Storming of Derbent
| Siege of Derbent | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Russo-Persian War (1796) | |||||||
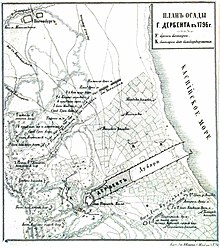 Plan of Derbent siege, published in 1886 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
Quba Khanate Derbent Khanate Gazikumukh Khanate | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
Shaykh Ali Khan Surkhay II | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 12,323 soldiers, 21 cannons.[2] |
10,000 soldiers.[3] including: 400 Gazikumukh cavalry 1,200–1,300 Qubans 90 Kaitags 800 Akushins 900 Kharbuks 34 cannons | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 3 officers and 47 soldiers killed, 8 officers and 160 soldiers wounded | Unknown | ||||||
The siege of Derbent (or "Storming of Derbent"; Russian: Штурм Дербента) took place on 21 May [O.S. 10 May] 1796 during the Persian Expedition of 1796. Derbent, an ancient city with thick walls has a favorable geopolitical position, which locks the coastal passage between the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian.
Background
In the spring of 1795, the Persians, led by the new ruler and founder of the Qajar dynasty, Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar, re-subjugated eastern Georgia (recently unified as the Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti) and the khanates of the region. In carrying out its obligations under the Treaty of Georgievsk of 1783, albeit belatedly, the Russian government sent a large army (about 13,000) from Kizlyar towards the Iranian possessions in the Caucasus. For the subsequent campaign in 1796, a strong Russian corps of two infantry and two cavalry brigades had been formed in Kizlyar. Command was given to Pavel Tsitsianov, Bulgakov, Alexander Korsakov, Baron Levin August, Count Fyodor Apraksin, and Matvei Platov, while the commander-in-chief was Lieutenant-General Count Valerian Zubov.
Russian forces
The first cavalry brigade, composed of the dragoon regiments of Vladimir and Nizhny Novgorod, was entrusted to Major-General Levin August von Bennigsen, and the second, formed from the Astrakhan and Taganrog dragoon regiments, put under the command of brigadier Count Apraksin. All irregular troops, making up the reserve, were subordinated to Major-General Platov, and before his arrival with the Chuguevsky regiment, they were under the control of Lieutenant-Colonel Baranov. The first infantry brigade, under the command of Major-General Bulgakov was composed of two battalions of the Kuban Jäger Corps and two of the Caucasian Grenadier Regiment; the second brigade, under the command of Major General Rimsky-Korsakov, was formed from the consolidated grenadier battalion, one Voronezh battalion and two Tiflis musketeer regiments. Tsitsianov on the other hand was left to coordinate in Kizlyar.
Army crossed the Terek River over the built bridge on April 21 but forced was to stop at the Lashurin outpost on the Kargin River because of the harsh and cold winter and the incessant blizzards. There was no pasture at all; supplies of food and fodder were very limited and therefore it was impossible to move on. Count Zubov returned to Kizlyar to take urgent measures to provide the troops with food. The mobile store was not yet formed and could not be transported across the Terek River before April 27, due to the lack of wagons and oxen as a means of transportation. Although commissioners were sent to various places in Russia to purchase them, but, according to information received from them, in the middle of April only a third of the oxen and wagons could be transported across the Don River and, therefore, they could arrive on the line only by the end of May. Therefore, in order not to stop the expedition before the onset of hot weather, Gudovich collected as many Nogai carts as possible and hired wagons from private individuals, with the obligation to pay them a monthly fee.[4]
Initial moves
Despite Zubov's troubles in Kizlyar, 4180 soldier strong vanguard troops under Ivan Savelyev's command was first to arrive at outskirts of Derbent. Initially, the general offered Shaykh Ali Khan to submit join forces against Agha Muhammad Shah Qajar. Young khan, trying to prolong negotiations at first replied to the message that he was afraid of Qajars and then said his religion forbids him to state infidels inside the city quarters. Savelyev responded by bombarding city walls twice. Shaykh Ali hoped for a Qajar or an Ottoman[5] relief to come and thus prolonged the negotiations. He sent an envoy named Haji beg to Ottoman Empire in April,[6] and an emissary named Qadir beg to Agha Muhammad Khan. Qadir beg returned with news of refusal from Agha Muhammad. His envoy to Ottomans however was killed on the road. According to the letter which was later recovered, Shaykh Ali denounced Dagestani leaders and Iranian shah, calling them traitors, while requesting from the Porte as the head of Islam.[7] Left without major allies, Shaykh Ali had to rely on reinforcements from Gazikumukh khan Surkhay II.
