Endocrine system
The endocrine system includes those organs of the body which produce hormones. It helps to regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, and plays a part also in mood.[1] The field of medicine that deals with disorders of endocrine glands is endocrinology.
In physiology, the endocrine system is a system of glands, each of which secretes a type of hormone directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body.
The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its chemicals using ducts.[2] The endocrine system is an information signal system like the nervous system, yet its effects and mechanism are different.
The endocrine system's effects are slow to start, and long-lasting in their response. The nervous system sends information quickly, and responses are generally short lived. Hormones are complex chemicals released from endocrine tissue into the bloodstream where they travel to target tissues and trigger a response.
Features of endocrine glands are, in general, they have no ducts, they have a good blood supply, and usually they have vacuoles or granules inside their cells, storing their hormones.
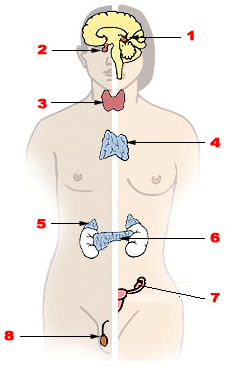
Endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete
Central nervous system
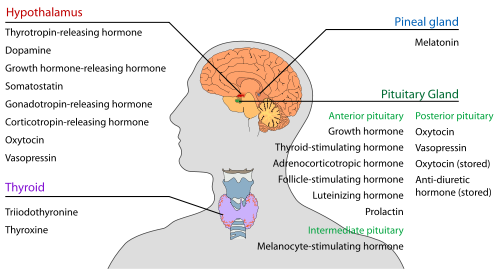
- Hypothalamus produces
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Neuroendocine cells of the Preoptic area
- Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) Neuroendocrine neurons of the Arcuate nucleus
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons
- Vasopressin Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons
- Somatostatin (SS; also GHIH, growth hormone-inhibiting hormone) Neuroendocrince cells of the Periventricular nucleus
- Prolactin inhibiting hormone or PIH or Dopamine (DA) Dopamine neurons of the arcuate nucleus
- Prolactin releasing hormone
- Pineal body produces
- Melatonin (mainly) Pinealocytes
- Pituitary gland (hypophysis) produces
- Anterior pituitary lobe (adenohypophysis)
- Growth hormone (GH) Somatotropes
- Prolactin (PRL) Lactotropes
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, corticotropin) Corticotropes
- Lipotropin Corticotropes
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) Thyrotropes
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Gonadotropes
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) Gonadotropes
- Posterior pituitary lobe (neurohypophysis)
- Oxytocin Magnocellular neurosecretory cells
- Vasopressin (AVP; also ADH, antidiuretic hormone) Magnocellular neurosecretory cells
- Intermediate pituitary lobe (pars intermedia)
- Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Melanotroph
- Anterior pituitary lobe (adenohypophysis)
Thyroid
- Thyroid produces
- Triiodothyronine (T3), the potent form of thyroid hormone Thyroid epithelial cell
- Thyroxine (T4), also known as tetraiodothyronine: it is a less active form of thyroid hormone (mainly) Thyroid epithelial cells
- Calcitonin Parafollicular cells
Parathyroid
- Parathyroid hormone PTH triggers an increase in blood calcium levels.
Muscles
- Striated muscle produces
- Thrombopoietin Myocytes
Alimentary system
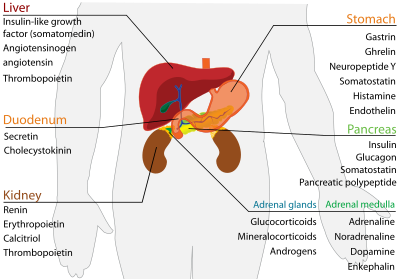
- Stomach produces
- Duodenum produces
- Cholecystokinin I cells
- Liver produces
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) (mainly) Hepatocytes
- Angiotensinogen Hepatocytes
- Thrombopoietin Hepatocytes
- Pancreas produces
- Insulin (mainly) β Islet cells
- Glucagon (also mainly) α Islet cells
- Somatostatin δ Islet cells
- Pancreatic polypeptide PP cells
Kidney
- Kidney produces
- Renin (Primarily) Juxtaglomerular cells
- Erythropoietin (EPO) Extraglomerular mesangial cells
- Calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D3)
- Thrombopoietin
Adrenal glands
- Adrenal glands
- Adrenal cortex produces
- Glucocorticoids (chiefly cortisol) Zona fasciculata and Zona reticularis cells
- Mineralocorticoids (chiefly aldosterone) Zona glomerulosa cells
- Androgens (including DHEA and testosterone) Zona fasciculata and Zona reticularis cells
- Adrenal medulla produces
- Adrenaline (epinephrine) (Primarily) Chromaffin cells
- Noradrenaline (norepinephrine) Chromaffin cells
- Dopamine Chromaffin cells
- Enkephalin Chromaffin cells
- Adrenal cortex produces
Reproductive system
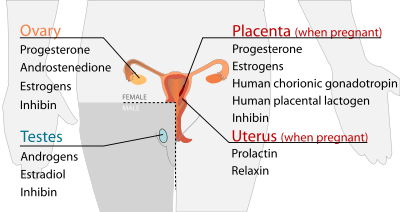
Male
- Testes
- Androgens (chiefly testosterone) Leydig cells
- Oestradiol Sertoli cells
- Inhibin Sertoli cells
Female
- Oestrous cycle
- Ovarian follicle/Corpus luteum
- Progesterone Granulosa cells, Theca cells
- Androstenedione Theca cells
- Oestrogens (mainly oestradiol) Granulosa cells
- Inhibin Granulosa cells
- Placenta (when a woman is pregnant)
- Progesterone (Primarily)
- Oestrogens (mainly oestriol) (Also primarily)
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) Syncytiotrophoblast
- Human placental lactogen (HPL) Syncytiotrophoblast
- Inhibin Fetal trophoblasts
- Uterus (when a woman is pregnant)
- Ovarian follicle/Corpus luteum
Calcium regulation
- Parathyroid produces
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Parathyroid chief cell
- Skin produces
- Vitamin D3 (calciferol)
Miscellaneous

- Heart produces
- Atrial-natriuretic peptide (ANP) Cardiac myocytes
- Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) Cardiac myocytes
- Adenosine Cardiac myocytes
- Adipose tissue
- Leptin (Primarily) Adipocytes
- Oestrogens (mainly oestrone) Adipocytes
- Bone marrow produces
- Thrombopoietin
Related pages
References
- ↑ Collier Judith; et al. (2006). Oxford Handbook of Clinical Specialties 7th edn. Oxford University Press. pp. 350 -351. ISBN 0-19-853085-4.
- ↑ It derives from the Greek words endo meaning inside, within, and crinis for secrete.
Other websites
- Journals Designed for Clinical Endocrinologists
- Islet cell antibody Archived 2007-11-03 at the Wayback Machine
- Binding of antibody to pancreas Archived 2009-03-16 at the Wayback Machine
- Kidshealth.org
| Endocrine system |
| Adrenal gland - Corpus luteum - Hypothalamus - Ovaries - Pancreas - Parathyroid gland - Pineal gland - Pituitary gland - Testes - Thyroid gland - Hormone |