너비 우선 탐색
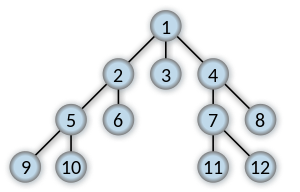 노드가 확장되는 순서 | |
| 분류 | 검색 알고리즘 |
|---|---|
| 자료 구조 | 그래프 |
| 최악 시간복잡도 | |
| 공간복잡도 | |
| 목록 |
|---|
|
| 관련 주제 |
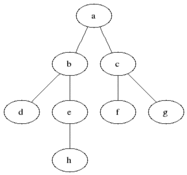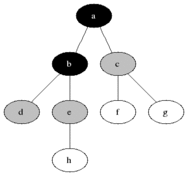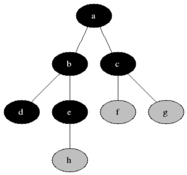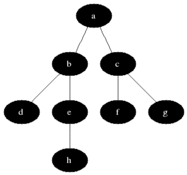
너비 우선 탐색(Breadth-first search, BFS)은 맹목적 탐색방법의 하나로 시작 정점을 방문한 후 시작 정점에 인접한 모든 정점들을 우선 방문하는 방법이다. 더 이상 방문하지 않은 정점이 없을 때까지 방문하지 않은 모든 정점들에 대해서도 너비 우선 검색을 적용한다. OPEN List는 큐를 사용해야만 레벨 순서대로 접근이 가능하다.
의사 코드
def breadth_first_search(problem):
# a FIFO open_set
open_set = Queue()
# an empty set to maintain visited nodes
closed_set = set()
# a dictionary to maintain meta information (used for path formation)
meta = dict() # key -> (parent state, action to reach child)
# initialize
start = problem.get_start_state()
meta[start] = (None, None)
open_set.enqueue(start)
while not open_set.is_empty():
parent_state = open_set.dequeue()
if problem.is_goal(parent_state):
return construct_path(parent_state, meta)
for (child_state, action) in problem.get_successors(parent_state):
if child_state in closed_set:
continue
if child_state not in open_set:
meta[child_state] = (parent_state, action)
open_set.enqueue(child_state)
closed_set.add(parent_state)
def construct_path(state, meta):
action_list = list()
while True:
row = meta[state]
if len(row) == 2:
state = row[0]
action = row[1]
action_list.append(action)
else:
break
return action_list.reverse()
장단점
- 장점
- 출발노드에서 목표노드까지의 최단 길이 경로를 보장한다.
- 단점
- 경로가 매우 길 경우에는 탐색 가지가 급격히 증가함에 따라 보다 많은 기억 공간을 필요로 하게 된다.
- 해가 존재하지 않는다면 유한 그래프(finite graph)의 경우에는 모든 그래프를 탐색한 후에 실패로 끝난다.
- 무한 그래프(infinite graph)의 경우에는 결코 해를 찾지도 못하고, 끝내지도 못한다.
같이 보기
| 이 글은 수학에 관한 토막글입니다. 여러분의 지식으로 알차게 문서를 완성해 갑시다. |

