റോക്കറ്റ്

ഒരു മിസൈലോ, ബഹിരാകാശവാഹനമോ, വിമാനമോ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ മറ്റു വാഹനങ്ങളോ അതിന്റെ സഞ്ചാരത്തിനാവശ്യമായ ശക്തി ഒരു റോക്കറ്റ് എഞ്ചിനിൽ നിന്നും സ്വീകരിച്ചാണ് സഞ്ചരിക്കുന്നതെങ്കിൽ അതിനെ ഒരു റോക്കറ്റ് എന്നു വിളിക്കും rocket (from Italian rocchetto "bobbin")[nb 1][1] റോക്കറ്റ് എഞ്ചിന്റെ നീക്കങ്ങൾക്കുള്ള ശക്തിമുഴുവൻ വിക്ഷേപണത്തിനുമുൻപുതന്നെ സംഭരിച്ചിട്ടുള്ള പ്രൊപ്പല്ലന്റിൽ നിന്നുമായിരിക്കും.[2] റോക്കറ്റ് എൻജിനുകളുടെ പ്രവർത്തനവും പ്രതിപ്രവർത്തനവും പുഷ് റോക്കറ്റുകൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ഉയർന്ന വേഗതയിൽ എതിർ ദിശയിൽ അവയുടെ മുഴുവൻ ശക്തിയും വിനിയോഗിച്ചുകൊണ്ട് ശൂന്യാകാശത്തിൽ പ്രവർത്തിക്കാൻ കഴിയുന്നു.
ചരിത്രം
-
Drawing of a Chinese soldier lighting a rocket's fuse (1890)
-
Depiction of a rocket (1405)


ഇനങ്ങൾ
രൂപകൽപ്പന
ഭാഗങ്ങൾ
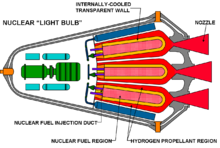
എഞ്ചിനുകൾ

ഇന്ധനം
ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ
സൈനികം

ശാസ്ത്രത്തിലും ഗവേഷണത്തിലും

ബഹിരാകാശയാത്രയ്ക്ക്
തിരികെയെടുക്കൽ

വിനോദാവശ്യത്തിന്
ശബ്ദം

ഭൗതികശാസ്ത്രം
പ്രവർത്തനം
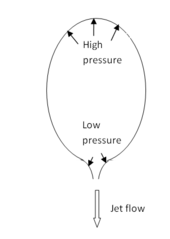

Forces on a rocket in flight
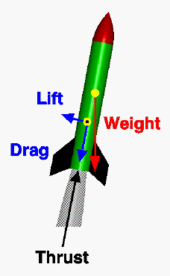
Drag
Net thrust

Ideally Expanded
Overexpanded
Grossly overexpanded
Total impulse
Specific impulse
| Rocket | Propellants | Isp, vacuum (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Space shuttleliquid engines | LOX/LH2 | 453[3] |
| Space shuttlesolid motors | APCP | 268[3] |
| Space shuttleOMS | NTO/MMH | 313[3] |
| Saturn Vstage 1 | LOX/RP-1 | 304[3] |
Delta-v (rocket equation)
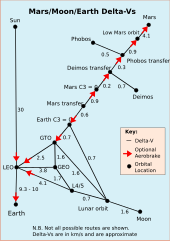
Mass ratios
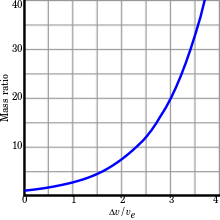
| Vehicle | Takeoff Mass | Final Mass | Mass ratio | Mass fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 (vehicle + payload) | 746,000 kg [6] (~1,645,000 lb) | 2,700 kg + 16,000 kg[6] (~6,000 lb + ~35,300 lb) | 39.9 | 0.975 |
| Titan 23G first stage | 117,020 kg (258,000 lb) | 4,760 kg (10,500 lb) | 24.6 | 0.959 |
| Saturn V | 3,038,500 kg[7] (~6,700,000 lb) | 13,300 kg + 118,000 kg[7] (~29,320 lb + ~260,150 lb) | 23.1 | 0.957 |
| Space Shuttle (vehicle + payload) | 2,040,000 kg (~4,500,000 lb) | 104,000 kg + 28,800 kg (~230,000 lb + ~63,500 lb) | 15.4 | 0.935 |
| Saturn 1B (stage only) | 448,648 kg[8] (989,100 lb) | 41,594 kg[8] (91,700 lb) | 10.7 | 0.907 |
| Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer | 10,024.39 kg (22,100 lb) | 1,678.3 kg (3,700 lb) | 6.0 | 0.83 |
| V-2 | 13,000 kg (~28,660 lb) (12.8 ton) | 3.85 | 0.74 [9] | |
| X-15 | 15,420 kg (34,000 lb) | 6,620 kg (14,600 lb) | 2.3 | 0.57[10] |
| Concorde | ~181,000 kg (400,000 lb [10]) | 2 | 0.5[10] | |
| Boeing 747 | ~363,000 kg (800,000 lb[10]) | 2 | 0.5[10] |
Staging


