Inner ear
| Inner ear | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Artery | labyrinthine artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | auris interna |
| MeSH | D007758 |
| TA | A15.3.03.001 |
| FMA | 60909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

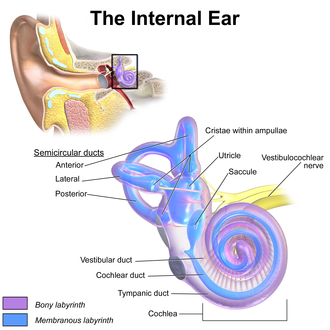
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. It is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance.[1] In mammals, it consists of two main working parts inside a bony labyrinth: [2]
- The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve.
- The balance system. This has three semi-circular canals, which are set at right angles to each other.
The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with many variations in form and function. The inner ear is supplied with the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates.