Results of the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries
| Results of the Democratic Party presidential primaries | |
|---|---|
← 2004 2012 → |
| Democratic Party | |
|---|---|
| Republican Party | |
| Minor parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
The results of the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries are the detailed outcomes of a series of contests by which members of the United States Democratic Party chose their candidate for the 2008 U.S. presidential election. The contests are held in each of the fifty U.S. states, as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Democrats Abroad. The Northern Mariana Islands was the lone U.S. state or territory which did not have a primary or caucus election in 2008. The outcomes include totals of delegates selected as well as popular votes.
In order to secure the nomination at the convention, a candidate must receive at least 2,117 votes from delegates (a simple majority of the 4,233 delegate votes, bearing in mind half-votes from Florida, Michigan, Democrats Abroad and the territories of Guam, American Samoa, and the U.S. Virgin Islands).
At the time of Hillary Clinton's suspending her campaign early on June 7, 2008, the superdelegate count was 246½ for her, and 478 for Barack Obama, with 99 still uncommitted[1] of the 823½ total then existing.
The breakdown by position for Clinton: 145 DNC, 52½ Representatives, 14 Senators, 17 add-ons, 10½ Governors, and 7½ DPLs.
The breakdown by position for Obama: 229 DNC, 157 Representatives, 34 Senators, 29 add-ons, 20 Governors, and 9 DPLs.
The breakdown for uncommitted voters was: 39 DNC, 22 Representatives, 1½ Senators, 32½ add-ons, 1 Governor, and 3 DPLs.
Dodd and Byrd are considered Senators, the DNC lists them as DPL. Rendell is a Governor, the DNC lists him as a DPL.[2]
National summary
The following table summarizes the results of the local contests below, thus providing a nationwide overview of the nomination process. The data contained in the row entitled Total bound pledged delegates is a subset of the data in the row entitled Total estimated pledged delegates. The bound delegates row does not include estimated delegates from contests in which the final allocation depends on the outcome of further caucuses or conventions.
| Candidates | Uncommitted[3] | Hillary Clinton |
Barack Obama |
John Edwards | ||||||
| Grand total estimated delegates (4,134 of 4,233, 98%; 2,117 to win) |
99 | 1,973 46% |
2,306½ 54% |
4½ <1% | ||||||
| Total estimated superdelegate endorsement[4] (724½ of 823½, 88% of 19%) |
99[5] | 246½ 34% |
478 66% |
0 | ||||||
| Total estimated pledged delegates[6] (3,409½ of 3,409½, 100% of 81%) |
0 | 1,726½ 49% |
1,828½ 51% |
4½ <1% | ||||||
| Total bound pledged delegates[7] (3,341½ of 3,409½, 98% of 81%) |
0 | 1,617½ 48% |
1,722½ 52% |
1½ <1% | ||||||
Local contests
The following table lists events that determine how many pledged delegates are allocated to each presidential candidate. Most states hold a single event to determine delegate allocation. For example, California's primary on February 5 determined how all 370 of that state's pledged delegates would be apportioned.
Some states, however, hold multiple events to determine delegate allocation. For example, Iowa uses a series of events to award pledged delegates. The precinct caucus held on January 3 provided an estimate of delegates to be awarded at later events, but the estimate changed as a result of the March 15 county conventions. Iowa delegates were not actually allocated to candidates until the district conventions on April 26 (when 29 of 45 delegates were awarded) and the state convention on June 14 (when the remaining 16 were awarded). In states with multiple events, like Iowa, the results for early events show the delegate split as it was projected at that time. The rows for later events show updated projections, and outdated projections are indicated with strikeout. In states with events that apportion some but not all of the state's delegates, both actual and estimated allocations are provided.
This table does not list nomination events that have no effect on the allocation of pledged delegates. For example, it does not list state conventions that determine which persons will fill the role of delegates but not the number of delegates awarded or to whom the delegates are pledged.
Additional notes:
- Except where indicated, data comes from the sources referenced at each state's primary or caucus Wikipedia article, available by clicking on a state's name.
