Kino-kino
| Kino-kino | |
|---|---|
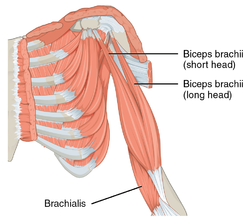 The biceps is a two-headed muscle and is one of the chief flexors of the forearm. Here is the left side, seen from the front. | |
| Mga detalye | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈbaɪsɛps ˈbreɪkiaɪ/ |
| Origin | Short head: coracoid process of the scapula. Long head: supraglenoid tubercle |
| Insertion | Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis into deep fascia on medial part of forearm |
| Artery | Brachial artery |
| Nerve | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C7)[1] |
| Mga aksyon | |
| Antagonista | Triceps brachii muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus biceps brachii |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.013 |
| TA2 | 2464 |
| Anatomikal na terminolohiya | |
An kino-kino iyo an sarong dakulang kalamnan na yaon sa atubangan kan itaas na takyag sa pag-oltanan kan abaga asin kan siko. Parehong payo kan kalamnan an minalataw sa scapula asin minaiba sa pagporma nin saro sanang muscles na tulak na nakatakod sa itaas na takyag. Mantang an kino-kino minalampas kapwa sa abaga asin mga pagsokmolan sa siko, an pangenot na trabaho kaiyan yaon sa siko kun saen binubulokon kaiyan an takyag. An duwang paghirong ini pareho ginagamit kun nagbubukas nin bote na may cork: An inot na mga biceps nag-higot sa cork (supination), dangan binubutong kaini an cork (flexion).[2]
Toltolan
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Cite warning:
<ref>tag with nameBogart2007cannot be previewed because it is defined outside the current section or not defined at all. - ↑ Lippert, Lynn S. (2006). Clinical kinesiology and anatomy
 (4th ed.). Philadelphia: F. A. Davis Company. pp. 126–7. ISBN 978-0-8036-1243-3.
(4th ed.). Philadelphia: F. A. Davis Company. pp. 126–7. ISBN 978-0-8036-1243-3.