Meanwhile, Zubov's army arrived at Tarki on 26 April, received submissions from Shamkhal of Tarki and other Dagestani leaders, who told him about alternative and secret narrow gorges in Dagestan that circumvents Derbent. Zubov sent his subordinate Bulgakov to take this road besiege Derbent from other side.
Bulgakov arrived at Darvag on May 11, Zubov arrived at Derbent on May 13–14.[5] His patrols were met with fire and arrows from Shaykh Ali's soldiers hiding in the mountains and ravines, four miles away from the city. This skirmish lasted more than three hours, until the Grebensky and Volga Cossacks dismounted and the third battalion of the Caucasian Jäger Corps forced the Derbentis out of the ambush, retreating into the fortress.
Bulgakov on the other hand had to travel with 6,000 soldiers[8] on 85 kilometers of road following the guidance of Ghāzī Rustam of Tabasaran. However, Ghāzī's brother secretly informed Shaykh Ali that there were no more than 8,000 Russian troops.[9] According to Russian reports the 3-km hike was so steep that it was very difficult to follow the artillery and the convoy, so that until noon only one battalion of infantry and Cossacks with their convoys could be transported over the mountain. Almost all the people and riding horses were used to help the draft. Later in the afternoon it began to rain, which continued until the next morning. The clay soil of the mountain became so slippery that to help six horses that harnessed to a 12-pound gun, they were forced to send up to 200 soldiers, but even they could hardly move the gun from its place.
Defending forces

The Derbent fortress was divided into three parts: the first or the upper one, almost adjoining the mountains, was very fortified by nature of the Narinkala castle; the second, actually called Derbent, consisted of a wall that surrounded the residential city and, finally, the third part, closest to the sea, and known under the name Dubari, although it was surrounded by a wall, but was not populated by inhabitants. This part was separated from the residential city by a transverse wall and served as a place where the Derbentis kept their cattle.
Up to 80 towers protruded from the walls, 10 of which were large. In addition, a special tower was built in front of the Narinkala on the western side. 9 copper and 3 cast-iron cannons and mortars, as well as 6 falconets were placed on the fortress walls.[10]
The fortress walls were armed with cannons and several falconets, for which the inhabitants prepared charges and made gunpowder daily. The defenders were most afraid of a night attack and therefore spent the whole night on the walls and slept during the day. The main body of the tower had a garrison of up to 100 people, the middle one had 50, and the small one had from 15 to 20 people; in the spaces between the towers, along the fortress wall, a chain was placed, and then all the other defenders were located in the city near the walls.
Having examined the city and made a reconnaissance of the surrounding area, Count Zubov saw that first of all it was necessary to capture the tower, which, covering most of the walls, prevented not only the construction of batteries, but also communication between the troops. He ordered several cannons to be fired at once on different parts of the city, and to direct the shots of one 12-pounder gun exclusively against the tower. The four shots fired did not produce any effect on its walls, however. Assuming that no more than seventy garrison men could fit inside it, Zubov decided to take it by storm.[11]
Storming

First stage
As soon as storming Zubov ordered the battalion of the Voronezh infantry regiment to seize the tower. This assault failed, having no ladders, they could only surround it, but not storm it. The frequent fire of the enemy forced them soon abandon the storming of the tower, which turned out to be four-tiered and very strong. The commander of the battalion, Colonel Krivtsov, and almost all the officers were wounded, and therefore General Rimsky-Korsakov, who was in charge of the assault, ordered the Voronezh regiment to retreat. The battalion withdrew to its former position, losing 25 men killed and 72 wounded. Later that day, Count Zubov ordered to lay down a battery of four cannon for action against the outer towers located on the north side of the Narin-Kale castle. For its part, Shaykh Ali brought about 500 garrison men to cover the advanced tower, which was located in the ditch between the wall and the tower.
Meanwhile, Bulgakov coming out of mountains besieged Derbent from south, captured five Armenians and one Azerbaijani. Now, Derbent was surrounded on all sides and neither the inhabitants had the opportunity to get out of the city, nor the allies of Shaykh Ali Khan managed to help him. Being cut off from all sides, the Derbentis tried to arrange a communication by sea, but they did not succeed either, since their boat was captured by cossacks too. Nevertheless, Shaykh Ali managed to send out the word to his allies Huseyngulu Khan and Surkhay II.
Captives informed Zubaov that there were 2,500 houses in the city, including up to 60 Armenian ones and that the Khan have up to 10,000 people armed with guns. 400 of them being mounted Gazikumukh soldiers, 1,200-1,300 Qubans, up to 90 Kaitag people, 800 Akushins and up to 900 people from various small mountain tribes.