- For past events, a dash (–) indicates that a candidate was not on the ballot.
- A The delegate numbers in brackets are estimates. Delegates will be officially allocated during later caucuses, primaries, or conventions.
- B These delegations use multiple caucus, primary, or convention processes to choose national delegates on different days. These processes are explained on each state's caucus article.
- To re-sort this table, click on the double-arrow symbol (
 ) at the top of a column.
) at the top of a column.
Key:
| 1st place delegates earned |
Withdrew prior to contest |
| Event date | Location | Uncommitted[3] | Hillary Clinton |
Barack Obama |
Mike Gravel |
John Edwards |
Dennis Kucinich |
Bill Richardson |
Joe Biden |
Chris Dodd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 3 | Iowa caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 45)[A][B] |
0% | 29% |
38% |
0% | 30% |
0% | 2% | 1% | 0% |
| January 8 | New Hampshire primary Pledged delegates: 22 |
– | 9 39% |
13 36% |
0% | 17% |
1% | 5% | 0% | 0% |
| January 15 | Michigan primary Pledged delegates: 128 |
40% |
69 55% |
59 – |
0% | – | 4% | – | – | 1% |
| January 19 | Nevada precinct caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 25)[A][B] |
0% | 51% |
45% |
0% | 4% | 0% | – | – | – |
| January 26 | South Carolina primary Pledged delegates: 45 |
– | 12 27% |
33 55% |
0% | 18% |
0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| January 29 | Florida primary Pledged delegates: 185 |
– | 105 50% |
67 33% |
0% | 3 14% |
1% | 1% | 1% | 0% |
| February 5 | Alabama primary Pledged delegates: 52 |
0% | 25 42% |
27 56% |
– | 1% | – | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Alaska caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 13)[A][B] |
0% | 25% |
75% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 5 | American Samoa caucus Pledged delegate votes: 3 |
– | 2 57% |
1 42% |
0% | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 5 | Arizona primary Pledged delegates: 56 |
– | 31 50% |
25 42% |
0% | 5% | 0% | 0% | – | 0% |
| February 5 | Arkansas primary Pledged delegates: 35 |
1% | 27 70% |
8 26% |
0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | California primary Pledged delegates: 370 |
– | 204 51% |
166 43% |
0% | 4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Colorado precinct caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 55)[A][B] |
1% | 32% |
67% |
0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Connecticut primary Pledged delegates: 48 |
1% | 22 47% |
26 51% |
0% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Delaware primary Pledged delegates: 15 |
– | 6 42% |
9 53% |
– | 1% | 0% | – | 3% | 0% |
| February 5 | Georgia primary Pledged delegates: 87 |
– | 27 31% |
60 66% |
0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Idaho county caucuses (6/12-14 conv.) Pledged delegates: 12 (of 18)[A][B] |
3% | 2 [ 3 ] 17% |
10 [ 15 ] 80% |
– | 1% | – | – | – | – |
| February 5 | Illinois primary Pledged delegates: 153 |
– | 49 33% |
104 65% |
– | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Kansas local unit conventions Pledged delegates: 21 (of 32)[A][B] |
– | 6 [ 9 ] 26% |
15 [ 23 ] 74% |
– | 0% | 0% | 0% | – | – |
| February 5 | Massachusetts primary Pledged delegates: 93 |
– | 55 56% |
38 41% |
0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Minnesota caucuses Pledged delegates: 72 |
1% | 24 32% |
48 66% |
– | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Missouri primary Pledged delegates: 72 |
0% | 36 48% |
36 49% |
0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | New Jersey primary Pledged delegates: 107 |
– | 59 54% |
48 44% |
– | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | – |
| February 5 | New Mexico caucuses Pledged delegates: 26 |
0% | 14 49% |
12 48% |
– | 1% | 0% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | New York primary Pledged delegates: 232 |
– | 139 57% |
93 40% |
– | 1% | – | – | – | – |
| February 5 | North Dakota precinct caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 13)[A][B] |
– | 37% |
61% |
– | 1% | – | – | – | – |
| February 5 | Oklahoma primary Pledged delegates: 38 |
– | 24 55% |
14 31% |
– | 10% | 1% | 2% | – | 1% |
| February 5 | Tennessee primary Pledged delegates: 68 |
1% | 40 54% |
28 40% |
