Namur Province
Namur
Nameur (Walloon) Namen (Dutch) | |
|---|---|
|
| |
 | |
| Coordinates: 50°27′51″N 4°51′42″E / 50.46417°N 4.86167°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Capital | Namur |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Denis Mathen |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,675 km2 (1,419 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2024)[2] | |
• Total | 503,895 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €14.697 billion (2021) |
| HDI (2021) | 0.905[4] very high · 9th of 11 |
| Website | Official site |
Namur (French: [namyʁ] ⓘ; Walloon: Nameur; Dutch: Namen [ˈnaːmə(n)] ⓘ) is a province of Wallonia, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the West) on the Walloon provinces of Hainaut, Walloon Brabant, Liège and Luxembourg in Belgium, and the French department of Ardennes. Its capital and largest city is the city of Namur. As of January 2024, the province of Namur has a population of about 0.5 million.
Subdivisions
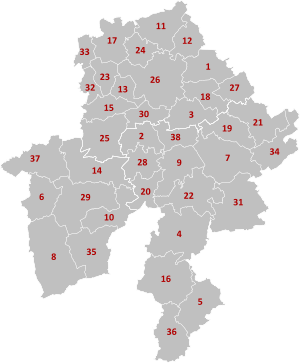
It has an area of 3,675 square kilometres (1,419 sq mi) and is divided into three administrative districts (arrondissements in French) containing a total of 38 municipalities (communes in French).
| Map no. | Municipality | Arrondissement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andenne | Namur |
| 2 | Anhée | Dinant |
| 3 | Assesse | Namur |
| 4 | Beauraing | Dinant |
| 5 | Bièvre | Dinant |
| 6 | Cerfontaine | Philippeville |
| 7 | Ciney | Dinant |
| 8 | Couvin | Philippeville |
| 9 | Dinant | Dinant |
| 10 | Doische | Philippeville |
| 11 | Éghezée | Namur |
| 12 | Fernelmont | Namur |
| 13 | Floreffe | Namur |
| 14 | Florennes | Philippeville |
| 15 | Fosses-la-Ville | Namur |
| 16 | Gedinne | Dinant |
| 17 | Gembloux | Namur |
| 18 | Gesves | Namur |
| 19 | Hamois | Dinant |
| 20 | Hastière | Dinant |
| 21 | Havelange | Dinant |
| 22 | Houyet | Dinant |
| 23 | Jemeppe-sur-Sambre | Namur |
| 24 | La Bruyère | Namur |
| 25 | Mettet | Namur |
| 26 | Namur | Namur |
| 27 | Ohey | Namur |
| 28 | Onhaye | Dinant |
| 29 | Philippeville | Philippeville |
| 30 | Profondeville | Namur |
| 31 | Rochefort | Dinant |
| 32 | Sambreville | Namur |
| 33 | Sombreffe | Namur |
| 34 | Somme-Leuze | Dinant |
| 35 | Viroinval | Philippeville |
| 36 | Vresse-sur-Semois | Dinant |
| 37 | Walcourt | Philippeville |
| 38 | Yvoir | Dinant |
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was 13.5 billion € in 2018, accounting for 2.9% of Belgium's economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 24,000 € or 80% of the EU27 average in the same year. GDP per person employed was 104% of the EU27 average.[5]
List of governors
- 1830–1834: Goswin de Stassart (Liberal)
- 1834–1840: Joseph Lebeau (Liberal)
- 1840–1847: Edouard d'Huart (Liberal)
- 1887–1848: Adolphe de Vrière (Liberal)
- 1848–1851: François Pirson (Liberal)
- 1853–1875: Charles de Baillet (Catholic Party)
- 1876–1877: D. de Mevius
- 1877–1881: Albert de Beauffort (Catholic Party)
- 1881–1882: Léon Pety de Thozée (Liberal)
- 1882–1884: Auguste Vergote
- 1884–1914: Charles de Montpellier de Vedrin
- 1919–1937: Pierre de Gaiffier d'Hestroy
- 1937–1944: François Bovesse (Liberal)
- 1945–1968: Robert Gruslin
- 1968–1977: René Close (PS)
- 1977–1980: Pierre Falize (PS)
- 1980–1987: Emile Lacroix
- 1987–1994: Emile Wauthy (PSC)
- 1994–2007: Amand Dalem (PSC)
- 2007–present: Denis Mathen (MR)
Twinning
The Province of Namur is twinned with:[6]
See also
References
- ^ "Be.STAT". Archived from the original on 2021-01-23. Retrieved 2020-01-11.
- ^ "Structuur van de bevolking | Statbel". statbel.fgov.be. Archived from the original on 2020-10-19. Retrieved 2024-07-31.
- ^ "EU regions by GDP, Eurostat". Archived from the original on 27 February 2023. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". Archived from the original on 2023-10-04. Retrieved 2023-09-29.
- ^ "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat. Archived from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2020-03-06.
- ^ "Service des relations extérieures et internationales". province.namur.be (in French). Archived from the original on 22 June 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2019.
External links
- Province de Namur's official website
- . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.