Acceleration and thrust-to-weight ratio
Energy
Energy efficiency

Oberth effect
ഇവയും കാണുക
Lists
- Chronology of Pakistan's rocket tests
- List of rockets
- Timeline of rocket and missile technology
- Timeline of spaceflight
General Rocketry
- Astrodynamics—the study of spaceflight trajectories
- Gantry
- Pendulum rocket fallacy—an instability of rockets
- Rocket garden—a place for viewing unlaunched rockets
- Rocket launch
- Rocket launch site
- Variable-mass system—the form of Newton's second law used for describing rocket motion
Propulsion and Propellant
- Ammonium Perchlorate Composite Propellant—Most common solid rocket propellant
- Bipropellant rocket—two-part liquid or gaseous fuelled rocket
- Hot Water rocket—powered by boiling water
- Pulsed Rocket Motors—solid rocket that burns in segments
- Spacecraft propulsion—describes many different propulsion systems for spacecraft
- Tripropellant rocket—variable propellant mixes can improve performance
Recreational Rockets
- High-powered rocket
- National Association of Rocketry
- Tripoli Rocketry Association
Recreational Pyrotechnic Rocketry
- Bottle rocket—small firework type rocket often launched from bottles
- Skyrocket—fireworks that typically explode at apogee
Weaponry
- Air-to-ground rockets
- Fire Arrow—one of the earliest types of rocket
- Katyusha rocket launcher—rack mounted rocket
- Rocket-propelled grenade—military use of rockets
- Shin Ki Chon—Korean variation of the Chinese fire arrow
- VA-111 Shkval—Russian rocket-propelled supercavitation torpedo
Rockets for Research
- Rocket plane—winged aircraft powered by rockets
- Rocket sled—used for high speeds along ground
- Sounding rocket—suborbital rocket used for atmospheric and other research
Misc
- Aircraft
- Equivalence principle—Einstein was able to show that the effects of gravity were completely equivalent to a rocket's acceleration in any small region of space
- Rocket Festival—Tradition bamboo rockets of Laos and Northeastern Thailand
- Rocket mail—the delivery of mail by rocket or missile.
കുറിപ്പുകൾ
- ↑ Bernhard, Jim (1 January 2007). Porcupine, Picayune, & Post: How Newspapers Get Their Names. University of Missouri Press. p. 126. ISBN 9780826266019. Archived from the original on 19 November 2017. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ Sutton, George P.; Biblarz, Oscar (2001). Rocket Propulsion Elements. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780471326427. Archived from the original on 12 January 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Braeunig, Robert A. (2008). "Rocket Propellants". Rocket & Space Technology.
- ↑ "table of cislunar/mars delta-vs". Archived from the original on 2007-07-01.
- ↑ "cislunar delta-vs". Strout.net. Archived from the original on 2000-03-12. Retrieved 2012-12-10.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Astronautix- Ariane 5g
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Astronautix - Saturn V
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Astronautix- Saturn IB
- ↑ Astronautix-V-2
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 AIAA2001-4619 RLVs
പുറത്തേക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
Governing agencies
- FAA Office of Commercial Space Transportation
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- National Association of Rocketry (USA)
- Tripoli Rocketry Association
- Asoc. Coheteria Experimental y Modelista de Argentina Archived 2020-10-27 at the Wayback Machine.
- United Kingdom Rocketry Association
- IMR - German/Austrian/Swiss Rocketry Association
- Canadian Association of Rocketry
- Indian Space Research Organisation
Information sites
- Encyclopedia Astronautica - Rocket and Missile Alphabetical Index
- Rocket and Space Technology
- Gunter's Space Page - Complete Rocket and Missile Lists
- Rocketdyne Technical Articles
- Relativity Calculator - Learn Tsiolkovsky's rocket equations
- Robert Goddard--America's Space Pioneer Archived 2009-02-05 at the Wayback Machine.