0% | 4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 5 | Utah primary Pledged delegates: 23 |
– | 9 39% |
14 57% |
0% | 3% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 9 | Louisiana primary Pledged delegates: 56 |
1% | 23 36% |
33 57% |
– | 3% | – | – | 2% | 1% |
| February 9 | Nebraska precinct caucuses (6/20-22 conv.) Pledged delegates: 16 (of 24)[A][B] |
0% | 5 [ 8 ] 32% |
11 [ 16 ] 68% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 9 | U.S. Virgin Islands territorial convention Pledged delegate votes: 3 |
3% | 7% | 3 90% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 9 | Washington precinct caucuses Pledged delegates: 0 (of 78)[A][B] |
1% | 31% |
68% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 10 | Maine municipal caucuses (conv. 5/31) Pledged delegates: 0 (of 24)[A][B] |
1% | 40% |
59% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 5–12 | Democrats Abroad primary Pledged delegate votes: 7 |
0% | 2½ 32% |
4½ 66% |
– | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% | – |
| February 12 | District of Columbia primary Pledged delegates: 15 |
0% | 2 24% |
13 75% |
– | 0% | 0% | 0% | – | – |
| February 12 | Maryland primary Pledged delegates: 70 |
1% | 27 36% |
43 61% |
0% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 12 | Virginia primary Pledged delegates: 83 |
– | 29 35% |
54 64% |
– | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | – |
| February 19 | Hawaii caucuses Pledged delegates: 20 |
0% | 6 24% |
14 76% |
– | 0% | 0% | – | – | – |
| February 19 | Wisconsin primary Pledged delegates: 74 |
0% | 32 41% |
42 58% |
0% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| March 4 | Ohio primary Pledged delegates: 141 |
– | 74 53% |
67 45% |
– | 2% | – | – | – | – |
| March 4 | Rhode Island primary Pledged delegates: 21 |
1% | 13 58% |
8 40% |
– | 1% | – | – | – | – |
| March 4 | Texas primary Pledged delegates: 126 (of 193)[B] |
– | 65 51% |
61 47% |
– | 1% | – | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| March 4 | Texas precinct conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 193)[A][B] |
0% | 44% |
56% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| March 4 | Vermont primary Pledged delegates: 15 |
– | 6 39% |
9 59% |
– | 1% | 1% | – | – | – |
| March 8 | Wyoming county caucuses Pledged delegates: 7 (of 12)[A][B] |
1% | 3 38% |
4 61% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| March 11 | Mississippi primary Pledged delegates: 33 |
0% | 13 37% |
20 61% |
0% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| February 19 – March 14 | North Dakota legislative district conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 13)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| March 15 | Iowa county conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 45)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| February 20 – March 17 | Colorado county assemblies/conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 55)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| March 29 | Texas county and senatorial district conventions (see 6/6-7) Pledged delegates: 0 (of 193)[A][B] |
– | [ 30 ] | [ 37 ] | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| April 4–6 | North Dakota state convention Pledged delegates: 13 (of 13)[B] |
– | 5 | 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| February 23 – April 12[8] | Nevada county conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 25)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| April 22 | Pennsylvania primary Pledged delegates: 158 |
– | 85 55% |
73 45% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| April 5–26 | Washington legislative district caucuses/county conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 78)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| April 26 | Iowa district conventions (see 6/14) Pledged delegates: 29 (of 45)[B] |
– | 9 [ 14 ] |
20 [ 28 ] |
– | [ 3 ] |
– | – | – | – |
| May 3 | Guam territorial convention Pledged delegate votes: 4 |
– | 2 50% |
2 50% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 6 | Indiana primary Pledged delegates: 72 |
– | 38 51% |
34 49% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 6 | North Carolina primary Pledged delegates: 115 |
1% | 48 42% |
67 56% |
1% | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 13 | West Virginia primary Pledged delegates: 28 |
– | 20 67% |
8 26% |
– | 7% | – | – | – | – |
| May 13–16 | Colorado congressional district conventions Pledged delegates: 36 (of 55)[B] |
– | 13 | 23 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 17 | Colorado state convention Pledged delegates: 19 (of 55)[B] |
– | 6 | 13 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 17 | Kansas state convention Pledged delegates: 11 (of 32)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 17 | Nevada state convention Pledged delegates: 25 (of 25)[B] |
– | 11 | 14 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 17 | Washington congressional district caucuses (6/13-15 conv.) Pledged delegates: 51 (of 78)[B] |
– | 17 [ 26 ] |
34 [ 52 ] |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 20 | Kentucky primary Pledged delegates: 51 |
2% | 37 66% |
14 30% |
– | 2% | – | – | – | – |
| May 20 | Oregon primary Pledged delegates: 52 |
- | 21 41% |
31 59% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 24 | Alaska state convention Pledged delegates: 13 (of 13)[B] |
– | 3 | 10 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 24 | Wyoming state convention Pledged delegates: 5 (of 12)[B] |
– | 2 | 3 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| May 31 | Maine state convention, (caucus 2/10) Pledged delegates: 24 (of 24)[B] |
– | 9 | 15 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 1 | Puerto Rico primary Pledged delegates: 55 |
– | 38 68% |
17 32% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 3 | Montana primary Pledged delegates: 16 |
2% |
7 41% |
9 56% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 3 | South Dakota primary Pledged delegates: 15 |
– | 9 55% |
6 45% |
– | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 6–7 | Texas state convention (see 3/29) Pledged delegates: 67 (of 193)[B] |
– | 29 | 38 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 1–10 | Nebraska county conventions Pledged delegates: 0 (of 24)[A][B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 12–14 | Idaho state convention (2/5 caucus) Pledged delegates: 6 (of 18)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 14 | Iowa state convention (4/26 conv.) Pledged delegates: 16 (of 45)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 13–15 | Washington state convention (5/17 caucus) Pledged delegates: 27 (of 78)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 21 | Puerto Rico commonwealth convention Pledged delegates: 0 (of 55)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| June 20–22 | Nebraska state convention (2/9 caucus) Pledged delegates: 8 (of 24)[B] |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
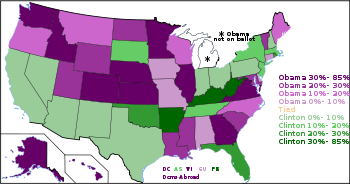
Popular vote

'We're winning the popular vote,' Hillary Clinton said last week.... 'More people have voted for me than for anyone who has ever run for the Democratic nomination.' These statements must be read with the sort of close grammatical and definitional care that used to inform her husband’s descriptions of his personal entanglements. They are not quite true in the normal sense, but if made under oath they would not be prosecutable for perjury, either.
— Henrik Hertzberg, The New Yorker[9]
This section reports popular vote data for the two leading candidates, Barack Obama and Hillary Clinton. Officially, the popular vote does not matter in the Democratic presidential nomination. However, political experts sometimes look to the popular vote as an indicator of candidate support and momentum. News media frequently report the popular vote on election night, declaring states "won" on this basis. Superdelegates may also consider the popular vote when making their decision about whom to support. Nevertheless, the popular vote count presents many problems and should be interpreted carefully.
After winning West Virginia, the Clinton campaign claimed a lead in the popular vote. However, the math behind this claim relied upon a number of points that were disputed by neutral political observers and by the Obama campaign.[10][11][9][12] Most problematically, the Clinton campaign count gave Clinton 328,309 votes and Obama 0 votes in the disputed Michigan primary as Obama had withdrawn his name from the ballot.
