and Finland.[31][94][260] | |
| 2S3 Akatsiya | 
|
152 mm | 267+[130] | |||
| 2S5 Giatsint-S | 
|
18+[130] | Captured Russian guns seen in use with the UAF.[261] | |||
| 2S19 Msta-S | 
|
2S19 Msta-S Captured:[179] 2S19 Msta-S 2S33 Msta-SM2 |
35+[130] | Some captured Russian guns are used by airborne brigades.[262] | ||
| ShKH vz. 77 DANA | 
|
vz. 77 DANA DANA M2 |
39 | Ukraine purchased 26 DANA M2s in 2022.[263] As of January 2023, Czechia has donated 13 ShKH vz. 77 DANAs.[264] | ||
| 2S22 Bohdana | 
|
155 mm | 4+ | As of July 2023, Ukraine have one prototype, and three Bohdanas in service.[265][266] | ||
| CAESAR |  
|
Caesar 6x6 Caesar 8x8 |
49 | As of January 2023, France had donated 30 Caesars (Renault Sherpa 5 (6x6)).[267] 19 Caesars (Tatra 817 (8x8)) have been donated by Denmark.[268] | ||
| PzH 2000 | 
|
128 | Donated by Germany, Italy and the Netherlands.[135] Ukraine has purchased 100 through the security capacity building fund.[269] | |||
| RCH-155 | 
|
18 | To be delivered.[19] | |||
| AHS Krab | 
|
72+ | 18 donated by Poland and 54 purchased with EU funding.[31] | |||
| ShKH Zuzana | 
|
ShKH Zuzana 2 | 24 | [168] | ||
| M109 |   |
M109A3GN M109A4BE M109A5Ö M109L M109A6 "Paladin" |
150+[168] | 51 donated by the UK, Latvia, and Norway.[135] Italy donated over 100 M109Ls,[84] while the US donated 18 M109A6 Paladins.[270] | ||
| Archer | 
|
8 | Donated by Sweden.[271] | |||
| AS-90 | 
|
32 | Supplied by the UK.[168] | |||
| T-155 Fırtına | 
|
? | Unknown number purchased by Ukraine.[168] | |||
| 2S7 Pion | 
|
203 mm | 2S7 Pion | 13+[130] | Up to 83 guns were in storage prior to the Russian invasion.[130] |
Multiple rocket launchers
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM-21 Grad |  
|
122 mm | 9P138[130] BM-21[130] BM-21K Bastion-1 Bastion-2 Verba |
209+[130] | More than 20 BM-21 Grads donated by Poland and the Czech Republic.[168] | |
| RM-70 | 
|
RM-70 RM-70 "Vampire" |
20+ | Supplied by the Czech Republic.[9] | ||
| APR-40 | 
|
N/A | Donated by Romania.[168] | |||
| BM-21MT Striga | 
|
N/A | [9] | |||
| Tornado-G | 
|
9K51M Tornado-G | Captured from Russian forces and pressed into Ukrainian service.[169] | |||
| BM-27 Uragan | 
|
220 mm | BM-27 Uragan Bureviy |
70 | [130] | |
| TOS-1 | 
|
Captured: TOS-1A[179] | At least 1 captured TOS-1A in service with the UAF.[272][273][274] | |||
| M270 | 
|
227 mm | M270B MARS II |
23[168] | Donated by the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Italy.[168] | |
| M142 HIMARS | 
|
M142 | 38 | [275] | ||
| TRG-230 | 
|
230 mm | TLRG-230 | Unknown | As of January 2023, Turkey donated an unspecified number of TLRG-230s.[276] | |
| BM-30 Smerch |  
|
300 mm | BM-30 Smerch Vilkha |
81+[130] |
Ground and sea launched missile systems
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTR-21 Tochka | 
|
Tactical/Short-range ballistic missile | Scarab-B | 90 launchers[130] | 500 missiles prior to the Russian invasion.[277] | |
| MGM-140 ATACMS | 
|
Block I | ? | Donated by the United States.[278] | ||
| Multi-role missiles | ||||||
| Brimstone | 
|
Short-range multi-role missile | Brimstone 1 single-mode and Brimstone 2 dual-mode | 800 + | Donated by the United Kingdom.[279][280] Some were seen in use with truck-mounted launchers.[281] | |
| Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System | 
|
Laser-guided | ? | Supplied by the US.[168] | ||
| RIM-7 | 
|
Ship-borne short-range anti-aircraft and anti-missile weapon system | ? | Supplied by the US.[275] | ||
| Ground Launched Small Diameter Bomb | 
|
Surface-to-surface missile | ? | Supplied by the US.[275] | ||
| Anti-ship missiles | ||||||
| RBS-17 | 
|
Short range | AGM-114C | 210 | Based on the maritime AGM-114 Hellfire variant, donated by Norway and Sweden.[135] | |
| Neptune | 
|
Over-the-horizon | RK-360MC | ? | In service with the Ukrainian Navy since March 2021.[282] It was used to sink the Russian cruiser Moskva, and was later modified to strike ground targets.[283] | |
| Harpoon | 
|
Over-the-horizon | RGM-84L-4[284] | 3+[284] | Supplied by Denmark, Netherlands, Spain, UK and US.[285] | |
| In development | ||||||
| Sapsan | 
|
Short range ballistic missile | Hrim-2 TBM OTRK Sapsan |
1 prototype[286] | In development, with a range of 480 km and a maximum payload of about 1.5 tons.[287] | |
| Korshun-2 | 
|
Short range cruise missile | TBA | In development, with a range of between 50 and 350 km and a payload of half a ton (around 450 kg). The missile has been in development since 2014.[288] | ||
Air defense systems
Long and medium air defense is under the authority of the Air Defense Forces of the Ukrainian Air Force. See their equipment.
Towed anti-aircraft guns
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZPU | 
|
Towed anti-aircraft gun | ? | Seen in use during the Russo-Ukrainian war.[289] | ||
| AZP S-60 | 
|
? | [156] | |||
| ZU-23-2 | 
|
2A13 23 ITK 61 ZU-23-2CP |
? | Finnish and Polish variants are also used by the AFU.[94][290] | ||
| Zastava M55 | 
|
M55 M75 |
200 | Donated by Slovenia.[168] | ||
| Bofors 40 mm L/70 | 
|
L/70 | 53 | Donated by Lithuania and the Netherlands.[168] | ||
| KS-19 | 
|
? | Used in the ground support role.[291] | |||
| MSI-DS Terrahawk Paladin | Unknown | Pledged by the United Kingdom.[292] |
Self-propelled anti-aircraft guns
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSU-23-4 Shilka | 
|
Tracked armoured self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | ZSU-23-4M3 | ? | Also used in the ground support role. Some were donated by Poland.[293] Shared between the UGF and Marine Corps.[130] | |
| Flakpanzer Gepard | 
|
1A2 | 49[19] | 3 pledged by Germany.[19] | ||
| Skynex | 
|
Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | 2[294] | First systems delivered in May 2023.[295] | ||
| MR2 Viktor | 115 | Supplied by Excalibur Army. 15 crowdfunded by Czech citizens and 100 paid for by the Netherlands.[81][296] | ||||
| Hibneryt | 
|
? | Donated by Poland.[168] |
Surface-to-air missile systems
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stormer HVM | 
|
Very short range | 6[135] | |||
| AN/TWQ-1 Avenger | 
|
12[297] | ||||
| 9K35 Strela-10 |  |
9K35M Strela-10M4 | 6+ | 6 donated by the Czech Republic in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[9] | ||
| 2K22 Tunguska |  |
2K22M | 75[130] | [298] | ||
| 9K33 Osa | 
|
Short range | Osa-AKM
Osa-AKM-P1 "Żądło" |
125 | Unknown number supplied by Poland[31] | |
| S-125 Pechora | 
|
Pechora 2D Newa SC |
Modernized to the S-125 2D standard.[299] Some S-125 Newa SC were donated by Poland.[31] | |||
| 9K330 Tor |  |
6[130] | ||||
| Crotale | 
|
Crotale NG | 4[135] | |||
| IRIS-T | 
|
IRIS-T SLS | 2 | 22 launchers pledged by Germany.[19] | ||
| 9K37 Buk | 
|
Medium range | 9K37M1 | 72[130] | Modified to fire AIM-7 Sparrow or RIM-7 Sea Sparrow missiles.[300] | |
| 2K12 Kub | 
|
M3/2D Kub-M2 |
1 2 |
One or two M3/2D units operational prior to the Russian invasion. 2 batteries donated by the Czech Republic.[301] | ||
| MIM-23 Hawk | 
|
MIM-23 Hawk Phase I MIM-23 Hawk Phase III |
1 | 1 battery pledged by Spain.[302] | ||
| IRIS-T | 
|
IRIS-T SLM | 3 | 5 batteries pledged by Germany.[19] | ||
| NASAMS |  |
Unknown | 2 | 8 batteries pledged by the US, Canada, and Norway.[303] | ||
| Aspide | 
|
Aspide 2000 Skyguard Spada |
3+ | Donated by Italy and Spain.[168] | ||
| Aster | 
|
Medium and long range | SAMP/T | 1[304] | ||
| S-200 | 
|
Long range | N/A | N/A | Retired on October 30, 2013,[305] but the weapon was brought back into service during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, primarily for use against land targets.[306][307] | |
| S-300 | 
|
S-300V1
S-300P/PS/PT S-300PMU |
250+[130] | One S-300PMU battery donated by Slovakia.[135] | ||
| MIM-104 Patriot |  |
2[19][275] | 1 battery pledged by Germany.[19] |
Radars
Radar for long and medium air defense are under Radiolocation Forces authority of the Ukrainian Air Force. See their equipment.
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-14 | 
|
Very high frequency early warning radar | N/A | [190] | ||
| P-18 | 
|
P-18C
P-18ML P-18 "Malakhit" |
Unknown | Being modernized to the P-18C standard.[308] The Lithuanian modernsation P-18ML and Ukrainian P-18 "Malakhit" modernisation have both been seen in use.[190] | ||
| P-19 | 
|
Wheeled Ultra high frequency mobile surveillance radar | N/A | [190] | ||
| P-35 | 
|
E band/F band early warning radar | N/A | [190] | ||
| 1L22 "Parol" | 
|
Wheeled mobile | N/A | [190] | ||
| PRV-11 | 
|
Towed | N/A | [190] | ||
| PRV-13 | 
|
Towed | N/A | [190] | ||
| PRV-16 | 
|
Wheeled mobile | PRV-16ML | N/A | The Lithuanian modernsation PRV-16ML has been seen in use.[190] | |
| ARK-1 | 
|
Tracked artillery locating mobile | N/A | [309] | ||
| SNAR-10 | 
|
N/A | [309] | |||
| PPRU-1 9S80 | 
|
Tracked 3D acquisition mobile | N/A | [309] | ||
| R-410 | 
|
tropospheric radio relay communication station | N/A | [190] | ||
| 36D6 "Tin Shield" | 
|
E/F Air Surveillance Radar | 1+ | Part of the S-300 complex. 1 donated by Slovakia.[310] | ||
| 5N66M "Clam Shell" | 
|
continuous-wave Doppler radar for target acquisition | 1+ | Part of the S-300 complex. 1 donated by Slovakia.[310] | ||
| 5N63S 'Flap Lid B' | 
|
Engagement/fire-control radar | 1+ | Part of the S-300 complex. 1 donated by Slovakia.[310] | ||
| SURN 1S91 | 
|
G/H band a target acquisition and distribution radar | 3+ | Part of the 2K12 Kub complex. At least 3 donated by the Czech Republic and Slovakia.[310][9] | ||
| Zoopark-1 | 
|
Counter-battery radar | 1L260
1L261 |
2 | At least 2 were captured from Russian forces.[179] | |
| 1AP1 "Polozhennya-2" | 
|
Tracked artillery locating mobile | 1+? | Acoustic detection device. Entered service with the AFU around 2020.[311] | ||
| 1L220U "Zoopark-2" | 
|
Wheeled artillery locating mobile | 1L220UK is modernized variant adopted by the Ukrainian army.[312] | |||
| AN/TPQ-36 |  |
39+ | [135] | |||
| AN/TPQ-48 |  |
Light counter mortar | 20 | [313] | ||
| AN/TPQ-49 | 
|
Light counterfire | 10+ | [314] | ||
| AN/MPQ-50 | 
|
Lightweight Counter Mortar Radar | N/A | [190] | ||
| AN/MPQ-61 | Towed air surveillance | 1 | Provided with the MIM-23 Hawk battery donated by Spain in December 2022.[49][315] | |||
| AN/MPQ-62 | 1 | |||||
| AN/MPQ-64 Sentinel | 
|
8 | Supplied by the US. Some used with the NASAMS systems.[135] | |||
| COBRA | 
|
Counter-battery radar | 1 | [19] | ||
| TRML |  |
Medium range early warning radar | TRML-4D | 4 | 4 pledged by Germany.[19] | |
| Thales SQUIRE | 
|
Ground Surveillance Radar | 2 | [168] | ||
| MAMBA/ARTHUR |  |
Counter-battery radar | 3+ | Unknown quantity supplied by the United Kingdom. 3 pledged by Norway.[168] | ||
| Ground Master 200 | 
|
Medium range air Surveillance Radar | 2+ | Pledged by France during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[98][316] Contract signed between Ukraine and Thales for 2 systems.[317] | ||
| Thomson-CSF RAC 3D | 1 | Provided by Spain with the Aspide 2000 battery.[49] | ||||
| PS-90 | 
|
Early warning Radar | N/A | [86] | ||
| VERA passive radar | Long range Passive radar | 4 | 4 pledged by the Netherlands.[168] |
Electronic warfare and communication
- Communication equipment
- Jammers
- Eavesdropping equipment
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP-1KSh | 
|
Stand alone unit | 1+ | [318] | ||
| 9S470M1 | 
|
Command vehicle | N/A | Command vehicle for the BUK-M1.[190] | ||
| R-149BMR Kushetka-B | 
|
Command and staff vehicle | 1 | 1 vehicle captured and pressed into Ukrainian service. Modified with a BRM-1K turret.[319] | ||
| Barnaul-T 9С932-1 | 
|
Automated system for air defence units | 1+ | At least 1 captured vehicle was pressed into Ukrainian service.[320] | ||
| LPG | 
|
Tracked command vehicle | WD WDSz |
N/A | [31] | |
| M577 | 
|
Armoured command center | 7+[52][321] | |||
| M7 Bradley | 
|
Fire Support Vehicle | 4 | [184] |
Electronic warfare and jammers
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-330 | 
|
Electronic warfare system | Mandat-B1E R-330UM | N/A | [322] | |
| NOTA | Counter unmanned aerial vehicle jammer | N/A | [322] | |||
| Bukovel-AD | 
|
N/A | [322] | |||
| Moruš | Wheeled vehicle-mounted, multi-functional Electronic warfare weapon system |
1+ | [9] | |||
| EDM4S | 
|
Counter-UAV jammer | 110 | [323] | ||
| Borisoglebsk-2 | 
|
Tracked vehicle-mounted, multi-functional Electronic warfare weapon system |
R-330BMV Borisoglebsk-2B: |
1+ | 1 captured from Russian forces in 2022.[324] |
Engineering
Recovery vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTS-4 | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 22+[130] | Based on the T-54/55 chassis.[325] | |
| BREM-1 | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 10[130] | ||
| BREM-2 | 
|
Tracked amphibious armoured recovery vehicle | 1+ | Modernized by the Zhytomyr Armoured Plant.[326] | |
| MT-T Aeneas | 
|
Tracked recovery vehicle | Unknown | Based on the T-64 chassis. Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[327] | |
| BREM-Ch | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 1 | At least 1 vehicle was captured from Russian forces and used by the AFU.[328] | |
| VT-72B | 
|
1+ | Supplied by the Czech Republic in 2014.[329] | ||
| REM-KL | 
|
Repair and recovery vehicle | 1+ | 1 seen captured and in use by Ukrainian Forces.[330][better source needed] | |
| BREM-84 "Atlet" | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 1 | [331] | |
| BREM-4K | 
|
Wheeled amphibious armoured recovery vehicle | 1+ | [332] | |
| BREM-4RM | 
|
1+ | At least one purchased in 2020.[333] | ||
| Bergepanzer 2 | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 15 | [19] | |
| NM189 Ingeniørpanservogns | 4 | Pledged by Norway.[168] | |||
| Bergepanzer 3 | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 2 | [19] | |
| M1089A1P2 | 
|
Wrecker | 104 | [168] | |
| M984A4 HEMTT recovery vehicle | 
|
Wrecker | [168] | ||
| M88 | 
|
Armored recovery vehicle | 8 | M88A1 and M88A2 Hercules donated by the US.[168] | |
| GMC TopKick rescue vehicle | Unknown | [334] | |||
| FV106 Samson | 
|
Tracked light armoured recovery vehicle | 5 | Pledged to Ukraine by the British government in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[223] | |
| CRARRV | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | To be delivered to Ukraine to support the delivery of Challenger 2 tanks by the United Kingdom.[335] | ||
| Bärgningsbandvagn 90 | 
|
Tracked armoured recovery vehicle | 1+ | [86] |
Clearing vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMR-2 | 
|
Tracked armoured obstacle clearing vehicle | ? | Inherited from the former Soviet Union, some were captured from Russian forces.[336] | |
| UR-77 Meteorit | 
|
Tracked amphibious mine clearing vehicle | ? | [337] | |
| M 58 MICLIC | 
|
Rocket-projected explosive line charge | ? | Provided by the United States as military aid in 2022.[338] | |
| Armtrac 400 | 
|
Mine clearing vehicle | ? | [339] | |
| Wisent 1 | 
|
10 | 32 to be delivered by Germany.[19] | ||
| Leopard 2R | 
|
6 | Donated by Finland.[94] | ||
| Bozena 4 | 
|
2 | Pledged by Slovakia.[340] | ||
| Bozena 5 | 
|
2 | [168] | ||
| K600 CEV | Combat engineer vehicle | 2 | To be supplied by South Korea.[341] | ||
| VAB Génie | Multipurpose clearance vehicle | ? | To be supplied by France.[342] | ||
| M1150 Assault Breacher Vehicle | 
|
Combat engineer vehicle | 1+ | Supplied by the US.[343] |
Minelayers
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMZ-3 | 
|
Tracked minelayer | 51+ | At least two vehicles have been captured from Russian forces during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[179] | |
| Shielder |  |
Unknown | [344] |
Construction vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAT-2 | 
|
Tracked armoured road laying machine | 53[130] | Some were repaired by the Kharkiv Automobile Plant.[345] At least 3 captured from Russian forces.[346] | |
| MDK-3 | 
|
Tracked trencher | N/A | [347] | |
| PZM-3 |  |
N/A | [348] | ||
| MAZ-5335 | 
|
Wheeled crane | N/A | Seen building bunkers in the Donbas.[349][better source needed] | |
| KrAZ-255B | 
|
Wheeled excavator | N/A | [190] | |
| Dachs | 
|
Armoured engineer vehicles | 5 | [19] | |
| FV434 |  |
Armoured Repair Vehicle | N/A | [344] |
Bridges
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMP | 
|
Wheeled |
? | [350] | |
| MT-55A | 
|
Tracked armoured vehicle-launched bridge | ? | [351] | |
| MTU-20 | 
|
? | [130] | ||
| MTU-72 | 
|
1+[179] | [351] | ||
| TMM-3 | 
|
Wheeled motorized bridge | ? | [351] | |
| M60 AVLB | 
|
Armored vehicle-launched bridge | ? | Supplied by the US.[351] | |
| Biber (Brückenlegepanzer) |   |
Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | 13 | 13 out of 26 delivered by Germany as of October 2023.[19] | |
| M3 Amphibious Rig | 
|
Amphibious bridge laying vehicle | ? | Pledged to be delivered by the Netherlands.[168] | |
| Pont flottant motorisé | 
|
Wheeled motorized bridge | ? | Pledged by France.[168] | |
| Engin de franchissement de l'avant | 
|
Amphibious bridge laying vehicle | ? | Pledged by France.[168] |
Ships and underwater vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMK-130 | 
|
Motor boat | N/A | [352] | |
| BMK-460 | 
|
Tugboat | N/A | [352] | |
| GALAXY Trident 8 | Motor boat | 2+ | Used by special forces.[353] | ||
| Willard Sea Force 730 |  |
10 | Used by special forces.[354] | ||
| Willard Sea Force 11M | Used by special forces.[354] | ||||
| Metal Shark 7M RIB |  |
10 | Provided by the US as aid in 2021.[355] | ||
| Wing P-series Boat | 70+ | Provided by the US as aid in 2021.[356] | |||
| 34-foot Dauntless Sea Ark | 
|
Patrol Boat | 10 | Provided by the US in a June 2022 aid package.[357] Seen in use in Ukraine in November 2022.[358] | |
| 40-foot Defiant Patrol Boat | 6 | Provided by the US in a June 2022 aid package.[357] Seen in use in Ukraine in November 2022.[359][360] | |||
| 35-foot small-unit Riverine Craft | 
|
Riverine Patrol boat | 2 | Provided by the US in a June 2022 aid package.[357] | |
| Armored Riverine Boat | 40 | Provided by the US in a November 2022 aid package.[361] | |||
| MK VI Patrol Boat | 
|
Patrol Boat | 8 | [362] | |
| UMS 600 | ? | Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[363] | |||
| SHERP the SHUTTLE |  |
Landing boat | 1+ | Seen in use during the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine.[364] | |
| SeaFox Autonomous Mine-Detecting Underwater Vehicles | 
|
Autonomous Mine-Detecting Underwater Vehicles | 2 | Provided by the Netherlands in 2022.[168] |
Medical
Tracked ambulances
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FV104 Samaritan | 
|
|
Tracked armored ambulance | Combat Vehicle Reconnaissance (Tracked) | 40[168] | Supplied by the United Kingdom.[223] Some were donated by private donors.[135] | ||
| M113A4 Armored Medical Evacuation Vehicle | 
|
100[168] | Sent by the United States.[365] | |||||
| M113A2 | 
|
3[366] | Donated by Portugal.[168] | |||||
| M577A2 | 
|
2[366] | Donated by Portugal.[168] | |||||
| Warthog armoured vehicle | 
|
Warthog ambulance | 10 | [19] | ||||
| THeMIS | 
|
UGV | MEDEVAC role | 14 | [19] |
Wheeled protected ambulances
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steyr-Puch Pinzgauer | 
|
Protected ambulance Protected mobility vehicle |
718 ambulances |
N/A | Former British Army stocks converted by the Venari Group. Some were donated by Luxembourg.[367] | |
| RG-31 Nyala | 
|
Light protected multi-pupose vehicle | Ambulance | 1+ (?) | At least one donated by Spain.[135] | |
| Terradyne Gurkha | 13[368] | |||||
| Alvis Tactica |  |
Ambulance | 1+ | Seen in use during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Likely was bought by volunteers.[369] |
Wheeled ambulances
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bogdan-2251 | 
|
Ambulance | Great Wall Wingle 5[citation needed] | 350 | [370] | |
| Unimog Ambulance | 
|
Unimog ambulance | 47+[19] | Former British army stock, converted by the Venari Group.[367] | ||
| HMMWV Ambulance |  |
40+ | Donated by a private donor.[371] |
Logistics
Utility vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAZ-452 | 
|
Van | UAZ-452 UAZ-452A |
? | [372] | |
| UAZ-469 | 
|
Military light utility vehicle | ? | To be replaced starting in 2021.[373] | ||
| KTM 450 EXC | 
|
Off-road motorcycle | 1+ | Used to transport troops and light weapons in rough terrain.[374] | ||
| Bogdan-2351 | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | Great Wall Wingle 5 | 350+ | Adopted in 2018, it's derived from the Chinese Great Wall Wingle 5.[375] | |
| Fiat Fullback | 
|
Pickup truck | 51 | Seen equipped with Mistral surface-to-air missile launchers.[376] | ||
| Volkswagen Amarok |  |
Pickup truck | 30+ | 30 armoured versions donated by Germany.[209] | ||
| Isuzu D-Max | 
|
Pickup truck | ? | Used as technicals.[377] | ||
| Mitsubishi L200 |  |
Pickup truck | ? | Used as technicals.[378] | ||
| Nissan Navara | 
|
Pickup truck | 50 | Pickups equipped with 12.7-mm DShK heavy machine gun and Mk19 grenade launchers.[379] | ||
| Toyota Land Cruiser J76 | 
|
Wagon | J76 | 43 | Provided by the United States in 2017.[380] | |
| Toyota Land Cruiser 70 series |  |
Multi-purpose vehicle | 43+ | Used by special forces.[381] | ||
| Toyota Mega Cruiser | 
|
100 | [382] | |||
| LV-Teh | All-terrain vehicle | 80[383] | Civilian all-terrain vehicles repurposed for the military.[384] | |||
| Tarpan Honker | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | Former Polish Army vehicles, donated by private donors in 2014.[385] | |||
| Santana Aníbal | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | 4+ | Donated by Spain.[49] | ||
| Ford Ranger | 
|
Pickup truck | ? | Seen equipped with armoured plates for extra protection.[377] | ||
| Ford Raptor | 
|
Pickup truck | Unknown | Seen modified into MLRS.[386] | ||
| Jeep Wrangler | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | 7 | Donated by Luxembourg in response to 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine[387] | ||
| Land Rover Defender | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | 55 | [388][389] | ||
| Peugeot P4 | 
|
Multi-purpose vehicle | ? | Delivered by France.[98] | ||
| Vityaz ATV | 
|
tracked articulated vehicle | Vityaz DT-30 | 2 | Two captured from Russian forces.[179] | |
| PTS-2 | 
|
Tracked Amphibious vehicle | ~15 | [390] | ||
| M548 | 
|
Tracked Cargo vehicle | 51+ | Donated by Denmark.[168] |
Cargo vehicles
Tractor units
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAZ-537 | 
|
(Pull 50 tonnes) | N/A | [190] | ||
| KrAZ-6446 | 
|
(Pull 30 tonnes) | N/A | [190] | ||
| KrAZ-6510TE | 
|
(Pull 70 tonnes) | KrAZ-6510TE | 3 | Order placed in 2019. Three were delivered in 2022.[391] | |
| M1070 HET | 
|
15 | 13 donated from Germany.[19] 2 were bought by a charity organization and donated to the 43rd artillery brigade.[392] | |||
| HX81 Heavy Equipment and Tank Transporters | 
|
Heavy Equipment and Tank Transporters | 85[19] | Supplied by Germany.[19] |
Trucks
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ural-4320 | 
|
Medium | [393] | |||||
| ZiL-131 | 
|
Medium | [393] | |||||
| GAZ-66 | 
|
Medium (2 tonnes) | ~2,000 (2014)[394] | [393] | ||||
| KamAZ-5320 | 
|
Heavy (8 tonnes) | [393] | |||||
| KamAZ-4310 | 
|
Heavy (6 tonnes) | [393] | |||||
| KamAZ-43114 | 
|
Heavy (6 tonnes) | Purchased prior to the Russo-Ukrainian war.[393] | |||||
| KrAZ-257 | 
|
Heavy (12 tonnes) | [393] | |||||
| KrAZ-255 | 
|
Heavy (12 tonnes) | KrAZ-255B | [393] | ||||
| KrAZ-260 | 
|
Heavy | KrAZ-260 ATs-10-260 |
[393] | ||||
| KrAZ-6322 | 
|
Heavy | 87+[393] | |||||
| KrAZ-6510 | 
|
Heavy | Dump truck | 16+[393] | ||||
| KrAZ-5233 | 
|
Heavy (6 tonnes) | KrAZ-5233VE KrAZ-5233NE |
[393] | ||||
| MAZ-4371 | 
|
Medium | MAZ-4371N2 | Used by the UAF and National Guard.[393] | ||||
| MAZ-5316 | 
|
Heavy (7.5 tonnes) | Bogdan-5316 | 32[393] | Assembled locally.[393] | |||
| MAZ-6317 | 
|
Heavy (11 tonnes) | Bogdan-6317 | 320[265] | Assembled locally,[393] with Chinese engines.[265] | |||
| Tatra T815 | 
|
Heavy | Т815-7Т3RC1 | Used on various Ukrainian weapon systems.[393] | ||||
| GAZ-53 | 
|
Medium | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| GAZ-63 | 
|
Medium | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| GAZ-3308 | 
|
Medium (2.5 tonnes) | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| KrAZ-214 | 
|
Heavy | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| ZiL-130 | 
|
Medium | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| ZiL-157 | 
|
Medium | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| ZiL-4331 | 
|
Medium | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | |||||
| MAZ-500 | 
|
Heavy | MAZ-AC-8-500A MAZ-TZ-500 |
Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | ||||
| MAZ-5337 | 
|
Heavy | Tanker truck | Seen in use during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[190] | ||||
| Ural-63704-0010 Tornado-U | 
|
Heavy (16 tonnes) | 6[179] | Captured from Russian forces. At least 2 put into Ukrainian service.[395][396] | ||||
| Saurer 2DM | 
|
Medium (4.9 tonnes) | (4x4) | 1 | Seen during the 2022 Kharkiv counteroffensive.[397] | |||
| MAN KAT1 |  
|
Heavy (7 tonnes) |
6x6
8x8 |
6+ | Used for towing FH70 howitzers.[398] | |||
| MAN HX | 
|
15 tonnes | 8x8 | 80 | [19] | |||
| Unimog |   |
Medium (2.5 tonnes) |
4+ | All 4 machines are used as medevac and were bought by volunteers for the Army in late 2014.[399][400] Unknown number of Unimogs delivered by Germany in February 2023.[209] | ||||
| MAN TG | 
|
4x4 | 13 | Donated by the EU.[401] | ||||
| LKW 15t mil gl MULTI | 
|
15 tonnes | 34 | Supplied by Germany.[19] | ||||
| Zetros | 
|
