V429 Geminorum
BD+20° 1790
V429 Geminorum
V429 Geminorum
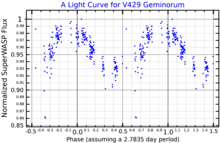
Courbe de lumière de V429 Geminorum, adaptée de Norton et al. (2007)[1].
| Ascension droite | 07h 23m 43,5893s[2] |
|---|---|
| Déclinaison | +20° 24′ 58,655″[2] |
| Constellation | Gémeaux |
| Magnitude apparente | 9,93 |
Localisation dans la constellation : Gémeaux | |
| Type spectral | K5Ve[3] |
|---|---|
| Magnitude apparente (B) | 11,08 |
| Magnitude apparente (I) | 8,9 |
| Magnitude apparente (R) | 9,43 |
| Magnitude apparente (J) | 7,643 |
| Magnitude apparente (H) | 7,032 |
| Magnitude apparente (K) | 6,879 |
| Indice B-V | 1,15 |
| Indice V-R | 0,50 |
| Indice R-I | 0,5 |
| Variabilité | BY Dra[4] |
| Vitesse radiale | +7,743 ± 0,003 km/s[5] |
|---|---|
| Mouvement propre |
μα = −65,576 mas/a[2] μδ = −230,952 mas/a[2] |
| Parallaxe | 35,976 6 ± 0,065 8 mas[2] |
| Distance | 27,795 8 ± 0,050 8 pc (∼90,7 al)[2] |
| Magnitude absolue | 7,86 |
| Masse | 0,63 M☉[6] |
|---|---|
| Rayon | 0,71 R☉[6] |
| Gravité de surface (log g) | 4,53[6] |
| Luminosité | 0,17 L☉[6] |
| Température | 4 410 K[6] |
| Métallicité | 0,30[6] |
| Rotation | 10,03 km/s[6] |
| Âge | 35-80 M a[6],[7] |
Désignations
V429 Geminorum (en abrégé V429 Gem) est une étoile située à une distance de ∼ 90,7 a.l. (∼ 27,8 pc) du Soleil[2], dans la constellation zodiacale des Gémeaux[9]. Aussi désignée BD+20°1790, elle est l'objet primaire d'un système planétaire dont l'unique objet secondaire connu est BD+20 1790 b, une planète confirmée[10],[11].
Notes et références
- ↑ (en) Norton et al., « New periodic variable stars coincident with ROSAT sources discovered using SuperWASP », Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol. 467, no 2, , p. 785–905 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361:20077084, Bibcode 2007A&A...467..785N, arXiv astro-ph/0702631).
- (en) A. G. A. Brown et al. (Gaia collaboration), « Gaia Data Release 2 : Summary of the contents and survey properties », Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol. 616, , article no A1 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051, Bibcode 2018A&A...616A...1G, arXiv 1804.09365). Notice Gaia DR2 pour cette source sur VizieR. .
- ↑ (en) C. A. O. Torres, G. R. Quast, C. H. F. Melo et M. F. Sterzik, « Young Nearby Loose Associations », Handbook of Star Forming Regions, Volume II: the Southern Sky ASP Monograph Publications, vol. 5, , p. 1–757 (Bibcode 2008hsf2.book..757T, arXiv 0808.3362).
- ↑ (en) N. N. Samus et O. V. Durlevich, « VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013) », VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs. Originally published in: 2009yCat....102025S, vol. 1, (Bibcode 2009yCat....102025S).
- ↑ (en) C. Soubiran et al., « Gaia Data Release 2. The catalogue of radial velocity standard stars », Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol. 616, , p. 8, article no A7 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/201832795, Bibcode 2018A&A...616A...7S, arXiv 1804.09370).
- (en) M. Hernán-Obispo, M. C. Gálvez-Ortiz, G. Anglada-Escudé, Kane, S. R., Barnes, J. R., de Castro, E. et Cornide, M., « Evidence of a massive planet candidate orbiting the young active K5V star BD+20 1790 », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 0912, , A45 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/200811000, Bibcode 2010A&A...512A..45H, arXiv 0912.2773).
- ↑ (en) John M. Carpenter, Jeroen Bouwman, Eric E. Mamajek, Meyer, Michael R., Hillenbrand, Lynne A., Backman, Dana E., Henning, Thomas, Hines, Dean C., Hollenbach, David, Jinyoung Serena Kim, Amaya Moro-Martin, Ilaria Pascucci, Murray D. Silverstone, John R. Stauffer et Sebastian Wolf, « Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems: Properties of Debris Dust Around Solar-Type Stars », The Astrophysical Journal Supplement, vol. 181, no 1, , p. 197–226 (DOI 10.1088/0067-0049/181/1/197, Bibcode 2009ApJS..181..197C, arXiv 0810.1003).
- ↑ (en) BD+20 1790 -- Variable of BY Dra type sur la base de données Simbad du Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg..
- ↑ (en) Résultats pour « V429 Gem » [html] sur l'application Compute constellation name from position de VizieR (consulté le 29 mars 2015)
- ↑ (en) « 2015 Exoplanet Archive New » [html], sur NASA Exoplanet Archive, (consulté le ).
- ↑ (en) Magdalena Hernán-Obispo et al., « Evidence of a massive planet candidate orbiting the young active K5V star BD+20 1790 », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 512, , id. A45, 11 p. (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/200811000, Bibcode 2010A&A...512A..45H, arXiv 0912.2773, résumé) Les coauteurs de l'article sont, outre Magdalena Hernán-Obispo : Maria-Cruz Gálvez-Ortiz, Guillem Anglada-Escudé, Stephen R. Kane, John R. Barnes, Elisa de Castro et Manuel Cornide..
L'article a été reçu par la revue Astronomy and Astrophysics le , accepté par son comité de lecture le et mis en ligne le .
Il a été prépublié sur arXiv le .
Liens externes
- Étoile
- (en) BD+20 1790 -- Variable of BY Dra type sur la base de données Simbad du Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- (en) BD+20 1790 sur la base de données NASA Exoplanet Archive
- Planète
- (en) BD+20 1790 b sur L'Encyclopédie des planètes extrasolaires de l'Observatoire de Paris.
- (en) BD+20 1790 b sur la base de données NASA Exoplanet Archive