Problems with popular vote metrics
Caucus states
The popular vote is easiest to tally in primary elections, where a simple vote for a candidate is recorded. In caucuses, the "popular vote" is often interpreted as the number of supporters who vote for each candidate at the conclusion of precinct-level caucuses. The table uses the official "popular vote" reported in all primary states and in the caucus states of Alaska, American Samoa, Colorado, Idaho, Minnesota, North Dakota, Nebraska, Hawaii, Wyoming, and Guam. Official numbers were not reported in the caucus states of Iowa, Nevada, Washington, and Maine. These four states have been estimated by RealClearPolitics based on other information released by the states.[13] In Texas, two-thirds of pledged delegates were selected through a primary, while one-third were selected through caucuses. However, voters were eligible to participate in the caucuses only if they also voted in the primary, so RealClearPolitics used the primary results and ignored the caucus in determining the popular vote.
Nationwide, the RealClearPolitics tally counted one caucus participant as equal to one primary participant. However, turnout is generally lower in caucuses, and as a result, the popular vote may overweight the influence of primary states.[14] For example, Hawaii and Rhode Island have similar populations, but the opinion of Rhode Islanders is weighted more heavily in the popular vote total. Clinton won the Rhode Island primary 58-40% and received 33,600 more votes than Obama. In contrast, Obama won the Hawaii caucuses 76-24%, but received only 19,500 more votes than Clinton.[13] Thus, some researchers argue that the popular vote underestimates the depth of Obama's support in caucus states.[15] If these states were to hold primaries and Obama were to win by a similar margin, his popular vote total would be considerably higher.[15] However, Clinton argued that she would have done better in these states if primaries were held.[16]
Florida and Michigan
Florida and Michigan were penalized by the Democratic party, and under the rules as they existed at the time of the elections, the delegates were not to be seated at the Democratic Convention. Toward the end of the primary season, on May 31, the Democratic National Committee restored "half votes" to the disputed primaries, as well as accepting a reapportionment of Michigan delegates proposed by the state party.
In Florida, where both candidates pledged not to campaign, Clinton beat Obama 50-33% in the disputed primary. In Michigan, where Obama and other candidates removed their name from the ballot, Clinton won against "Uncommitted" 55-40%. Exit poll respondents said that if all candidates had been on the ballot, they would have voted 46% Clinton, 35% Obama, 12% Edwards, 3% other.[17] These results do not record the preferences of voters who chose to stay home, believing that their votes would not count.
The Clinton campaign argued that popular vote totals should include Florida and Michigan and that Obama should receive 0 votes in Michigan.[9] Obama's supporters, and some neutral observers, countered that his standing would have improved in these states if the race had been contested normally and that most or all of the "uncommitted" votes in Michigan should be counted as votes for him.[12] Obama argued that the nullified primaries do not represent a true test of popular support, noting that primaries where the candidates are not allowed to campaign amount to little more than a "referendum on name recognition".[18]
Nomination rules
Finally, the nomination was decided by delegates under the Democratic Party's rules, so the candidates campaigned to maximize their delegate advantage. If the nomination were decided by popular vote, they likely would have campaigned differently, in order to run up the vote in populous states like New York and Illinois. House Speaker Nancy Pelosi has said that the popular vote should have no effect under the current rules: "It’s a delegate race. The way the system works is that the delegates choose the nominee."[19] Obama's chief strategist suggested that the Clinton campaign's focus on the popular vote was a distraction tactic: "When they started off, it was all about delegates.... Now that we have more delegates, it’s all about the popular vote. And if that does not work out, they will probably challenge us to a game of cribbage to choose the nominee."[19] Nevertheless, polls have shown that a plurality of Democrats think superdelegates should consider the popular vote when deciding which candidate to support.[20]
Popular vote table
The table below presents various combinations of the "popular vote," accounting for some, but not all, of the problems noted above. The source for the popular vote totals in each state is RealClearPolitics,[13] which aggregates data from official state results and news sources. Not all combinations are reported, only those most commonly cited as popular vote estimates. For example, the table does not reflect exit poll findings on how many voters would have voted for Obama had Obama's name been on the Michigan ballot, since there are many ways to generate this estimate.