224 | 26 pledged by Germany.[19] | |||||
| Iveco Trakker |  |
Heavy (9 tonnes) |
20+ | First Ivecos bought for engineering purposes with United States aid money.[402] Iveco dump trucks and aircraft refuelling trucks donated by Germany in February 2023.[209] | ||||
| Iveco ACM 90 | 
|
Medium (4 tonnes) |
4x4 | Donated by Italy.[84] Some units of Iveco ACL 90 delivered by Germany for the use as Border Protection Vehicles.[209] | ||||
| Iveco Astra SM 66.40 | 6x6 | unknown | Used for towing FH-70 155mm howitzers.[84] | |||||
| Iveco VM 90 | 
|
unknown | Unknown number of VM 90 delivered by Germany for use as Border Protection Vehicles.[209] | |||||
| MTV | 
|
|
Medium | 600+ | Used for towing and hauling equipment.[184] | |||
| Renault GBC 180 | 
|
Medium (5 tonnes) | 6x6 | Unknown | Delivered by France prior to October 2022.[98] | |||
| Renault TRM 2000 | 
|
Medium (2 tonnes) | 4x4 | Unknown | Delivered by France in August and September 2022.[98] Further units delivered by Germany for use as Border Protection Vehicles.[209] | |||
| Renault TRM 10000 | 
|
10 tonnes truck | 6x6 | Unknown | Seen towing TRF1 155mm howitzers and ammunition.[403] | |||
| Renault Trucks D | 
|
Medium | 90 | Off-road vehicles donated by the EU, are primarily used for humanitarian purposes in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[404] | ||||
| Ashok Leyland Stallion | 
|
1 | Bought commercially by Petro Poroshenko, together with 10 DAF Leyland T244 trucks, Nissan Pathfinder, UAVs. Ukrainian military received this donation in October 2022 [405] | |||||
| Leyland DAF | 
|
Medium (4 tonnes) | 10 | 10 military Leyland DAFs have been bought from old stocks of the British Army by the Fund of Ukrainian ex-president Poroshenko, and handed over to the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[406][better source needed] | ||||
| Foden 8x6 Carrier | 
|
20 | Ukrainian volunteers, with the support of the Petro Poroshenko Foundation, bought 20 Foden 8x6 Carrier trucks for the AFU, capable of transporting cargo weighing up to 18 tons.[407] | |||||
| DAF YA-4442 | 
|
4 tonnes truck | ~300 | Delivered by the Netherlands in November 2022.[43] | ||||
| DAF YAZ-2300 | 
|
10 tonnes truck | Unknown | Delivered by the Netherlands in November 2022.[43] | ||||
| DAF YA-328 | 
|
1 | One donated for use by Ukrainian Forces.[408] | |||||
| Volvo Fassi N10 | 
|
150 | 90 pledged by Belgium[39] | |||||
| Scania P92 | 
|
Unknown | Scania P92 Trucks With Crane donated by Norway.[409] | |||||
| Scania P113 | Scania P113 Trucks With Hook Lift donated by Norway.[409] | |||||||
| Star 266 |  
|
Medium | Star 266 Star 266M2 |
2+ | Donated by Poland.[31] | |||
| Jelcz P882 D53 | 
|
Medium | 1+ | Delivered by Poland.[31] |
Ammunition carriers
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9T452 | 
|
Wheeled | 9T452 | Ammo carrier for the BM-27 Uragan multiple rocket launcher.[190] | ||||
| 9T217 transloader | 
|
for 9K33 Osa [410] | ||||||
| TZM-T | 
|
Tracked | 5+ (?) | Reloader for the TOS-1. By 14 April 2022, four vehicles had been captured from Russian forces.[179] | ||||
| M 992 Field Artillery Ammunition Support Vehicle | 
|
|
Tracked | 30 | delivered by United States along the 18 M109s [168] |
Aircraft
Fixed-wing aircraft
| Aircraft | Image | Origin | Type | Variants | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat aircraft | ||||||
| General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon | 
|
Multirole fighter | F-16A/B
F-16AM /BM |
19+ (F-16 A /B)
42+ (F-16 AM/BM) |
To be transferred by Denmark, Norway, and the Netherlands.[168] Belgium has pledged an undisclosed number of aircraft to Ukraine from 2025 onwards.[411] | |
| Mikoyan MiG-29 | 
|
MiG-29MU1 MiG-29MU2 MiG-29AS MiG-29A/UB |
78 | 8 are used for conversion training.[412] 14 to be donated by Poland and 13 by Slovakia.[413][414][168] | ||
| Sukhoi Su-27 | 
|
Air superiority fighter | Su-27P1M | 32 | 6 are used for conversion training.[412] | |
| Sukhoi Su-25 | 
|
Close air support / Attack aircraft | Su-25M | 35 | 14 were purchased from Bulgaria by NATO member states and delivered to Ukraine and 4 by North Macedonia.[412][168] | |
| Sukhoi Su-24 | 
|
Interdictor | Su-24M | 14[412][415] | Reportedly equipped with decommissoned RAF Panavia Tornados pylons to fire Storm Shadow missiles.[416] | |
| Maritime patrol aircraft | ||||||
| Beriev Be-12 | 
|
Maritime patrol aircraft | 2[412] | |||
| Reconnaissance | ||||||
| Antonov An-30 | 
|
Reconnaissance aircraft | An-30B | 3[412] | ||
| Transport | ||||||
| Antonov An-26 | 
|
Transport | An-26B-100 An-26 Vita |
22 | [412] | |
| Antonov An-70 | 
|
Transport | 1 | [412] | ||
| Antonov An-72 | 
|
Transport | An-72B | 2+ | Used by the National Guard.[417] | |
| Antonov An-178 | 
|
Transport | (+3) | 3 on order.[412] | ||
| Ilyushin Il-76 | 
|
Airlift aircraft | Il-76MD | 7 | [412] | |
| Trainer aircraft | ||||||
| Aero L-39 Albatros | 
|
Jet trainer | 47[412] | |||
Helicopters
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBB Bo 105 | 
|
Utility | Bo 150 Bo 150E4 |
2 | 1 demilitarised unit donated by Oleksandr Hromyko in 2022.[418] In 2023 the Ministry of Defense adopted the Bo 150E4 into service.[374] | |
| PZL Mi-2 | 
|
Transport | Mi-2MSB Mi-2 |
10[412] 3 |
Upgraded to the Mi-2MSB standard.[419] 3 donated by Latvia and Slovakia.[168][420] | |
| Mil Mi-8 | 
|
Transport | Mi-8 Mi-9 Mi-8T Mi-8PS Mi-8MT Mi-8MTV-1 Mi-8MTV-1VA Mi-8AMTSh |
74[130] 17 Captured: 1 |
Lithuania, Croatia, and the United States donated Mi-8s in response to the Russian invasion.[168] In August 2023, a Russian defector handed over his Mi-8AMTSh helicopter to the Ukrainian forces.[421] | |
| Mil Mi-14 | 
|
Search and rescue / Anti-submarine warfare | 4 | Used by the Ukrainian Navy.[422] | ||
| Mil Mi-17 | 
|
Transport / Armed | 28 | Donated by Latvia, Slovakia, and the United States.[168] | ||
| Mil Mi-24 | 
|
Attack | Mi-24VP Mi-24V Mi-24P Mi-24K |
35+[130] | Donated by Poland, Czech Republic, and North Macedonia.[168] | |
| Airbus H225 | Transport | H225 | 12[135] | |||
| Kamov Ka-226 | 
|
Utility | 1 | Used by the Ukrainian Navy.[422] | ||
| Kamov Ka-32 | 
|
Transport | KA-32 A11BC | 6 | The Portuguese Ministrer of National Defence, Helena Carreiras, announced in October 2022, that Portugal will send to Ukraine six Kamov helicopters.[423] | |
| Westland Sea King | 
|
Anti-submarine warfare, search and rescue, and utility helicopter | Westland WS-61 Sea King | 3 | British licence-built version of the American Sikorsky S-61 Helicopter.Provided by the United Kingdom as military aid in November 2022.[424] | |
| UH-60 | 
|
UH-60A | 1 | One example spotted. It appears to be an ex-US Army helicopter refurbished and upgraded by Ace Aeronautics, LLC.[425][426] |
Air Armaments
| Name | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-to-Air Missiles | |||||||
| R-73 | 
|
Short-range | R-73E | Former Soviet Union stock,100 donated by Poland in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[31][427] | |||
| R-60 | 
|
Short-range | R-60MK | Former Soviet Union stock, Domestically upgraded version with UA-96 modification.[428] Also donated by North Macedonia.[429] | |||
| R-27 | 
|
Medium-range | R-27ET
R-27ER R-27R1 |
Former Soviet Union stock.[427] | |||
| Sungur IIR-guided MANPADS | Short-range | For Bayraktar TB2.[168] | |||||
| AIM-7 Sparrow | 
|
|
Medium range | 287 to be provided by Canada.[429] Unknown number supplied by the US.[275] | |||
| AIM-9 Sidewinder | 
|
Short range | 43 to be provided by Canada.[429] Unknown number supplied by the US.[275] | ||||
| AIM-120 AMRAAM | Medium range | UK donated AMRAAM in the wake of Russian missile attacks in October 2022.[430] The Pentagon ordered AMRAAM missiles worth $1.15 billion to supply Ukraine.[431] | |||||
| Anti-radiation missile | |||||||
| AGM-88 HARM | 
|
|
Anti-Radiation Missile | [427] | |||
| Air-to-surface missile | |||||||
| Kh-29 | 
|
KH-29T | [427] | ||||
| Kh-25 | 
|
KH-25ML
KH-25M |
[427] | ||||
| Cruise missile | |||||||
| Storm Shadow | 
|
Provided by the United Kingdom & France.[432] Used on modified Su-24 tactical bombers.[416] | |||||
| Guided Bombs | |||||||
| KAB-1500L | 
|
[433] | |||||
| KAB-500KR | 
|
[433] | |||||
| MAM-L | 
|
For Bayraktar TB2[168] | |||||
| MAM-C | 
|
For Bayraktar TB2[168] | |||||
| Joint Direct Attack Munition |
|
JDAMs to be provided in 2023 by the United States during the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[434][435] | |||||
| Unguided Bombs | |||||||
| OFAB-100-120 | 
|
[436] | |||||
| OFAB 250-270 | 
|
High explosive Fragmentation[437] | |||||
| FAB-250 | 
|
[436] | |||||
| FAB-500 | 
|
OFAB-500ShR | parachute retarded fragmentation bomb.[438] | ||||
| Unguided Rockets | |||||||
| Hydra 70 | 
|
|
70mm | More than 20,000 supplied by the United States.[184] | |||
| Zuni | 
|
|
127mm | More than 6,000 delivered by the United States.[184] | |||
| S-5 | 
|
57mm | Also used in a ground-ground MRLS role.[439] | ||||
| S-8 | 
|
80mm | [436] | ||||
| S-13 | 
|
122mm | B-13L | [440] | |||
| S-24 | 
|
240mm | S-24B | [440] | |||
| S-25 | 
|
266mm | S-25OF
S-25OFM |
[440] | |||
| Illumination Bombs | |||||||
| SAB-250-200 | 
|
[441] | |||||
| Decoy Armaments | |||||||
| ADM-160 MALD | 
|
|
Unknown amount delivered by an unknown country.[442] | ||||
Unmanned aerial vehicles and autonomous vehicles
Reconnaissance unmanned aerial vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leleka-100 |  |
Short range | Unknown | Used by Ukrainian soldiers, one of the main reconnaissance UAVs of Ukrainian army.[443] | |
| A-1-CM- Furia |  |
Unknown | Used by Ukrainian army, some were lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[444] | ||
| ASU-1 Valkyrja |  |
Unknown | Used by Ukrainian army, some were lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[444] | ||
| Orlik | Unknown | Used by Ukrainian army, some were lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[444] | |||
| UJ-22 Airborne[445] | Unknown | Possibly used in the 30 May 2023 Moscow drone strikes[446] | |||
| ITEC Skif | Unknown | Used by the Ukrainian army.[447] | |||
| Ukrspecsystems PD-1 |  |
Medium range | Unknown | Used by Ukrainian army, some have been lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[448][better source needed] | |
| Ukrspecsystems PD-2 | 
|
Unknown | VTOL variant used by the Ukrainian Ground Forces.[449] | ||
| Shark |  |
14+ | Used by Ukrainian army for directing artillery fire under electronic warfare conditions, some were lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[450][451] | ||
| Spectator-M1 |  |
Unknown | Used by Ukrainian army, some were lost during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. | ||
| Sych | Long range | 2 | As of July 2023 the Come Back Alive Foundation donated 2 Sychs to the Armed Forces of Ukraine.[452] | ||
| DJI Mini 2 | 
|
Short range | Hundreds | [453] | |
| DJI Mavic 3 | 
|
[454] | |||
| DJI Phantom 3 | 
|
[455] | |||
| AtlasPRO | Short range | 345 | The "Come Back Alive" foundation has purchased 100 sets of Atlas unmanned drones for the Ukrainian ground forces. It includes 300 drones, ground control stations, transponders and a set of spare parts. The Atlas team is working on the next delivery to Ukraine ordered by the foundation.[456][457] | ||
| Penguin C UAV Factory | 
|
Unknown | Used by the Ukrainian army.[447] | ||
| WB Electronics FlyEye | 
|
Short range | Donated by Poland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. 20 donated by a crowdfunding campaign.[31] | ||
| Tekever AR3 | Short range | Unknown | The British Ministry of Defence announced that International Fund for Ukraine will send some Tekever AR3 VTOL to Ukraine.[458][459] | ||
| Baykar Bayraktar Mini UAV | 
|
Short range | 24[240] | [460] | |
| Vector & Scorpion UAV | 
|
Short range | 138+[461] | In April, after the war began, drones were sold to Ukraine for reconnaissance purposes at 180,000 euros each.[462][463] | |
| AeroVironment RQ-11 Raven | 
|
Short range | 72 | The United States announced that it would make these drones available to Ukraine in 2015.[464] | |
| AeroVironment RQ-20 Puma | 
|
Unknown | Delivered by the US in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[184] | ||
| AeroVironment
Quantix Recon |
100+ | Donated by AeroVironment.[168] | |||
| Boeing Insitu ScanEagle | 
|
Medium range | 15+[168] | Donated by the US.[184] | |
| AeroVironment Jump 20 | Unknown | Dobated by the US.[184] | |||
| AREAI Altius-600 | Unknown | Donated by the US.[184] | |||
| Sky-Watch Heidrun | Short range | 25 | Donated by Denmark.[465][168] | ||
| Black Hornet Nano | 
|
Very short range | 850 | To be supplied by the United Kingdom and Norway.[466][467] | |
| Evolve 2 | Short range | 10 | VTOL drone donated by XDynamics.[468] | ||
| Bivoj | Short range | 3 | Crowdfunded by Czech citizens.[9] | ||
| Primoco One 150 | 
|