Second stage
Second stage of the attack began on the night of May 17, when Russians built a second breach-battery with three guns. However, walls remained unharmed even after 80 shots. It was not possible to lay a trench against the tower due to the stony ground; consequently, the only means of capturing it was an assault. The earlier two grenadier companies of the Voronezh regiment and the third battalion of the Caucasian Jäger Corps again were order to assault the tower. Assault was a success, but soon enough Dagestani reinforcements arrived and attacked Bulgakov's regiments transporting supplies. Intensifying bombardment, Zubov wanted to start a fire in the city without success.
With walls ranging from one and a half to two arns thick, each house presented a view of a fortified castle, which could only be taken by storm. With the narrow streets inherent in all Asian cities, such an assault turned out to be very difficult for the attacker and, on the contrary, represented all the benefits for the defender.[12]
Despite initial success, fearing a long siege might turn the inhabitants against himself, Shaikh Ali Khan sent Khizir beg Gorchu on May 20 to Russian camp to negotiate. Finally May 21, the city was captured as town surrendered[5] and handed over the keys of the city.[1] According to Dubrovin, keys were handed by a 120-year-old man, who also handed over the keys to Peter the Great 74 years earlier.[13]
Aftermath
Zubov received the Order of St. George of the 2nd degree, a cross and a star with diamonds of St. Apostle Andrew the Called One and a diamond pen. Generals Bulgakov, Saveliev, Rimsky-Korsakov and Baron Benningsen were awarded the Order of St. Anna, foreman Count Apraksin got the Order of St. Vladimir 3rd degree. Six crosses of the orders of St. George and St. Vladimir of the fourth degrees and a ruble per person distributed for higher and lower ranks respectively.[14] Zubov moved on to conquer Baku and took Shaykh Ali Khan with himself, appointing his pro-Russian half-sister Pari Jahan Khanum as head of the Derbent Khanate.[15]
The capture of Derbent by Zuvov was glorified by the Russian court poet Gavrila Derzhavin in his poem "Na Pokorenie Derbenta" (On the conquest of Derbent).[16] Empress Catherine waxed jubilant at Zubov's rapid progress, which in two months had exceeded the gains of Peter the Great's costly Persian campaign in two years.[17] Shaykh Ali Khan was taken prisoner. Despite this success, when Paul I ascended the Russian throne, foreign policy changed, and the Russian troops were withdrawn from the Caucasus (in December 1796), and all the conquered areas were returned to Qajar Iran.[1]
References
- ^ a b c Mikaberidze 2011, p. 763.
- ^ История русской армии от зарождения Руси до войны 1812 г. — СПб.: Полигон, 2003. (in Russian)
- ^ А.В. Потто. Кавказская война (в 5-ти томах) (in Russian)
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, p. 95.
- ^ a b c Bournoutian 2021, p. 19.
- ^ Mustafazade 2005, p. 185.
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, pp. 104–105.
- ^ Mustafazade 2005, p. 177.
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, p. 108.
- ^ Шляпникова Е. А. (2012). "Персидский поход русских войск 1796 года". Военно-исторический журнал (in Russian) (5). Moscow: Ministry of Defence of Russia: 59–62. ISSN 0321-0626.
- ^ Shishkevich, Mikhail (2003). "Персидский поход графа Зубова" [Persian campaign of Count Zubov]. История русской армии [History of the Russian army] (in Russian). Vol. 2. N. L. Volkovskiĭ. Saint Petersburg: Poligon. pp. 472–473. ISBN 5-89173-212-2. OCLC 54863280.
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, p. 114.
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, p. 115.
- ^ Dubrovin 1886, p. 117.
- ^ Hajieva, Sakinat (1999). Дагестанские азербайджанцы XIX-начало XX в: историко-этнографическое исследование [Dagestan Azerbaijanis in the 19th-beginning of the 20th centuries: a historical and ethnographic study] (PDF) (in Russian). Moscow: Vostochnaya Literatura. p. 171.
- ^ Ram 2006, p. 96.
- ^ Alexander 1989, p. 321.
Sources
- Alexander, John T. (1989). Catherine the Great: Life and Legend. Oxford Paperbacks. ISBN 978-0199874309.
- Bournoutian, George (2021). From the Kur to the Aras: A Military History of Russia's Move into the South Caucasus and the First Russo-Iranian War, 1801–1813. Brill. ISBN 978-9004445154.
- Dubrovin, Nikolai (1886). История войны и владычества русских на Кавказе [The history of the war and domination of Russians in the Caucasus] (in Russian). Saint Petersburg.
{cite book}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Mikaberidze, Alexander, ed. (2011). Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia (Vol. 1). ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1598843378.
- Mustafazade, Tofig (2005). Quba xanlığı [Khanate of Quba] (in Azerbaijani). Baku: Elm. ISBN 5-8066-1747-5.
- Ram, Harsha (2006). The Imperial Sublime: A Russian Poetics of Empire. Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0299181949.