PARK7
Protein-deglikaza DJ-1, znana i kao protein 7 Parkinsonove bolesti, jest protein/enzim koji je kod ljudi kodiran genom PARK7 sa hromosoma 1.[5]
Aminokiselinska sekvenca
Dužina polipeptidnog lanca je 189 aminokiselina, a molekulska težina 19.891 Da.[6]
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MASKRALVIL | AKGAEEMETV | IPVDVMRRAG | IKVTVAGLAG | KDPVQCSRDV | ||||
| VICPDASLED | AKKEGPYDVV | VLPGGNLGAQ | NLSESAAVKE | ILKEQENRKG | ||||
| LIAAICAGPT | ALLAHEIGFG | SKVTTHPLAK | DKMMNGGHYT | YSENRVEKDG | ||||
| LILTSRGPGT | SFEFALAIVE | ALNGKEVAAQ | VKAPLVLKD |
Struktura
Gen
Gen PARK7, također poznat kao DJ-1, kodira protein iz porodice peptidaza C56. Ljudski gen PARK7 ima osam egzona i nalazi se na hromozomskom pojasu 1p36.23.[5]
Protein
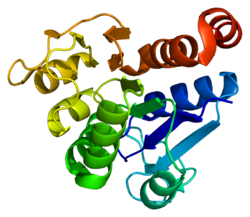
Ljudska proteinska deglikaza DJ-1 je veličine 20 kDa i sastoji se od 189 aminokiselina sa ukupno sedam β-lanaca i devet α-heliksa i prisutna je kao dimer.[7][8][9] Proteinske strukture ljudskog proteina DJ-1, šaperona Hsp31Escherichia coli, YhbO i YajL i proteaze Archaea evolucijski su konzervirane.[10]
Funkcija
U oksidativnom stanju, protein deglikaza DJ-1 inhibira agregaciju α-sinukleina putem svoje prateće aktivnosti,[11][12] funkcionifajući na taj način kao redoks-senzitivni šaperon i kao senzor za oksidativnog stresa. U skladu s tim, DJ-1 očigledno štiti neurone od oksidativnog stresa i ćelijske smrti.[5] Paralelno, protein DJ-1 djeluje kao pozitivan regulator transkripcije zavisne od androgenoreceptorski ovisne transkripcije. DJ-1 se eksprimira u neurvmojoj retini, mrežnjsčnom pigmentnom sloju i njenom epitelu kod sisara, gdje ima neuroprotektivnu ulogu protiv oksidativnog stresa i u fiziološkim i u patološkim stanjima.[13][14]
Pokazalo se da pirolokvnolin-kvinon (PQQ) smanjuje samooksidaciju DJ-1 proteina, što je rani korak u nastanku nekih oblika Parkinsonove bolesti.[15]
Pokazalo se da funkcionalni DJ-1 protein veže metale i štiti od citotoksičnosti izazvane metalima bakar i živa.[16]
Klinički značaj
Defekti ovog gena uzrok su autosomno recesivnog ranog početka Parkinsonova bolest 7.[5][17]
Interakcije
Pokazalo se da je PARK7 u interakciji sa:
Također pogledajte
Reference
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000116288 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028964 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b c d "Entrez Gene: PARK7".
- ^ "UniProt, Q99497" (jezik: eng.). Pristupljeno 3. 12. 2021.CS1 održavanje: nepoznati jezik (link)
- ^ "Uniprot: Q99497 - PARK7_HUMAN".
- ^ Honbou K, Suzuki NN, Horiuchi M, Niki T, Taira T, Ariga H, Inagaki F (Aug 2003). "The crystal structure of DJ-1, a protein related to male fertility and Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (33): 31380–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305878200. PMID 12796482.
- ^ Tao X, Tong L (Aug 2003). "Crystal structure of human DJ-1, a protein associated with early onset Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (33): 31372–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304221200. PMID 12761214.
- ^ Lee SJ, Kim SJ, Kim IK, Ko J, Jeong CS, Kim GH, Park C, Kang SO, Suh PG, Lee HS, Cha SS (Nov 2003). "Crystal structures of human DJ-1 and Escherichia coli Hsp31, which share an evolutionarily conserved domain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (45): 44552–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304517200. PMID 12939276.