Medium range | 15 | Donated by Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Belgium.[168] |
Unmanned combat aerial vehicle
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baykar Bayraktar TB2 | 
|
Unmanned combat aerial vehicle | 37+ | Provided by Turkey in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[168][469] |
Improvised multirole unmanned aerial vehicles
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tupolev Tu-141 | 
|
Loitering munition/Unmanned combat aerial vehicle | ? | Modified to be used in a Kamikaze and Cruise missile role during the Russian invasion of Ukraine[470] | |
| Tupolev Tu-143 | 
|
? |
Loitering munitions
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DefendTex D40 | Loitering munition | 300 | To be delivered by Australia in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[168] | ||
| WB Electronics Warmate | 
|
Loitering munition | 203 | 150 donated by Poland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[135] 10 donated by the WB Group and 43 crowdfunded.[31] | |
| Phoenix Ghost | Loitering munition | 1,800 | 1,000 out of 1,800 donated by the US in 2022.[135] | ||
| AeroVironment Switchblade | 
|
Loitering munition | Switchblade 300: 100[168] Switchblade 600: 10[471] |
By 22 July 2022, the United States delivered over 700 systems.[161] | |
| RAM II | Loitering munition | [472] | |||
| Bober | Loitering munition | Long range loitering munition, possibly used in the 30 May 2023 Moscow drone strikes[446] |
Ordnance dropping drones
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revolver 860 | Ordnance dropping drone | 800[473] | Purchased by Poland and transferred to Ukraine.[474] | ||
| UA Dynamics Punisher | Ordnance dropping drone | Unknown | [475] |
Cargo drones
| Model | Image | Country of origin | Type | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malloy Aeronautics T150s | Cargo drone | ? | To be delivered in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[168] |
Uniforms
Camouflages
| Name | Photo | Country of origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM14 | 
|
Standard issue camouflage, adopted in 2016. The MM14 is a pixelated camouflage, inspired by NATO-style patterns, and was adopted as part of the broader modernization, Ukrainization, and decommunization process of the military.[476][477] | |
| Varan ZSU | 
|
The differential characteristic of "Varan" camouflage is its drawing which uses elements of three-dimensional net structure. This structure combined with the background gives a unique "effect of solubility".[478] | |
| DPM | 
|
British-surplus uniforms seen in use during the Rapid Trident 2015 exercise.[479] | |
| MTP | 
|
Mainly volunteers seen wearing MTP uniforms supplied by donations of British surplus.[480] Also donated to Ukraine by the United Kingdom[481] | |
| M81 Woodland | 
|
Known to be used by the Bohdan Company and Chernihiv Company. A local variant is made to resemble Croatian-made Woodland camos.[482] | |
| MARPAT | 
|
Used by regular Ukrainian Armed Forces[482] | |
| MultiCam | 
|
Standard issue camouflage for special forces. Widely issued to regular troops and volunteers[5] | |
| OCP | 
|
Used by regular Ukrainian Armed forces and reservists. Supplied by the United States Armed Forces from 2022 onwards[482] | |
| UCP | 
|
Used by regular Ukrainian Armed Forces (slightly different color palette), and some special units[483] | |
| Type II brown-dominant winter pattern [ja] | 
|
Donated by Japan in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[484] | |
| Camouflage Central Europe | 
|
Donated by France in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[485] |
Armor
| Name | Photo | Country of origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSh-68 | 
|
Used during the War in Donbas[486] | |
| Kaska-1M | 
|
One of the standard helmets, in widespread use. Produced domestically by TEMP3000[487] | |
| TOR, TOR-D, TOR-BT | 
|
One of the standard helmets, in widespread use. Produced domestically by UaRms[488] | |
| Gefechtshelm M92 | 
|
23,000 were donated by Germany to Ukraine in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Belgium donated an unknown number.[19] | |
| Combat Bullet-Proof Vest | 
|
Provided by Japan in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Mainly used by Territorial Defense Forces[489] | |
| Type 3 Bulletproof vest | 
|
Japanese Bulletproof Vest Type 3, provided by Japan in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Mainly used by Territorial Defense Forces[490] | |
| Type 88 helmet | 
|
Donated by Japan[491] | |
| Hełm wz. 2005 | 
|
42,000 were donated to Ukraine by Poland in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[31] | |
| Hjälm 90 | 
|
5,000 were donated by Sweden to Ukraine in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[492] | |
| Kroppsskydd 12 Combat Vest | 5054 were donated by Sweden to Ukraine in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[86] | ||
| Mk 6 helmet | 
|
Some were supplied in 2014. Further helmet donations were made in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[493] | |
| Mk 7 helmet | 
|
Thousands were donated to Ukraine by the United Kingdom in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[493] | |
| Personnel Armor System for Ground Troops | 
|
Used by the Aidar and Donbas Battalions[494] | |
| FAST helmet | 
|
Used by Ukrainian Spetsnaz forces.[5] | |
| STRONG Helmet | 
|
Dutch-made version of the Modular Integrated Communications Helmet donated by he Netherlands[43] | |
| Hjelm Helmet | 5,000 helmets donated by Norway in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[495] | ||
| CG634 Helmet | 
|
Donated by Canada in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[15] | |
| Gevechtshelm Composiet M95 Helmets | 3,000 donated by the Netherlands in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[43] |
Hazmat equipment
| Name | Photo | Country of origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 18 Hazmat Suit | 
|
Donated by Japan in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[484] | |
| AlphaTec Chemical Protective Suits | Donated by Sweden in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[496] | ||
| Avon Protection C-50 Gas Mask | 
|
Donated by Luxembourg in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[497] | |
| Mobile decontamination vehicles HEP 70 including decontamination material | Donated by Germany[19] | ||
| ARS-14 decontamination and degassing vehicle | 
|
[190] |
Night vision
| Name | Photo | Country of origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVS-14 | 
|
Given by the United States in 2018.[498] More donated by Luxembourg in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine[497] | |
| PVS-31 | 
|
Donated by the United States[499] | |
| Thales OB70 Lucie | 
|
Donated by France[342] |
See also
Current War:
- List of military aid to Ukraine during the Russo-Ukrainian War
- List of Russo-Ukrainian War military equipment
References
- ^ a b c "Чим воює Україна. Арсенал АТО". espreso.tv (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ^ Jarosh, Gregory; Tsarenok, O.O.; Beh, S.M. (13 March 2022). "Ukraine's Department of Military Training turns 95". CONTACT magazine. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g Galeotti 2019, p. 47.
- ^ a b c "wiw_eu_ukraine - worldinventory". 3 June 2016. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Trevithick, Joseph (8 June 2017). "Ukrainian Spetnaz's Weapons and Gear May Show an American Touch". The Drive. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ Thompson 2022, pp. 30−31.
- ^ Nechet, Tatiana. "Жене министра информполитики Стеця дали наградной пистолет и 8 патронов". KP.UA (in Russian). Archived from the original on 11 January 2019. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ^ "Buy CZ 75 pistol". www.weaponstoukraine.com (in Czech). Archived from the original on 13 February 2023. Retrieved 23 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Bohemian Brotherhood: List Of Czech Weapons Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx.
- ^ Galeotti 2019, p. 60.
- ^ a b "Журнал для спецназа "Братишка" - Профессионалы: Украинская "Альфа": терроризм не пройдет". 23 September 2015. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ "И в бою, и на охоте, и по банкам пострелять: чем оружейники порадовали украинскую публику..." [And in battle, and hunting, and shooting at riverbanks: how did the gunsmiths please the Ukrainian public?]. www.unian.net (in Russian). Archived from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ "Guns Seen in Ukraine War". 5D Tactical. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Vast Arsenal of Ukrainian Special Forces: Guns From All Around the World". Defense Express. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost (12 September 2022). "Enabling Victory: Canadian Military Support To Ukraine". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 12 April 2023.
- ^ 🇺🇦 Ukraine Weapons Tracker [@UAWeapons] (6 June 2022). "#Ukraine: A collection of a few of the weapons currently used by Ukrainian army: FN F2000 Tactical and M4A1 assault rifles + Beretta M9 and Glock 19 Gen 5, donated by allies. Classic Soviet Tokarev and Stechkin APS pistols + a modded AKS-74U are also seen. t.co/yCJU6YJatd" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 9 July 2022. Retrieved 5 August 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Kimber Rushes R7 Makos, Rifles to Ukraine". Guns.com. Archived from the original on 14 May 2023.
- ^ War Noir [@war_noir] (1 June 2022). "#Russia #Ukraine 🇷🇺🇺🇦: A brand-new 9x19mm Sig Sauer "P320-M18" pistol recently obtained by a #Ukrainian combatant along with 3 spare magazines. It seems to be a part of military aids by #USA 🇺🇸" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 18 August 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai "Military support for Ukraine | Federal Government". Website of the Federal Government | Bundesregierung. 13 October 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ "Рекомендовано до друку рішенням ученої ради Національної академії Державної прикордонної служби України від 28.01.2019, протокол № 7" [Recommended for publication by the decision of the Academic Council of the National Academy of the State Border Service of Ukraine dated January 28, 2019, protocol No. 7]. Збірник наукових праць Національної академії Державної прикордонної служби України. Серія: Педагогічні Науки [Collection of scientific works of the National Academy of the State Border Guard Service of Ukraine. Series: Pedagogical Sciences] (in Ukrainian). Національна академія Державної прикордонної служби України [National Academy of the State Border Guard Service of Ukraine]. 16 (1). 2019. doi:10.32453/pedzbirnyk.v16i1. ISSN 2617-8230. Archived from the original on 9 March 2022.
- ^ Newsnpr (7 February 2022). "Western arms shipments to Ukraine". Newsnpr. Archived from the original on 17 October 2022. Retrieved 17 June 2022.
- ^ Pike, Travis (12 October 2023). "These Weapons Made Ukraine's Foreign Legion a Nightmare for Russia". The National Interest. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ Pike, Travis. "Saiga 12: The Russian 12-Gauge Man Stopper". SOFREP. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ a b c "Savage Arms Rifles in Ukraine". The Armourers Bench. 17 April 2022. Archived from the original on 15 February 2023. Retrieved 9 July 2022.
- ^ Moss, Matthew (11 March 2022). "Adams Arms Shipping Carbines To Ukraine". The Firearm Blog. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ "Adams Arms Shipping Rifle P1 5.56 16" 5.56mm NATO Tactical AR-15 Carbines to Ukraine". DefenseReview.com (DR): An online tactical technology and military defense technology magazine with particular focus on the latest and greatest tactical firearms news (tactical gun news), tactical gear news and tactical shooting news. Archived from the original on 6 April 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ Goodman, Joshua (18 March 2022). "American gunmakers help Ukrainians fight back against Putin". AP News. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, pp. 30−31.
- ^ Galeotti 2019, p. 53.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 24.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t "The Kielbasa Connection: Polish Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 30.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (11 March 2022). "Ukraine's Indigenous "Malyuk" Bullpup Rifle Is The Weapon Of Choice For Its Special Operators". The Drive. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Special Forces Equip With Advanced UAR-15 Rifle Models". Militarnyi. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian forces using Serbian weapons". N1. 15 March 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2022.
