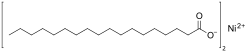
Nickel(II) stearate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Nickel distearate, nickel dioctadecanoate, nickel(2+) octadecanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.041 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 36H 70NiO 4 | |
| Molar mass | 625.63 |
| Appearance | green powder |
| Density | 1.13 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| Boiling point | 359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H317, H334, H341, H350, H360, H372, H410 | |
| Flash point | 162.4 °C (324.3 °F; 435.5 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nickel(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of nickel and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70NiO
4.[1][2] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.[3] The compound is harmful if swallowed and may cause skin sensitization.[4]
Synthesis
An exchange reaction of sodium stearate and nickel dichloride:
Physical properties
Nickel(II) stearate forms a green powder.[5]
The compound is insoluble in water, methanol, ethanol, or ether, soluble in carbon tetrachloride and pyridine, slightly soluble in acetone.
Uses
The compound is used as a lubricant and in various industrial applications.
References
- ^ "Nickel(II) stearate". Sigma Aldrich. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ "Nickel(II) Stearate". American Elements. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ "Nickel(II) stearate | CAS 2223-95-2". Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ User guide and indices to the initial inventory, substance name index. U.S. Government Printing Office. 1979. p. 998. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ "Nickel(II) stearate - Hazardous Agents | Haz-Map". haz-map.com. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