| Popular vote (through June 4, 2008)[13] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | Vote estimate | ||||
| Include caucus estimates (IA, NV, WA, ME)[21] |
Include Florida |
Include Michigan |
Michigan "uncommitted" allotted to Obama |
Clinton | Obama |
| yes | yes | yes | all | 18,045,829 | 18,107,587 |
| yes | yes | yes | none | 18,045,829 | 17,869,419 |
| yes | yes | no | - | 17,717,520 | 17,869,419 |
| yes | no | no | - | 16,846,534 | 17,293,205 |
| no | yes | yes | all | 17,821,967 | 17,773,503 |
| no | yes | yes | none | 17,821,967 | 17,535,335 |
| no | yes | no | - | 17,493,658 | 17,535,335 |
| no | no | no | - | 16,622,672 | 16,959,121 |
Graphical representations
In all graphs below, purple represents Obama, green represents Clinton, and orange represents Edwards. Yellow represents a tie.
 |
 |
 |
 |
See also
- Nationwide opinion polling for the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries
- Statewide opinion polling for the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries
- Results of the 2008 Republican Party presidential primaries
References
- ^ "The Silent Superdelegates". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2008-06-07.
- ^ "Superdelegates by Position". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. 2008-06-07. Retrieved 2008-06-08.
- ^ a b Except where noted otherwise, this column displays the number of delegates who have voted as uncommitted, not the number of potential delegates that have yet to be selected in future primaries or caucuses.
- ^ "2008 Democratic Convention Watch". 20 March 2008., DCW estimates.
- ^ "Superdelegate endorsements for Friday 6/6". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2008-06-08.
- ^ Sum of estimated delegates in each contest in the table.
- ^ Sum of bound delegates in each contest in the table.
- ^ All of Nevada's county conventions took place on February 23, but one county's convention (Clark County) had attendance that overwhelmed its ability to continue. That convention was therefore recessed to April 12.
- ^ a b c Hertzberg, Henrik (2008-06-02). "Memory Lapse". The New Yorker. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff; Patrick Healy (2008-05-20). "Obama Expected to Hit Milestone in Tuesday's Vote". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
- ^ Political Ticker (2008-05-14). "Clinton campaign: We're ahead in the popular vote". CNN. Archived from the original on May 17, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
- ^ a b Alter, Jonathan. "Popular Vote Poison". Newsweek.
- ^ a b c d "2008 Democratic Popular Vote". RealClearPolitics.
- ^ Beam, Christopher (2008-04-23). "Clinton's New Favorite Metric". Slate.com. Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ^ a b "New Study Shows Obama Would Have Won Primaries in Caucus States". DemocraticCourage.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2008-04-23. See also Glenn Horowitz and Gregory P. Nini, "How Would Primaries Have Changed the Results in Caucus States?", manuscript, 2008-04-8.
- ^ Hamby, Peter (2008-02-11). "Clinton dismisses weekend losses". CNN. Archived from the original on February 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ^ "Exit poll for Democratic Results". CBS News. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ Smith, Adam (2008-05-22). "Obama suggests halving Florida delegation". St. Petersburg Times. Archived from the original on September 11, 2012. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ a b Simon, Roger (2008-03-17). "Obama camp: HRC is taking the low road". Politico. Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ^ -Abc, This (2008-05-07). "Washington Post-ABC Poll". Washington Post. Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ^ The official popular vote numbers reported in all primary contests and in the caucus contests of Alaska, American Samoa, Colorado, Idaho, Minnesota, North Dakota, Nebraska, Hawaii, Wyoming, and Guam are included in all rows of this table. However, the official popular vote was not reported in IA, NV, WA, ME, and so RealClearPolitics estimated the popular vote in these states based on other figures. This column provides two options: Include those four states or don't include those four states. All other contests are always included.