- ^ "Britain purchased Zastava M70 assault rifles for Ukrainian soldiers training". Archived from the original on 18 November 2022. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ a b c "The Involuntary Ally: Iranian Arms in Ukraine". www.oryxspioenkop.com. Oryx. 3 September 2022. Archived from the original on 14 October 2022.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (14 February 2023). "Seized Iranian Weapons Could Go To Ukraine: Report". The Drive. Retrieved 9 November 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "A Show Of Shame - Belgian Weapons Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx.
- ^ Helfrich, Emma (23 May 2022). "Futuristic Belgian F2000 Rifles Have Been Spotted In Ukrainian Hands". The Drive. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ^ "MSBS Grot w rękach żołnierzy ukraińskich". defence24.pl (in Polish). 11 May 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ a b Parken, Oliver (8 March 2022). "Captured Russian AK-12 Rifles Appear To Be The Trophy Guns Of Choice For Ukrainians". The Drive. Archived from the original on 3 June 2023. Retrieved 24 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Going Dutch Revisited: Dutch Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. 9 September 2022.
- ^ "Dutch C7s in Ukraine: Inside the Dutch Effort to Arm Ukraine". youtube.com. The Armourer's Bench. 30 April 2022. Archived from the original on 21 May 2023. Retrieved 7 June 2023.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ a b c "More interesting guns being used in Ukraine". Battle Born Review. 30 March 2022. Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ "M16A4s in Ukraine". The Armourer's Bench. 29 January 2023. Archived from the original on 22 May 2023.
- ^ a b "SALW Guide: Ukraine Country Report" (PDF). BICC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2022.
- ^ Wetz, Andreas (22 May 2022). "Austro-Waffen für Russland und die Ukraine". news.at (in German). Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Oryx. "Guns N' Gazpacho: Spanish Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ Bostock, Ian (August 2023). "Thales supplies ACAR weapons to Ukraine" (PDF). Defence Technology Review. No. 100. p. 16. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ Richard Jones; Leland S. Ness (2009). Jane's infantry weapons, 2009-2010 2009/2010 (35th ed.). Coulsdon: Jane's Information Group. ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5. OCLC 769660119.
- ^ a b c d Oryx. "Leopards From Lisbon: Portuguese Arms Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian military received FN FAL PARA rifles". Militarnyi. Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ^ miroslav-trinko. "Die ukrainischen Soldaten begannen, automatische FN FAL-Gewehre zu verwenden, eine der bekanntesten und am weitesten verbreiteten Waffen der Welt". gagadget.com (in German). Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Janovsky, Jakub; naalsio26; Aloha; Dan; Kemal. "Tallinn's Tally: Estonia's Weapons Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h Galeotti 2019, p. 48.
- ^ "Stiletto Systems Debuts New Ukrainian Sniper Rifle - STL-016 -". The Firearm Blog. 26 October 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2022.
- ^ "Get to Know the Small Arms of the Ukrainian Army: Part Two". 16 June 2022.
- ^ "VPR-308: Повна інформація". www.ngu.com.ua. Retrieved 17 June 2022.
- ^ Galeotti 2019, p. 58.
- ^ "Ukrainian copies of Swiss Brügger & Thomet APR rifles used during protests in Kiev - Armament Research Services (ARES)". armamentresearch.com. 24 February 2014. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Pickrell, Ryan. "Ukrainian snipers say they don't care for big leafy ghillie suits, but they're fans of these Western rifles". Business Insider. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ TAB (19 March 2023). "M110 in Ukraine". The Armourers Bench. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ "Timeline". deserttech.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ a b Plaster, John L. (5 July 2022). "Sniping In Ukraine". American Rifleman. National Rifle Association. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ "Kimber America | Kimber America | Kimber Press Releases".
- ^ Eastwood, Brent M. (24 March 2022). "We Think We Know Why Russia's Generals Keep Getting Killed in Ukraine". 19FortyFive. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ a b "Ukraine to receive ex-Dutch sniper rifles". www.shephardmedia.com. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ "Get to Know the Small Arms of the Ukrainian Army: Part Two". 14 May 2022.
- ^ "Rusové vypadají pořád opile, popisuje český velitel, jenž bojuje na Donbasu - Seznam Zprávy". www.seznamzpravy.cz.
- ^ Cᴀʟɪʙʀᴇ Oʙsᴄᴜʀᴀ [@CalibreObscura] (8 April 2023). "#Ukraine: Rarities with the 93rd Brigade; original IMI Uzi submachine guns. Judging by the markings, these are export guns subsequently sent to the AFU by a European country" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 9 April 2023. Retrieved 8 April 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Uzis in Ukraine". youtube.com. The Armourer's Bench. 14 March 2023. Archived from the original on 6 June 2023. Retrieved 7 June 2023.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Cᴀʟɪʙʀᴇ Oʙsᴄᴜʀᴀ [@CalibreObscura] (26 December 2022). "#Russia: In a very rarely seen incident, a Ukrainian SSO/Sabotage team was found & killed by Russian security forces in #Bryansk Oblast. Note Sig MPX (In an interesting config) & M112 block demolition charges. Gives a glimpse of what teams carrying out this very risky work use. t.co/jF0aJZhIM7" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 27 December 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Plokšto & Demeško 2017, pp. 65–66.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (5 February 2020). "Ukrainian Troops Are Still Using This Pre-World War I-Era Maxim Machine Gun In Combat". The Drive. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ Gault, Matthew (21 March 2023). "Ukraine Is Successfully Using a 140-Year-Old Machine Gun Against Russia". Vice. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d Plokšto & Demeško 2017, p. 65.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 34.
- ^ "Ukrainian Brigades Receive Bulgarian MG-1M Machine Guns with Donors' Help". Militarnyi. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ a b "UNROCA (United Nations Register of Conventional Arms)". www.unroca.org. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b Fiorenza, Nicholas. "IDET 2023: Excalibur Army Viktor light air-defence vehicles supplied to Ukraine". Janes.com. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Modified DSHK with Buttstock, Picatinny Rail, and Bipod in Ground Role -". 19 December 2017.
- ^ "Ukraine received Romanian DShKM". 9 December 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Oryx. "Guns Not Gnocchi: Italian Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- ^ "https://twitter.com/war_noir/status/1714233195271467331?s=20". X (formerly Twitter). Retrieved 17 October 2023.
{cite web}: External link in|title= - ^ a b c d e f g Oryx. "No Assembly Required: Swedish Arms Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 30 September 2023.
- ^ French VAB APC's are in Ukraine and seen armed with AA 52 7 62x51mm machine guns. Ukraine Military Power. 29 July 2022. Archived from the original on 10 November 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b c Moss, Matthew (11 July 2023). "How a Ukrainian Furniture Company Started Producing Ammo Belt Boxes for Ground Troops". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "España enviará 1.370 lanzagranadas y 700.000 cartuchos de fusiles y ametralladoras a Ucrania". 2 March 2022. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Las armas que envía España a Ucrania, de bajo calibre y nada de misiles tierra-aire". 4 March 2022. Archived from the original on 17 October 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Roblin, Sébastien (23 February 2023). "The Witch of Ukraine Reveals How 'Teeny-Weeny' American Weapons Are Beating Russians". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ Soylu, Ragip. "Turkey supplies Ukraine with hundreds of heavy machine guns". Middle East Eye. Istanbul. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "The Ukrainian Armed Forces use the legendary American M18 smoke grenades".
- ^ a b c d e f g Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost (5 September 2022). "Joining NATO, Joining The Cause: Finnish Aid To Ukraine". Oryx Blog.
- ^ a b c d e f "Military showed Western handgrenades collection". Militarnyi. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 50.
- ^ War Noir [@war_noir] (5 April 2022). "#Russia #Ukraine 🇷🇺🇺🇦: Daniil Dashuk from #Belarus 🇧🇾 (ex-#Tornado Battalion member) released a new video. He can be seen with an AK-74 rifle (equipped with a GP-25 UBGL), #British HE L109 A2 hand grenade and two 9M133F "Kornet" Thermobaric ATGMs —captured from #Russian Troops. t.co/ZrxlFVmqoM" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 21 August 2022. Retrieved 29 September 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ a b c d e "Arms For Ukraine: French Weapons Deliveries To Kyiv". Oryx. 13 July 2022.
- ^ Oryx. "Ukraine's Armsbasket: How Bulgaria Arms Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian forces showed their night-time UAV attacks on the occupational forces positions". Militarnyi. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ "How Ukraine Uses Obsolete Soviet Grenades To Destroy Russian Tanks From Above". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 5 May 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 46.
- ^ "Ukraine's Standalone Stock for GP-25 Grenade Launcher" (video). youtube.com. The Armourer's Bench. 5 March 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian UAG-40 automatic grenade launcher - Armament Research Services (ARES)". 12 August 2019.
- ^ "Ukraine presents light grenade launcher for special forces in Donbas".
- ^ "Десантникам передали сотні нових гранатометів Форт-600А". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 7 November 2023.
- ^ "M32A1 Revolving Grenade Launcher in the Hands of Ukrainian Soldiers". Defense Express. Archived from the original on 27 October 2022. Retrieved 25 July 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 26.
- ^ "Ukrainian Defense Industry in the "Hybrid War" with Russia. Part 2". Borysfen Intel. 15 November 2014. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "The Weird + Wonderful Firearms of Ukraine: Bullpups, Anti-Tank Rifles, More Bullpups & AR-15s -". The Firearm Blog. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ^ "Вітчизняні снайперські гвинтівки презентують іноземним замовникам". armyinform.com.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ Lemberg, Radio. "Canadian Sniper Rifles to Ukraine for the Fight Against Russia' Invasion". radiolemberg.com (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 17 April 2022.
- ^ "Canada will supply Ukraine sniper rifle". weaponews.com. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ "DESERT TECH - Tomorrow's Weapons". deserttech.com. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ Noir, War. "Weaponry of the Georgian Combatants in Ukraine's Territorial Defence Forces Following the Invasion". www.militantwire.com. Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ "Вітчизняні снайперські гвинтівки презентують іноземним замовникам". armyinform.com.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ McCardle, Guy (14 May 2022). "Get To Know the Small Arms of the Ukrainian Army: Part Two". SOFREP. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ "Військові взяли на озброєння українську великокаліберну гвинтівку "Алігатор"". Українська правда.
- ^ "Operators of the Special Operations Forces master Ukrainian Snipex T-REX anti-materiel rifles". Militarnyi. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ "The Sniper Weapon Systems of Russian Forces in Syria". The Hoplite. Armament Research Services (ARES). 6 August 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian paratroopers equipped with SPG-9 are destroying the equipment and trenches of Russian infantry". Militarnyi. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ "Bangalore torpedoes have been handed over to the military to fight barriers". Militarnyi. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ^ a b c d Plokšto & Demeško 2017, p. 67.
- ^ a b "Sammler: Infanteristische Panzerabwehrmittel im Ukraine-Krieg". soldat-und-technik.de (in German). 14 March 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ "Greece disclosed the amount and types of weapons handed over to Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Військові України отримали російсько-йорданські РПГ-32 "Nashshab"". mil.in.ua (in Ukrainian). 17 August 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ "Small Country, Great Deeds: North Macedonia's Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 23 June 2023.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (26 January 2022). "Here's What Those 'Bunker-Defeat' Rockets The U.S. Sent To Ukraine Are Actually Capable Of". The Drive. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ Helfrich, Emma (7 July 2022). "Ukrainian Missile Teams Are Using Old School Motorcycles with Sidecars". The Drive.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz IISS 2022.
- ^ "Українська ракета Р-2С завершила сертифікацію за стандартами НАТО". 14 December 2015. Archived from the original on 15 January 2019. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- ^ ""Комбат", але не "батяня"..." 6 March 2017. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017.
- ^ "DKKB Luch to Unveil its Stugna-P ATGM Upgrade in 2021 | Defense Express". en.defence-ua.com. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "One Ukrainian ATGM operation destroyed two Russian armored vehicles". Militarnyi. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj "Trade Registers". Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ U.S. Department of Defense 2023, p. 3.
- ^ Powis, Gaétan (10 November 2023). "Confirmation : la France a livré des missiles antichars dernière génération Akeron à l'Ukraine". Air et Cosmos (in French). Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ "Вогнеметники ЗСУ відстріляли з РПВ-16". Militarniy. 30 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ "Ukrainian army gets several hundred new flamethrowers". Ukrinform. 5 November 2020. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ "Air defense systems are being sent to Ukraine -CNN".
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 52.
- ^ "The West Needs to Keep Supporting Ukraine with MANPADS". GMFUS. Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ Romanenko, Valentyna. "National Guards tell how they destroyed Russian helicopter with Igla MANPADS". Ukrainska Pravda. Retrieved 2 September 2023.
- ^ "Norway provides an air defense system to Ukraine". Norwegian Ministry of Defense. 20 April 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ^ "Has Ukraine used British missile the UK Armed Forces has only just accessed?". Forces Network. 13 April 2022. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ "Fact Sheet on U.S. Security Assistance to Ukraine" (PDF). Retrieved 10 November 2022.
- ^ a b "Ukraine boosts mortar capability with four new systems". Janes.com. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- ^ "MILITARY SUPPORT TO UKRAINE - Portugal" (PDF).
- ^ "Батальон "Феникс" вооружили минометами 1943-го года выпуска". www.unian.net (in Russian). Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ "Latest from the OSCE Special Monitoring Mission to Ukraine (SMM), based on information received as of 19:30, 15 April 2019". osce.org (Press release). Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Vladyslav Belbas: "We are currently more than just a manufacturer of armored vehicles" | Defense Express". en.defence-ua.com. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Військові сил оборони України отримали міномети M69A калібру 82 мм". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ "Українські артилеристи отримали азербайджанські міномети "20N5"". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Armor Company delivers 600 mortars since the beginning of the invasion". Militarnyi. Retrieved 2 September 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine intends to buy Bulgarian mortars". KyivPost. Interfax-Ukraine. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ a b c d IISS 2023, p. 202.