- ^ Shendelman S, Jonason A, Martinat C, Leete T, Abeliovich A (Nov 2004). "DJ-1 is a redox-dependent molecular chaperone that inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregate formation". PLOS Biology. 2 (11): e362. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020362. PMC 521177. PMID 15502874.
- ^ Zhou W, Zhu M, Wilson MA, Petsko GA, Fink AL (Mar 2006). "The oxidation state of DJ-1 regulates its chaperone activity toward alpha-synuclein". Journal of Molecular Biology. 356 (4): 1036–48. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.030. PMID 16403519.
- ^ Martín-Nieto, José; Uribe, Mary Luz; Esteve-Rudd, Julián; Herrero, María Trinidad; Campello, Laura (2019). "A role for DJ-1 against oxidative stress in the mammalian retina". Neuroscience Letters (jezik: engleski). 708: 134361. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134361. hdl:10045/94474. PMID 31276729. S2CID 195813073.
- ^ Shadrach, Karen G.; Rayborn, Mary E.; Hollyfield, Joe G.; Bonilha, Vera L. (2013). Shi, Xianglin (ured.). "DJ-1-Dependent Regulation of Oxidative Stress in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE)". PLOS ONE (jezik: engleski). 8 (7): e67983. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...867983S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067983. PMC 3699467. PMID 23844142.
- ^ Nunome K, Miyazaki S, Nakano M, Iguchi-Ariga S, Ariga H (Jul 2008). "Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents oxidative stress-induced neuronal death probably through changes in oxidative status of DJ-1". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 31 (7): 1321–6. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.1321. hdl:2115/53726. PMID 18591768.
- ^ Björkblom B, Adilbayeva A, Maple-Grødem J, Piston D, Ökvist M, Xu XM, Brede C, Larsen JP, Møller SG (2013). "Parkinson disease protein DJ-1 binds metals and protects against metal-induced cytotoxicity". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288 (31): 22809–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.482091. PMC 3829365. PMID 23792957.
- ^ Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (Jan 2003). "Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism". Science. 299 (5604): 256–9. Bibcode:2003Sci...299..256B. doi:10.1126/science.1077209. PMID 12446870. S2CID 27186691.
- ^ Mukherjee K, Slawson JB, Christmann BL, Griffith LC (2014). "Neuron-specific protein interactions of Drosophila CASK-β are revealed by mass spectrometry". Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 7: 58. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2014.00058. PMC 4075472. PMID 25071438.
- ^ Niki T, Takahashi-Niki K, Taira T, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Feb 2003). "DJBP: a novel DJ-1-binding protein, negatively regulates the androgen receptor by recruiting histone deacetylase complex, and DJ-1 antagonizes this inhibition by abrogation of this complex". Molecular Cancer Research. 1 (4): 247–61. PMID 12612053.
- ^ Takahashi K, Taira T, Niki T, Seino C, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Oct 2001). "DJ-1 positively regulates the androgen receptor by impairing the binding of PIASx alpha to the receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37556–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101730200. PMID 11477070.
Dopunska literatura
- Cookson MR (Jan 2003). "Pathways to Parkinsonism". Neuron. 37 (1): 7–10. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)01166-2. PMID 12526767. S2CID 14513509.
- Bonifati V, Oostra BA, Heutink P (Mar 2004). "Linking DJ-1 to neurodegeneration offers novel insights for understanding the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease". Journal of Molecular Medicine. 82 (3): 163–74. doi:10.1007/s00109-003-0512-1. PMID 14712351. S2CID 32685319.
- Le W, Appel SH (Feb 2004). "Mutant genes responsible for Parkinson's disease". Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 4 (1): 79–84. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2003.09.005. PMID 15018843.
- Abou-Sleiman PM, Healy DG, Wood NW (Oct 2004). "Causes of Parkinson's disease: genetics of DJ-1". Cell and Tissue Research. 318 (1): 185–8. doi:10.1007/s00441-004-0922-6. PMID 15503154. S2CID 9453283.
- Pankratz N, Foroud T (Apr 2004). "Genetics of Parkinson disease". NeuroRx. 1 (2): 235–42. doi:10.1602/neurorx.1.2.235. PMC 534935. PMID 15717024.
