หัวใจหยุดเต้น
| Cardiac arrest | |
|---|---|
| ชื่ออื่น | Cardiopulmonary arrest, circulatory arrest, sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), sudden cardiac death (SCD)[1] |
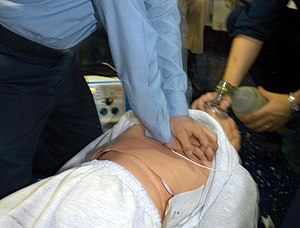 | |
| CPR being administered during a simulation of cardiac arrest. | |
| สาขาวิชา | Cardiology, emergency medicine |
| อาการ | Loss of consciousness, abnormal or no breathing[1][2] |
| การตั้งต้น | Older age[3] |
| สาเหตุ | Coronary artery disease, congenital heart defect, major blood loss, lack of oxygen, very low potassium, heart failure[4] |
| วิธีวินิจฉัย | Finding no pulse[1] |
| การป้องกัน | Not smoking, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, healthy eating[5] |
| การรักษา | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation[6] |
| พยากรณ์โรค | Survival rate ~ 10% (outside of hospital) 25% (in hospital)[7][8] |
| ความชุก | 13 per 10,000 people per year (outside hospital in the US)[9] |
| การเสียชีวิต | > 425,000 per year (U.S.)[10] |
หัวใจหยุดเต้น (อังกฤษ: cardiac arrest) คือภาวะซึ่งหัวใจไม่มีการบีบตัว ทำงานผิดปกติ หรือทำงานช้าลง ทำให้ไม่มีการไหลเวียนเลือด ทำให้ไม่มีการลำเลียงออกซิเจนไปเลี้ยงร่างกายส่วนต่างๆ เกิดอาการของการทำงานผิดปกติที่อวัยวะต่างๆ ที่เห็นได้อย่างหนึ่งคือการทำงานของสมอง ซึ่งเมื่อไม่มีเลือดเลี้ยงทำให้หมดสติ หากหัวใจหยุดเต้นนานกว่า 5 นาที มีโอกาสเกิดความเสียหายต่อเนื้อสมองได้มาก การช่วยเหลือในทันทีจึงเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ป่วยรอดชีวิตและมีการฟื้นตัวของสมองที่ดี[11]
หัวใจหยุดเต้นเป็นภาวะฉุกเฉินทางการแพทย์ บางครั้งหากได้รับการรักษาทันท่วงทีอาจทำให้หัวใจกลับมาเต้นใหม่ได้ หากมีหัวใจหยุดเต้นเฉียบพลันโดยไม่คาดฝันจนเสียชีวิตใช้ศัพท์ว่า sudden cardiac death วิธีสำคัญในการรักษาภาวะหัวใจหยุดเต้นคือการช่วยกู้ชีพ (CPR) เพื่อสร้างการไหลเวียนของเลือดให้มีเลือดไปเลี้ยงร่างกาย พิจารณาสัญญาณไฟฟ้าหัวใจว่าเป็นชนิดที่สามารถช็อกไฟฟ้าเพื่อช่วยเหลือได้หรือไม่และให้การรักษาตามความเหมาะสม[12]
อ้างอิง
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameFie2009cannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameNIH2016Signcannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameNIH2016Riskcannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameNIH2016Cacannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameNIH2016Precannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameNIH2016Txcannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameAdam2012cannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ Andersen, LW; Holmberg, MJ; Berg, KM; Donnino, MW; Granfeldt, A (26 March 2019). "In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Review". JAMA. 321 (12): 1200–1210. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.1696. PMC 6482460. PMID 30912843.
- ↑ คำเตือนการอ้างอิง:
<ref>tag with nameAHA2015Part4cannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ Meaney, PA; Bobrow, BJ; Mancini, ME; Christenson, J; de Caen, AR; Bhanji, F; Abella, BS; Kleinman, ME; Edelson, DP; Berg, RA; Aufderheide, TP; Menon, V; Leary, M; CPR Quality Summit Investigators, the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee, and the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and, Resuscitation. (23 July 2013). "Cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: [corrected] improving cardiac resuscitation outcomes both inside and outside the hospital: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association". Circulation. 128 (4): 417–35. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829d8654. PMID 23801105.
{cite journal}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (ลิงก์) - ↑ "การช่วยฟื้นคืนชีพ ( Cardiopulmonary resuscitation )" (PDF). คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2010-08-28. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2012-05-11.
- ↑ การจัดการภาวะหัวใจหยุดเต้น