- ^ "Україна отримала міномети MO-120-RT61". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ a b c d "The Ukrainian military neutralized a mine corridor in the Kharkiv region". Militarnyi. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- ^ Panella, Chris. "Photo captures Ukrainian troops using grunt robots to plant deadly anti-personnel mines". Business Insider. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ "Landmine Use in Ukraine". Human Rights Watch. 13 June 2023. Retrieved 29 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Fact Sheet on U.S. Security Assistance to Ukraine" (PDF). US Department of Defense. 22 July 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ^ a b Plokšto & Demeško 2017, p. 79.
- ^ "Deutschland liefert offenbar auch kaum leichte Waffen". n-tv.de (in German). Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Germany sends Ukraine more weapons". 17 May 2022. Archived from the original on 7 December 2022.
- ^ "Deutschland liefert Panzerabwehrrichtminen in die Ukraine". soldat-und-technik.de. 26 April 2022.
- ^ "Fact Sheet on U.S. Security Assistance to Ukraine" (PDF). 28 October 2022. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2023.
- ^ "French HPD2A2 Mines in Ukraine". The Armourer's Bench. 7 November 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg "Answering The Call: Heavy Weaponry Supplied To Ukraine". Oryx. Archived from the original on 8 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s IISS 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine's Territorials Need Tanks. They're Getting Them ... From Russia". Forbes. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ Boffey, Daniel (3 February 2023). "The Ukraine repair shop: where Russian tanks go to change sides". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian volunteers transform T-62 tanks into heavy infantry fighting vehicles". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian T-64s will be repaired in the Czech Republic". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine's Military Told How They Have Been Beating the Occupiers With the Trophy T-72B3 For Eight Months". Defense Express. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "A Ukrainian Officer's Captured Russian Tank Wasn't Working. So He Called Tech Support—In Russia". Forbes. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Soldiers of the 93rd Mechanized Brigade told about their trophy T-80BVM Tank". Militarnyi. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ Loginov, Yegor (14 July 2022). "Ukrainian Soldiers Test-Drive Prized T-80 Trophy Tank". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Russia's T-80UK Failed Tank Biathlon, Now a Trophy For the Armed Forces of Ukraine (Tank Specification)". Defense Express. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Janovsky, Jakub; naalsio26; Aloha; Dan; Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost; Kemal. "Attack On Europe: Documenting Russian Equipment Losses During The Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "The USA sent the trophy T-90A tank to the training ground". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ Epstein, Jake. "Retreating Russian troops are arming Ukraine with modern T-90 tanks as Putin's army digs 60-year-old armor out of storage, Ukraine's military says". Business Insider. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Danmark donerer Leopard 2-kampvogne til Ukraine". 21 April 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine's M-1 Abrams Tanks Are 'Situational Awareness' Models: Not The Best M-1s, But Available In Large Numbers". Forbes. Retrieved 27 November 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m U.S. Department of Defense 2023, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ukrainian troops use self-propelled anti-tank guns in the battles for Bakhmut". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Спецпризначенці отримали БРДМ-2 з модулем "Амулет"". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Миколаївський бронетанковий завод відновив та модернізував для ЗСУ декілька десятків БРДМ-2". Ukrainian Military Pages. 20 September 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "Миколаївський бронетанковий завод модернізував 50 БРДМ". Ukrainian Military Pages. 8 September 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ Oryx. "Attrition In Action: List Of Ukrainian Army Equipment Not Yet Destroyed By Russia". Oryx. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av "Attack On Europe: Documenting Ukrainian Equipment Losses During The 2022 Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian servicemen showcased a trophy: Russian BMP with full ammo". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Air Assault Forces armed with captured BMP "Basurmanin"". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ a b "ČR chce na Ukrajinu posílat víc modernizovaných tanků T-72".
- ^ "Belarusian volunteers are armed with BMP-2". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Ukrainian marines put trophy Russian vehicles to use in Donetsk Region". Militarnyi. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ Yann. "Defending Kyiv Region: Interview with Omega Special Unit Operator". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine and Sweden to jointly produce 1,000 CV-90 fighting vehicles". Ukrainska Pravda. Retrieved 26 September 2023.
- ^ Tangalakis-Lippert, Katherine. "Zelenskyy says Ukraine is working with Sweden to produce 'cool vehicles' like CV90s: 'Just what is needed at the front'". Business Insider. Retrieved 26 September 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian military captured Russians BMD-2 in Kherson Region". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ "Volunteers restored the captured BTR-MD "Rakushka" for Ukrainian paratroopers". Militarnyi. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Petro Poroshenko bought CVR (T)-family armored vehicles in Britain". Militarnyi. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ "FV430 Bulldog APC to be part of new UK military aid package for Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (16 January 2023). "Meet The Tanks And Other Armor The U.K. Is Sending To Ukraine". The Drive. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine's Ex-Bulgarian BTR-60 Personnel Carriers Wouldn't Last Long On The Front Line". Forbes. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ "Special Operations Forces captured trophy APCs and the Msta-B howitzer". Militarnyi. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ a b c IISS 2023, p. 204.
- ^ "Пластуни придбали БТР OT-64 SKOT для ТрО". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine May Have Secretly Acquired Valuk Armored Personnel Carriers from Slovenia". Militarnyi. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost. "Fact Sheet On German Military Aid To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "Rheinmetall". Rheinmetall. Retrieved 30 September 2023.
- ^ a b IISS 2023, pp. 202−204.
- ^ "ЗСУ отримали кілька десятків бронеавтомобілів «Козак-2". 12 December 2020.
- ^ IISS 2023, pp. 203−204.
- ^ a b Bogdan Motors: new projects for the army | Defense Express (defence-ua.com)
- ^ "Армія отримала одразу 40 новітніх бронеавтомобілів "Новатор" від "Української бронетехніки"". 15 November 2019.
- ^ "Soldiers of the Armed Forces of Ukraine order a rare "Ovid" armored vehicle at the front (photo)". Defense Express.
- ^ "How Essex man's military Land Rover will help the battle for Ukraine". Echo. 17 April 2022. Retrieved 11 May 2022.
- ^ "Ukrainian military get medical vehicles from Latvian government". ukrinform.net. 25 February 2021. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ^ "Antique Ferret Armored Car Shows Up In Ukraine". www.thedrive.com/the-war-zone. 17 August 2022. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ Cardy, Phil (19 September 2015). "If you fancy buying a second-hand tank, check out this used-car lot". mirror.
- ^ "Бронетранспортер Saxon AT105: служба в ЗСУ". Ukrainian Military Pages (in Ukrainian). 16 March 2015. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ Oryx. "Attack On Europe: Documenting Ukrainian Equipment Losses During The 2022 Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 8 March 2023.
- ^ a b c Adams, Harry (13 April 2022). "What armoured vehicles is the UK sending to Ukraine?". Forces Network. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Trinko, Myroslav. "Come Back Alive bought armored LC-79 APC-SH Fighter-2 vehicles based on the Toyota Land Cruiser 79 for 2,332,000 euros for the AFU". gagadget.com. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ Petrenko, Roman. "Trophy Russian Tigr is on patrol in Kharkiv". Ukrainska Pravda. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Armed Forces received Turkish-made Kirpi armored vehicles". Militarnyi. 9 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine obtained BATT UMG armored vehicles, might purchase them on its own". Militarnyi. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ "Germany will send MRAP to Ukraine instead of armored personnel carriers – BILD". Militarnyi. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ "Are Israel-made armored vehicles being used in Ukraine?". The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com. 12 November 2022. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ^ "Israeli-made Amir MRAP used by Ukrainian military seen in Kherson Region". Militarnyi. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ^ "Kariuomenė įsigijo šarvuotų visureigių už 15 mln. litų". DELFI.
- ^ "Lithuania handed over seven Toyota Land Cruiser 200 armored SUVs to Ukraine".
- ^ "Ukrainian forces field rare Russian light armored vehicle". defence-blog.com. 25 October 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ 𝕻𝖗𝖆𝖎𝖘𝖊 𝕿𝖍𝖊 𝕾𝖙𝖊𝖕𝖍 [@praisethesteph] (30 December 2022). "#Ukraine/#Russia 🇺🇦🇷🇺: 🇺🇦#Ukrainian BPM-97 (KamAZ-43269) Vystrel 4x4 APC captured from 🇷🇺#Russian forces t.co/ADHPItM2LK" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 15 January 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Trophy Typhoon-K KAMAZ-63968 was taken into service by the 93rd Mechanized Brigade". Militarnyi. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine captures one of Russia's most advanced multirole vehicle". defence-blog.com. 7 October 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ @naalsio26 (5 February 2023). "A rare GAZ-3937 'Vodnik' in operation by Ukrainian forces" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Neutral Switzerland finds out how its armoured vehicles ended up in Ukraine". Ukrainska Pravda. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ^ "Swiss investigate sighting of Swiss-built tank in Ukraine". SWI swissinfo.ch. 23 March 2023. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ^ a b Oryx. "The Stalwart Ally: Türkiye's Arms Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ Roblin, Sébastien (3 August 2023). "Hey, Ukraine: World War II Called. It Wants Its Guns Back". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ a b Plokšto & Demeško 2017, p. 77.
- ^ "Ukrainian Armed Forces have been armed with BS-3 field guns". Militarnyi. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (7 February 2022). "Ukraine Rolls Out Soviet-Era Radar-Equipped Anti-Tank Guns". The Drive. Retrieved 18 June 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine's Kraken Unit Uses the MT-LB Mounted With the 100mm MT-12 Rapira Anti-Tank Gun (Video)". Defense Express. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Captured Nona mortars received American rounds". Militarnyi. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "The Biggest Mortars In Ukraine Are Slow, Devastating Siege Weapons". Forbes. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "120-мм автоматизований мобільний мінометний комплекс UKR-MMC від ДП "Укроборонсервіс"". 29 October 2017. Retrieved 22 March 2022.
- ^ Santos@aldesantos, Ángel Luis de (27 January 2022). "Guerra Rusia-Ucrania: Así es el Alakran, el sistema de mortero español que Ucrania desplegaría ante un ataque ruso". La Razón.
- ^ "Lithuania sends armored vehicles, ammunition to Ukraine". Kyiv Independent. 14 November 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2022.
- ^ Oryx. "Answering The Call: Heavy Weaponry Supplied To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ "Українські артилеристи показали гаубиці M119A3". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ "Fact Sheet on U.S. Security Assistance to Ukraine" (PDF). Retrieved 6 January 2023.
- ^ "Leopards From Lisbon: Portuguese Arms Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. 9 June 2023. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "BAE Systems to produce L119 howitzers in Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 31 August 2023.
- ^ "Government of the Republic of Croatia - Croatia sending emergency aid to Ukraine".
- ^ "Croatia donates M-46 field guns to Ukraine | Shephard". www.shephardmedia.com.
- ^ Syngaivska, Sofiia. "The Ukrainian Military Successfully Deploys Trophy D-20 Gun-Howitzer Against Russian Forces". Defense Express. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine receives Romanian М1981 howitzers". mil.in.ua. 16 May 2023.
- ^ "The Czech Republic to Send 2S1 Gvozdika Self-Propelled Guns to Ukraine". Defense Express. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ "In the Donetsk region, the Armed Forces of Ukraine hit the Russian invaders with the trophy Giatsint-S self-propelled guns". Militarnyi. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Airborne Brigade soldiers use captured Russian Msta-S ACS". Militarnyi. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrajina nakoupí 26 českých samohybných houfnic DANA". armadninoviny.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ "Vojenská pomoc Ukrajině - Na Ukrajinu odjely i houfnice Dana a raketomety RM-70 Grad" [Czech military aid to Ukraine - Dana howitzers and RM-70 Grad rocket launchers also left for Ukraine] (in Czech). echo24.cz. 14 April 2022.
- ^ a b c Roblin, Sébastien (13 July 2023). "It Took Forever, but Ukraine Is Finally Fielding Western-Caliber Howitzers". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ "2S22 Bohdana self-propelled guns moved to Tatra chassis". Militarnyi. Retrieved 23 July 2023.
- ^ "La France va envoyer des véhicules de transport blindés en Ukraine". Le Point (in French). 28 June 2022. Retrieved 28 June 2022.
- ^ "Danmark donerer artilleri til Ukraine". Forsvarsministeriet (in Danish). Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ "Germany authorizes production of 100 howitzers for Ukraine". 27 July 2022. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ^ Altman, Howard (18 September 2023). "Ukraine Situation Report: M109 Paladins Are Proving Too Wily For Russian Gunners". The Drive. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine Finally Deploys Its Ex-Swedish Archer Howitzers. They're Some Of The Best Big Guns In The War". Forbes. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
- ^ Axe, David (17 April 2022). "Ukrainian Troops Reportedly Fired A Captured Russian Rocket Launcher ... Back At The Russians". Forbes.
- ^ "The Armed Forces of Ukraine use the trophy TOS-1". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "The Defense Forces of Ukraine used the trophy TOS-1A Solntsepyok - Militarnyi". mil.in.ua. Retrieved 9 July 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f U.S. Department of Defense 2023, p. 1.
- ^ "Turkey supplied laser-guided missiles to Ukraine". Middle East Eye. 23 November 2022. Retrieved 23 November 2022.
- ^ "OTR-21 Tochka (SS-21)". Missile Threat. Center for Strategic and International Studies. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Newdick, Thomas (17 October 2023). "ATACMS Hits Battlefield Ukraine In Spectacular Fashion (Updated)". The Drive. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ Newdick, Thomas (28 April 2022). "Brimstone Precision-Guided Missiles Are Headed To Ukraine Within Weeks". The Drive. Retrieved 18 June 2022.
- ^ "UK to send 600 Brimstone missiles to Ukraine - Defence minister". Reuters. 19 January 2023. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ Helfrich, Emma; Rogoway, Tyler (12 May 2022). "Truck-Mounted Brimstone Missile Launcher Emerges In Ukraine". The Drive. Retrieved 18 June 2022.
- ^ Ponomarenko, Illia (15 March 2021). "Ukraine's navy acquires first Neptune cruise missiles". kyivpost.com. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ Axe, David. "To Blow Up Russia's S-400 Battery In Crimea, Ukraine Tweaked Its Cruiser-Sinking Neptune Missile". Forbes. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Ukraine Blasts Russian Tug Near Snake Island With Land-Based Harpoon Missiles". Forbes. 17 June 2022. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ^ Axe, David. "All It Takes To Arm Ukraine's F-16s With Harpoon Anti-Ship Missiles Is One Small Electronic Box". Forbes. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ "Russia claimed for the first time that Ukraine used Hrim-2 TBM". Militarnyi. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ^ "New high-tech developments for Ukrainian armed forces". 7 October 2014. Archived from the original on 7 February 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Operational tactical missile system Korshun 2. Project of the cruise missile "Korshun" (Ukraine). Cruise missiles Neptune". coppershop.ru. Retrieved 3 April 2022.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 54.
- ^ "Poland continues to prepare arms for Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Desperate For Artillery, Ukraine And Russia Are Reactivating Guns From The 1940s And '50s". Forbes. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ Ministry of Defence; Shapps, Grant. "Major new package of support for Ukraine's counter-offensive announced by Grant Shapps". GOV.UK. Retrieved 12 October 2023.
- ^ "Marines use Shilka SPAAG to destroy ground targets". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Rheinmetall to supply Ukraine with Skynex after confirming Qatar delivery". Janes.com. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ "Italy-produced 'Swiss' weapons 'active in Ukraine'". SWI swissinfo.ch. 7 May 2023. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine's air defense fortified as Viktor system enters operational service". Militarnyi. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ Balmforth, Tom; Karazy, Sergiy (20 June 2023). MacSwan, Angus (ed.). "Ukraine builds layered air defences as Russia ramps up strikes". Reuters. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 70.
- ^ "Armed Forces of Ukraine showcased the operation of Ukrainian S-125 air defense systems". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (13 October 2023). "Ukraine Situation Report: 'FrankenSAM' To Speed Delivery Of Air Defenses". The Drive. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Roblin, Sébastien (30 August 2023). "The Three Fingers of Death Have Arrived in Ukraine". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 31 August 2023.
- ^ "Armed Forces of Ukraine showcase the use of the Hawk air defense system". Militarnyi. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine may have gotten long-range missiles for the NASAMS air defense system". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "SAMP/T SAM has been deployed in Ukraine - Macron". Militarnyi. Retrieved 25 August 2023.
- ^ "Україна остаточно відмовилася від ЗРК С-200 - Український мілітарний портал". 16 July 2014. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Newdick, Thomas (10 July 2023). "Is Ukraine Using Old S-200 SAMs In The Land-Attack Role?". The Drive. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine's Newest Deep-Strike Missile Is An Ex-Soviet Antique—With a Few Tweaks". Forbes. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ "What Characteristics Has Modernized P-18C Radar and How It Can Strengthen Ukraine's Air Defense". Defense Express. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Plokšto & Demeško 2017, p. 81.
- ^ a b c d Oryx. "Slovak Showdown: Slovak Arms Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 30 September 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian counter-battery warfare means". MENADEFENSE. 14 October 2020. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ Shulga, Oleg (20 August 2018). "The 24L1UK newest Ukrainian counterbalanced radar will show at the 220 parade in Kyiv this August". Archived from the original on 21 August 2018. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- ^ Cronk, Terri Moon. "U.S. Delivers Radar Systems to Ukraine". U.S. Department of Defense (Press release). Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "USA submitted radar complexes AN/TPQ-36 and AN/TPQ-49 to Ukraine". defence-blog.com. 2 July 2016.
- ^ "Improved Hawk Phase III SAM from Spain for Ukraine: Capabilities and Characteristics | Defense Express". en.defence-ua.com. Retrieved 27 September 2023.
- ^ "Thales виготовить для України РЛС GM200". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- ^ "Під SAMP/T Україна отримає дві РЛС GM200". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 68.
- ^ "Territorial defense forces of Ukraine equip captured armored vehicle with firepower". Militarnyi. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (30 March 2022). "One Of Russia's Newest Air Defense Systems Has Been Captured In Ukraine". The Drive. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost. "Baltic Biceps To The Rescue - Lithuanian Weapons Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Babu, Sunil JB; Williams, Huw. "Ukraine conflict: Ukraine's electronic warfare systems in focus". Janes.com. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "110 Lithuanian EDM4S anti-drone rifles for the Armed Forces • Mezha.Media". mezha.media. 13 June 2022. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- ^ "The Ukrainian Armed Forces seize Russian electronic warfare weapon system Borisoglebsk-2". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Cranny-Evans, Samuel. "Ukraine upgrades BTS-4 armoured recovery vehicle". Janes.com. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ "Zhytomyr Armoured Plant Has Given a Batch of Repaired BMP-2 and BREM-2 to the Armed Forces of Ukraine". Defense Intelligence of the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine. State sites of Ukraine. 4 November 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ "Unique Towing Vehicle Spotted in the Hands of Ukrainian Military (Photo)". Defense Express. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Armed Forces Uses Rare Brem-Ch Vehicle to Gather Trophies Left by Russians on Retreat". Defense Express. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "A Rare Czech Engineering Vehicle Has Showed Up On Both Sides Of The Ukraine War". Forbes. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "Captured #Russian repair and recovery vehicle REM-KL based on Ural-532362. Location: near #Sumy #Sumy region; Date: 01.03.2022". Twitter. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ А. Тарасенко. Бронетанковая техника Украины: итоги, потенциал, перспективы... // журнал "Техника и вооружение", No. 1, 2008. стр.44-48
- ^ "Latest from the OSCE Special Monitoring Mission to Ukraine (SMM), based on information received as of 19:30, 7 August 2019". www.osce.org. Kyiv. 8 August 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ Malyasov, Dylan. "UkrOboronProm receives Ukrainian Army order for 75 BTR-4 combat vehicles". Defence Blog. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ "Special equipment of the Armed Forces of Ukraine: GMC TopKick rescue vehicles - Спецтехніка в Україні". specmachinery.com.ua. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ "Defence Secretary oral statement on war in Ukraine". GOV.UK. 16 January 2023. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "The Collapsing Soviet Army Left Behind Dozens Of IMR-2 Engineering Vehicles. The Ukrainian Army Eagerly Snatched Them Up". Forbes. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine's Armed Forces begin to de-mine territory for upcoming counteroffensive – The Washington Post". Ukrainska Pravda. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine received M58 MICLIC line charges". Militarnyi. Retrieved 6 November 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine acquires British-made mine clearing vehicle". defence-blog.com. 28 October 2022. Retrieved 6 January 2023.
- ^ "Slovakia to Finance Two Bozena-4 Demining Units for Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "South Korean Breaching Vehicles Will Help Ukraine Replace Its Counteroffensive Losses". Forbes. Retrieved 19 September 2023.
- ^ a b Oryx. "Arms For Ukraine: French Weapons Deliveries To Kyiv". Oryx. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "The United States Quietly Gave Ukraine the Assault Breacher, a Special Vehicle For Breaking Through Russian Defenses". Forbes. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Spendensammlung: Komiker kauft 100 gepanzerte Fahrzeuge für die Ukraine". www.t-online.de (in German). 4 March 2023. Retrieved 4 March 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian military got a batch of repaired BAT-2 route clearance bulldozer". Militarnyi. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine Has Captured Three of Russia's Giant Engineering Vehicles. They're About To Become Very Useful". Forbes. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ Ferguson & Jenzen-Jones 2014, p. 79.
- ^ Axe, David. "A Very Rare Combat Vehicle Just Appeared in Southern Ukraine: A High-Speed Trench-Digger". Forbes. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ 2-га лінія оборони на Луганщині: журналісти "5-го" бачили будівництво [2nd line of defense in Lugansk region: journalists of the 5th saw construction]. 5 канал. 9 June 2015. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ Axe, David. "Ukraine's Pontoon Regiment Could Bridge A 750-Foot River In Eight Minutes". Forbes. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ a b c d Roblin, Sébastien (7 March 2023). "Ukraine Is Getting Bridge-Laying Patton Tanks—Here's Why They Didn't Receive the Abrams Version". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Latest from the OSCE Special Monitoring Mission to Ukraine (SMM), based on information received as of 19:30, 15 May 2018". www.osce.org. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Special Forces receive GALAXY Trident 8 boats". Militarnyi. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ a b Shmigel, Pete. "Incredible Video Shows Ukrainian Seals Raiding Russian-Occupied Island in the Dnipro". KyivPost. Retrieved 9 November 2023.
- ^ "У ВМС України освоюють швидкісні човни отримані від США". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ "ВМС отримали швидкісні човни від США". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ a b c Shoaib, Alia. "New US weapons package for Ukraine includes 18 patrol boats to help protect its riverways from the Russian invasion". Business Insider. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ "New pictures released of Ukrainian Dauntless Sea Ark Patrol Boat". Navy Recognition. 18 November 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ^ Sutton, H. I. (2 November 2022). "Ukraine's New U.S. Supplied Combat Boats Already Patrolling Black Sea". Naval News. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian Marines Received Metal Shark's '40 Defiant' Patrol Boats (Photo)". Defense Express. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ^ "$400 Million in Additional Security Assistance for Ukraine". U.S. Department of Defense. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Ozberk, Tayfun (26 January 2023). "Ukraine's First MK VI Patrol Boat Breaks Cover". Naval News. Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ^ "Attack On Europe: Documenting Ukrainian Equipment Losses During The 2022 Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian military received SHERP the SHUTTLE landing boats". Militarnyi. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "The Ukrainian Army's Speedy M-113 Ambulances Help It Save More Wounded Troops". Forbes. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Portugal sends armoured ambulances to Ukraine". www.portugal.gov.pt (Press release). Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ a b Brassart, Pierre (17 March 2023). "Le Luxembourg offre des ambulances blindées à l'Ukraine". À l'Avant-Garde (in French). Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "13 armored vehicles purchased for military medics". mil.in.ua. 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Тест-драйв бронированной медички Alvis Tactica - Auto24". auto.24tv.ua. 26 September 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2023.
- ^ "Командування Медичних сил розповіло скільки всього техніки було отримано за 5 років". Ukrainian Military Pages. 5 February 2021. Archived from the original on 6 February 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ "A benefactor from the US purchased sanitary HMMWVs for Ukraine". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Latest from the OSCE Special Monitoring Mission to Ukraine (SMM), based on information received as of 19:30, 13 May 2018". www.osce.org. Retrieved 11 November 2023.
- ^ Reyes, Hercules (1 September 2021). "Ukraine to Replace Soviet-Era Vehicles With New 4x4s". The Defense Post. Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- ^ a b "The Ministry of Defense of Ukraine received a Bo 105-Е4 helicopter and a KTM 450 ЕХС motorcycle". Militarnyi. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ "В Украине началось производство внедорожников для замены армейских УАЗов: Авто новини від AUTO-Consulting - Богдан". www.autoconsulting.com.ua. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ Helfrich, Emma (5 May 2022). "Ukraine Is Turning Fiat Trucks Into Mobile Surface-To-Air Missile Systems". The Drive.
- ^ a b "Civilian Fords and Toyotas turned into battle trucks for Ukraine's forces". Business Insider.
- ^ "Downed Ka-52 are Useful to Ukrainian Armed Forces in Unexpected Way". Defense Express. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainians fit pickup trucks with grenade launchers".
- ^ "SUVs of the Ukraine Military: Humvee, Land Cruiser, and More". 9 March 2022.
- ^ "USA delivered Toyota Land Cruiser vehicles to Ukrainian Armed Forces". Militarnyi. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ Oryx. "Doubling Down: Japan's Military Donations". Oryx. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ "Uz Ukrainu dosies pirmā par ziedojumiem sagādātā Latvijā ražotā militārās tehnikas krava". www.facebook.com. 25 January 2023. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ^ "Latvian quad bikes against Russian tanks". neatkariga.com. Archived from the original on 15 May 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "Polska sprzeda ukraińskiej armii Tarpany Honkery". forsal.pl. 15 September 2010. Archived from the original on 13 October 2014. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
- ^ Buckby, Jack (8 December 2022). "Russia Should Worry: Ukraine Rigs Improvised Rocket Launchers On Trucks". 19FortyFive. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ "Lotsakit From Luxembourg: The Duchy's Arms Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "МИНОБОРОНЫ, СБУ, МВД И ГОСПОГРАНСЛУЖБА УКРАИНЫ ПОЛУЧИЛИ ОТ ГОСУДАРСТВА НОВЫЕ АВТОМОБИЛИ СКОРОЙ МЕДИЦИНСКОЙ ПОМОЩИ". Archived from the original on 24 February 2015.
- ^ "Державна прикордонна служба України отримала сучасну автомобільну техніку та обладнання майже на 135 мільйонів гривень". Archived from the original on 13 February 2015.
- ^ Axe, David. "Amphibious Tractors With Tank Engines: The Secret Weapons Of Ukraine's River-Crossing Offensive". Forbes. Retrieved 9 November 2023.
- ^ "КрАЗ передав ЗСУ три сідельні тягачі КрАЗ-6510ТЕ". Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "43-я артбригада отримала тягач Oshkosh M1070". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q B., Volodymyr. "Unified truck platform for the Ukrainian Defense Forces: KrAZ, MAZ, or Tatra?". Militarnyi. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ Цензор.НЕТ (13 July 2014). "Программа бронирования техники: быстро, дешево, эффективно". Цензор.НЕТ (in Russian). Archived from the original on 31 December 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ "The Armed Forces of Ukraine Will Destroy the Occupiers Using Seized Tornado-U Armored Truck Equipped with American Weapons". Defense Express. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ "Tornado-U trophy armored vehicle restored for Kraken Regiment". Militarnyi. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ "Western armored vehicles in offensive operation in the Kharkiv Region - Militarnyi". mil.in.ua. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ "Військові отримали вантажівки MAN Kat для гаубиць FH70". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ "Армия получила два первых в Украине медицинских вездехода Mercedes-Benz Unimog". www.unian.net (in Russian). Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ Спецпризначенці Збройних Сил України отримали від волонтерів медичні автомобілі для виконання завдань в зоні АТО Archived 17 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine — Міністерство оборони України, 04 грудня 2014
- ^ "The European Union hands over trucks to the Ukrainian Armed Forces". Militarnyi. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ^ "Українська армія отримає 20 одиниць спеціальної техніки на шасі MAN IVECO". Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- ^ "Azov Brigade soldiers demonstrate the French TRF1 howitzer in action". Militarnyi. Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ "European Union Delivers More Than 90 Off-Road Trucks for Armed Forces of Ukraine". Defense Express.