- Heutink P (2006). "PINK-1 and DJ-1--new genes for autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa. 70 (70): 215–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-211-45295-0_33. ISBN 978-3-211-28927-3. PMID 17017532.
- Lev N, Roncevic D, Roncevich D, Ickowicz D, Melamed E, Offen D (2007). "Role of DJ-1 in Parkinson's disease". Journal of Molecular Neuroscience. 29 (3): 215–25. doi:10.1385/JMN:29:3:215. PMID 17085780. S2CID 85481215.
- Nagakubo D, Taira T, Kitaura H, Ikeda M, Tamai K, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Feb 1997). "DJ-1, a novel oncogene which transforms mouse NIH3T3 cells in cooperation with ras". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 231 (2): 509–13. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6132. PMID 9070310.
- Taira T, Takahashi K, Kitagawa R, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Jan 2001). "Molecular cloning of human and mouse DJ-1 genes and identification of Sp1-dependent activation of the human DJ-1 promoter". Gene. 263 (1–2): 285–92. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00590-4. PMID 11223268.
- van Duijn CM, Dekker MC, Bonifati V, Galjaard RJ, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Snijders PJ, Testers L, Breedveld GJ, Horstink M, Sandkuijl LA, van Swieten JC, Oostra BA, Heutink P (Sep 2001). "Park7, a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, on chromosome 1p36". American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (3): 629–34. doi:10.1086/322996. PMC 1235491. PMID 11462174.
- Takahashi K, Taira T, Niki T, Seino C, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Oct 2001). "DJ-1 positively regulates the androgen receptor by impairing the binding of PIASx alpha to the receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37556–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101730200. PMID 11477070.
- Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (Jan 2003). "Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism". Science. 299 (5604): 256–9. Bibcode:2003Sci...299..256B. doi:10.1126/science.1077209. PMID 12446870. S2CID 27186691.
- Bonifati V, Dekker MC, Vanacore N, Fabbrini G, Squitieri F, Marconi R, Antonini A, Brustenghi P, Dalla Libera A, De Mari M, Stocchi F, Montagna P, Gallai V, Rizzu P, van Swieten JC, Oostra B, van Duijn CM, Meco G, Heutink P (Sep 2002). "Autosomal recessive early onset parkinsonism is linked to three loci: PARK2, PARK6, and PARK7". Neurological Sciences. 23 Suppl 2: S59-60. doi:10.1007/s100720200069. PMID 12548343. S2CID 13625056.
- Niki T, Takahashi-Niki K, Taira T, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Feb 2003). "DJBP: a novel DJ-1-binding protein, negatively regulates the androgen receptor by recruiting histone deacetylase complex, and DJ-1 antagonizes this inhibition by abrogation of this complex". Molecular Cancer Research. 1 (4): 247–61. PMID 12612053.
- Tao X, Tong L (Aug 2003). "Crystal structure of human DJ-1, a protein associated with early onset Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (33): 31372–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304221200. PMID 12761214.
- Honbou K, Suzuki NN, Horiuchi M, Niki T, Taira T, Ariga H, Inagaki F (Aug 2003). "The crystal structure of DJ-1, a protein related to male fertility and Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (33): 31380–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305878200. PMID 12796482.
- Dekker M, Bonifati V, van Swieten J, Leenders N, Galjaard RJ, Snijders P, Horstink M, Heutink P, Oostra B, van Duijn C (Jul 2003). "Clinical features and neuroimaging of PARK7-linked parkinsonism". Movement Disorders. 18 (7): 751–7. doi:10.1002/mds.10422. PMID 12815653. S2CID 44253517.
- Miller DW, Ahmad R, Hague S, Baptista MJ, Canet-Aviles R, McLendon C, Carter DM, Zhu PP, Stadler J, Chandran J, Klinefelter GR, Blackstone C, Cookson MR (Sep 2003). "L166P mutant DJ-1, causative for recessive Parkinson's disease, is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome system". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (38): 36588–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304272200. PMID 12851414.
Vanjski linkovi
Ovaj članak uključuje tekst iz Nacionalne medicinske biblioteke Sjedinjenih Država, koji je u javnom vlasništvu.