빗질 정렬
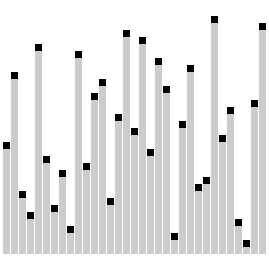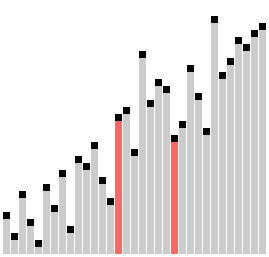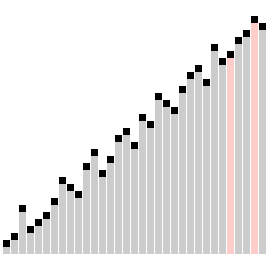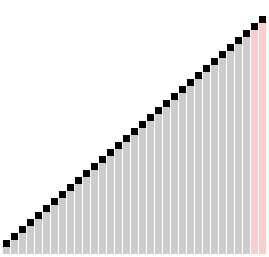 Comb sort with shrink factor k=1.24733 | |
| 분류 | 정렬 알고리즘 |
|---|---|
| 자료 구조 | 배열 |
| 최악 시간복잡도 | [1] |
| 최선 시간복잡도 | |
| 평균 시간복잡도 | : 여기서 p는 증가 수[1] |
| 공간복잡도 | |
빗질 정렬(comb sort)은 버블 정렬을 개선한 정렬 알고리즘으로, 1980년 Włodzimierz Dobosiewicz가 설계하였다. 다른 정렬 알고리즘에 비해 상대적으로 단순하다.[1][2] 1991년에 스테판 레이시(영어: Stephen Lacey)와 리차드 박스(영어: Richard Box)가 재발견하였다.[3]
알고리즘
기본 개념은 리스트의 끝 가까이의 작은 값들("거북이"라고 함)을 제거하는 것인데, 그 이유는 거품 정렬이 이 상황에서 정렬의 속도를 떨어트리기 때문이다. 목록 처음 가까이에 있는 큰 값들("토끼"라고 함)은 거품 정렬에 문제를 일으키지 않는다.
의사코드
function combsort(array input)
gap := input.size // Initialize gap size
shrink := 1.3 // Set the gap shrink factor
sorted := false
loop while sorted = false
// Update the gap value for a next comb
gap := floor(gap / shrink)
if gap > 1
sorted := false // We are never sorted as long as gap > 1
else
gap := 1
sorted := true // If there are no swaps this pass, we are done
end if
// A single "comb" over the input list
i := 0
loop while i + gap < input.size // See Shell sort for a similar idea
if input[i] > input[i+gap]
swap (input[i], input[i+gap])
sorted := false
// If this assignment never happens within the loop,
// then there have been no swaps and the list is sorted.
end if
i := i + 1
end loop
end loop
end function
import math
def comb_sort(arr):
gap = len(arr)
shrink = 1.3
sorted = False
while not sorted:
gap = math.floor(gap / shrink)
if gap > 1:
sorted = False
else:
gap = 1
sorted = True
i = 0
while i + gap < len(arr):
if arr[i] > arr[i+gap]:
arr[i], arr[i+gap] = arr[i+gap], arr[i]
sorted = False
i = i + 1
return arr
같이 보기
각주
- ↑ 가 나 다 Brejová, B. (2001년 9월 15일). “Analyzing variants of Shellsort”. 《Inf. Process. Lett.》 79 (5): 223–227. doi:10.1016/S0020-0190(00)00223-4.
- ↑ Wlodzimierz Dobosiewicz (1980). “An efficient variation of bubble sort”. 《Information Processing Letters》 11: 5–6. doi:10.1016/0020-0190(80)90022-8.
- ↑ "A Fast Easy Sort" Archived 2012년 4월 14일 - 웨이백 머신, Byte Magazine, April 1991