- ^ "This Ashok Leyland Stallion was bought commercially by Petro Poroshenko, together with 10 DAF Leyland T244 trucks, Nissan Pathfinder, UAVs. Ukrainian military received this donation on 14th of October, 2022". Twitter. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ Порошенко, Петро [@poroshenko] (22 August 2022). "Нарешті! Перші із цих крутих машин — 10 британських вантажівок Leyland DAF — завтра ми передаємо до бригад ЗСУ! Це — гарний подарунок від нас з вами, волонтерів @SpravaHromad, Фонду Порошенка до Дня Прапора та Дня Незалежності. Не залишимо оркам жодного шансу. Україна переможе! t.co/YwBh0pZmcT" [Finally! The first of these cool machines — 10 British Leyland DAF trucks — we are handing over to the Armed Forces brigades tomorrow! This is a nice gift from you and me, volunteers of @SpravaHromad, the Poroshenko Foundation for Flag Day and Independence Day. Let's not leave the orcs a chance. Ukraine will win!] (Tweet) (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Ukrainian volunteers, with the support of the Petro Poroshenko Foundation, bought 20 Foden 8x6 Carrier trucks for the AFU, capable of transporting cargo weighing up to 18 tons". Twitter. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ "An old Dutch DAF YA-328 military truck that was donated for use by the Ukrainian armed forces. This truck was produced between 1952 and 1958". Twitter. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
- ^ a b Oryx. "Vikings For Victory: Norwegian Arms Transfers To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 3 October 2023.
- ^ Oryx. "Attack On Europe: Documenting Ukrainian Equipment Losses During The 2022 Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ "Belgium to supply Ukraine with F-16s from 2025". www.ukrinform.net. 11 October 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "World Air Forces 2022". Flightglobal Insight. 2022. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ "Poland to send at least four MiG-29 fighter jets to Ukraine". Sky News. Retrieved 18 March 2023.
- ^ Koshiw, Isobel (17 March 2023). "Slovakia to donate 13 MiG-29 warplanes to Ukraine". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 18 March 2023.
- ^ Axe, David. "Where Are Ukraine's Bombers?". Forbes. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ a b "Ukrainian Su-24s are using Tornado weapon pylons". Militarnyi. Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ^ "Парад на честь 30-ї річниці незалежності України. Авіаційна частина параду - Авіамузей". aviamuseum.com.ua.
- ^ "The Ukrainian Armed Forces received a demilitarized German MBB Bo 105 helicopter". Militarnyi. 21 June 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ^ Андрій Яцик. Мi-2: український вариант // «Народна армія», No. 22 (5554) вiд 31 травня 2018. стор.6
- ^ "Latvia donates helicopters and howitzers to Ukraine". LSM. 15 August 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- ^ "Russian pilot hands over Mi-8 helicopter with spare parts for fighter jets to Ukraine's Defence Intelligence". Militarnyi. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ a b "World Air Forces 2022". Flightglobal. Flightglobal Insight. 2022. Retrieved 18 March 2022.
- ^ "Portugal sends six unlicensed Kamov helicopters to Ukraine". West Observer. 13 October 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ "UK sending helicopters to Ukraine for first time, says Ben Wallace". the Guardian. 23 November 2022. Retrieved 23 November 2022.
- ^ "Mi-24 and UH-60 Black Hawk helicopters of military intelligence of Ukraine ". Twitter. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ "The Black Hawk in #Ukraine: the Ukrainian Military Intelligence (GUR) Aviation forces have revealed a new helicopter type in service- at least one Sikorsky UH-60A. By the livery, this appears to be an ex-US Army helicopter refurbished and upgraded by Ace Aeronautics, LLC". Twitter. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e IISS 2023, p. 203.
- ^ 1997-04-09T00:00:00+01:00. "Arsenal upgrades Molniya R-60 missile". Flight Global. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
{cite web}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Oryx. "Answering The Call: Heavy Weaponry Supplied To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- ^ "Britain to donate air defence missiles to Ukraine". Reuters. 12 October 2022. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ "Pentagon orders AMRAAM missiles worth over $1 billion for Ukraine". Yahoo News. 21 June 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Page, Lewis (11 May 2023). "Storm Shadow missiles to Ukraine will transform the nature of battle". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 12 May 2023.
- ^ a b Newdick, Thomas (10 August 2022). "Ukrainian Su-24 Back In The Fight And Armed With A Laser-Guided Missile". The Drive. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ "US Is Giving Ukraine a Long-Range GPS-Guided Bomb That Can Hit Targets Miles Away". Bloomberg.com. 21 February 2023. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ^ "The USA handed over the GPS-guided JDAM bombs to Ukraine – Bloomberg". Militarnyi. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ^ a b c "ANALYSIS: What is the current status of the Ukrainian Air Force?". www.key.aero. 18 April 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ^ "How is Ukraine's fearsome Su-25 Frogfoot fleet helping to turn the tide of the war?". www.key.aero. 10 October 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine-Russia War: An expert analysis of the first year". www.key.aero. 24 February 2023. Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "Sumy region border strengthened by mobile MLRS with S-5 missiles". Militarnyi. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
- ^ a b c "How is Ukraine's fearsome Su-25 Frogfoot fleet helping to turn the tide of the war?". www.key.aero. 10 October 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ^ "ANALYSIS: What is the current status of the Ukrainian Air Force?". www.key.aero. 18 April 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ^ Altman, Howard; Trevithick, Joseph; Rogoway, Tyler (12 May 2023). "Evidence Of ADM-160 Miniature Air-Launched Decoy Use By Ukraine Emerges". The Drive. Retrieved 2 November 2023.
- ^ "Leleka-100 Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), Ukraine". Army Technology. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ a b c "List Of Aircraft Losses During The 2022 Russian Invasion Of Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ "UJ-22 Airborne UAS". Ukrjet. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ a b Newdick, Thomas (30 May 2023). "Putin Admits Moscow's Air Defenses "Need Work" After Multi-Drone Attack". The Drive. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Almost Thousand UAVs in Ukraine's "Army of Drones" And They Are Deadly to the russians (Video)". Defense Express. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ 🇺🇦 Ukraine Weapons Tracker [@UAWeapons] (20 September 2022). "#Ukraine: A Ukrainian UKRSPECSYSTEMS PD-1 multipurpose UAV in transport containers along with the technical documentation was captured by the Russian forces. Precise date and location is unknown. t.co/dY62xkiDXP" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "PD-2 Unmanned Aerial System, Ukraine". Army Technology. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ^ "Ukrspecsystems unveiled its new SHARK UAV". Militarnyi. Retrieved 29 July 2023.
- ^ "Donors purchased 25 SHARK UAVs to replace the downed ones". Militarnyi. Retrieved 29 July 2023.
- ^ "Ukrainian intelligence receives the Sych unmanned system". Militarnyi. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "187 DJI Mini 2 sollen Kriegsverbrechen in der Ukraine filmen". Drone-Zone.de (in German). 9 March 2022. Retrieved 3 June 2022.
- ^ "Ukrainian Army Uses DJI Mavic 3 To Guide Mortars". 1 April 2022. Retrieved 10 May 2022.
- ^ "Wie die Ukraine günstige Drohnen für ihre Verteidigung nutzt". Focus Online (in German). Retrieved 10 May 2022.
- ^ "Latvijā ražots bezpilota lidaparāts iztur praktisko testu Ukrainā". sargs.lv (in Latvian). 16 August 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- ^ "Ukrainai paredzētā drona "Bayraktar" iegādei saziedotie līdzekļi tiks novirzīti akūtākām vajadzībām". sargs.lv (in Latvian). 22 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Gosselin-Malo, Elisabeth (16 June 2023). "Portuguese firm to provide drones to Ukraine through British-led fund". Defense News. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- ^ Oryx. "Leopards From Lisbon: Portuguese Arms Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- ^ "New Bayraktar UAVs Spotted In Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 10 May 2022.
- ^ "Міноборони України замовило 105 БПЛА Vector в Німеччині". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 29 January 2023.
- ^ Panasovskyi, Maksim. "Die Streitkräfte der Ukraine haben eine hochmoderne deutsche VECTOR-Drohne für 7,1 Mio. UAH erhalten". gagadget.com (in German). Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ^ "Das Start-up, das den Ukrainern Aufklärungsdrohnen liefert". capital.de (in German). 8 May 2022. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ^ Lamothe, Dan (11 March 2015). "U.S. to send Humvees and unarmed drones to Ukraine — but still no weapons". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Se videoen: Her afslører dansk drone et russisk krigshovedkvarter ved fronten". 11 August 2022.
- ^ Ensor, Josie (24 August 2022). "The six-inch Black Hornet "microdrones" that can enter Russian buildings". The Telegraph.
- ^ "Norwegian-developed drone to Ukraine". Government.no. 24 August 2022.
- ^ "A Kindred Spirit: Taiwan's Aid To War-Torn Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ "Розвідникам передали два БПЛА Bayraktar TB2". Мілітарний (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ^ "Cruise Missile or Suicide Drone - Russia Shoots Down Invading Tu-143 Inside Its Airspace with Buk Missile". July 2022.
- ^ "U.S. sending Switchblade drones to Ukraine in $800 million package". Politico. 16 March 2022. Archived from the original on 17 March 2022. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- ^ "RAM II loitering munition destroyed the Russian SAM in the Kherson region". Militarnyi. 11 October 2022. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
- ^ "Taiwan's Revolver 860 combat drones being used by Ukrainians on battlefield". 18 August 2022.
- ^ "A Kindred Spirit: Taiwan's Aid to War-Torn Ukraine".
- ^ Waldmann, Nils (7 March 2022). ""Punisher Drohne" soll "Erfolge" in der Ukraine feiern". Drone-Zone.de (in German). Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ "Fashion statement: Ukrainian troops debut post-Soviet uniforms". The Washington Times.
- ^ Times, The Moscow (24 August 2016). "Ukrainian Army Moves Further West With New NATO-Style Uniforms". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ "Military field brand P1G-Tac". P1GTac.com. Retrieved 12 April 2022.
- ^ Galeotti 2019, p. 63.
- ^ "UK equipment supplier inundated with Ukrainian orders". Reuters. 2 March 2022 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ "Defence Secretary Ben Wallace visits Armed Forces of Ukraine as training programme starts across the UK".
- ^ a b c "Ukrainian Camouflage Patterns". Hangzhou Fashion Outdoor Co.,Ltd. Retrieved 12 May 2022.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Ukrainian Camouflage Patterns - News - Hangzhou Fashion Outdoor Co.,Ltd". m.aplce.com. Retrieved 16 May 2022.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b "Aid from Asia: Japan's Military Support to Ukraine".
- ^ Oryx. "Arms For Ukraine: French Weapons Deliveries To Kyiv". Oryx. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ Galeotti 2019, p. 42.
- ^ "Improvement of Ballistic Helmet for the Ukrainian Ground Forces". 27 March 2018.
- ^ "UaRms". uarms. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ "Japan sends bulletproof vests from defense forces to Ukraine". Kyodo News+.
- ^ "ウクライナに供与した防弾チョッキ3型は改良型の新型、防弾チョッキ3型改" [Bulletproof vest type 3 provided to Ukraine is a new and improved model, modified type 3 vest] (in Japanese). 15 April 2022. Archived from the original on 29 November 2022. Retrieved 6 November 2022.
- ^ "防弾チョッキ提供 日本がウクライナに武器輸出?支援の舞台裏" [Japan provides weapons and bulletproof vests to Ukraine? Behind the scenes of assistance]. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Här är vapnet Sverige skickar till Ukraina: "Kommer ge effekt"" [ere is the weapon Sweden is sending to Ukraine: "It will have an effect"]. www.aftonbladet.se. 27 February 2022.
- ^ a b "Army donates thousands of helmets to Ukraine Military". www.army.mod.uk. Retrieved 11 May 2022.
- ^ "70 helmets got into the hands of Donbas and Aidar battalions". 17 September 2014. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023.
- ^ "Vikings for Victory: Norwegian Arms Transfers to Ukraine".
- ^ Oryx. "No Assembly Required: Swedish Arms Deliveries To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ a b Mitzer, Stijin; Oliemans, Joost. "Lotsakit From Luxembourg: The Duchy's Arms Supplies To Ukraine". Oryx. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ Ponomarenko, Illia. "US donates 2,500 night-vision devices to Ukraine's Armed Forces (VIDEO)". Get the Latest Ukraine News Today - KyivPost. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Smith, Jordan (11 November 2022). "Defence Intelligence of Ukraine: Rulers of the Stars". Grey Dynamics. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
Bibliography
- Galeotti, Mark (18 June 2019). Armies of Russia's War in Ukraine. Bloomsbury USA. ISBN 978-1-4728-3344-0.
- Plokšto, Artur; Demeško, Andriej (30 June 2017). "Armaments used in the Ukrainian conflict 2014–2015". Security and Defence Quarterly. 15 (2): 54–84. doi:10.35467/sdq/103190. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- Ferguson, Jonathan; Jenzen-Jones, N.R. (November 2014). Raising Red Flags: An Examination of Arms & Munitions in the Ongoing Conflict in Ukraine, 2014 (PDF) (Report). Australia: Armament Research Services (ARES). ISBN 978-0-9924624-3-7. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2022). The Military Balance 2022 (Report). Abingdon, Oxon. pp. 212–214. ISBN 978-1032279008.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (15 February 2023). The Military Balance 2023 (Report) (1st ed.). Routledge. pp. 201−204. ISBN 978-1032508955.
- U.S. Department of Defense (21 September 2023). Fact Sheet on U.S. Security Assistance to Ukraine (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- Thompson, Leroy (27 October 2022). Soviet Pistols: Tokarev, Makarov, Stechkin and others. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4728-5349-3. Retrieved 8 July 2023.
External links
 Media related to Military equipment of Ukraine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Military equipment of Ukraine at Wikimedia Commons


