Taurus (buruj)
| Taurus | |
|---|---|
| Buruj | |
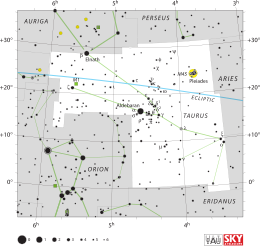 | |
| Nama Latin | Taurus |
| Singkatan | Tau[1][2] |
| Genitif | Tauri[1] |
| Sebutan | |
| Simbolisme | Lembu Jantan[1] |
| Pencerapan | |
| (Epok J2000) | |
| 4.9[4] | |
| Keserongan | 19[4] |
| Sukuan | NQ1 |
| Keluarga | Zodiak |
| Keluasan | 797 darjah persegi (ke-17) |
| Bintang | |
| Bintang utama | 19 |
Bintang Bayer/Flamsteed | 132 |
Bintang dengan planet | 9 calon[a] |
Bintang terang (lebih daripada 3.00m) | 4 |
Bintang dalam 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 1[b] |
Bintang paling terang | Aldebaran (α Tau) (0.85m) |
| Bintang terhampir | Gliese 176 (30.72 tc, 9.42 pc) |
| Objek | |
| Objek Messier | 2 |
| Pancuran meteor |
|
| Buruj bersempadan | |
| Catatan | |
| Boleh dilihat pada garis lintang antara +90° dan −65°. Penglihatan terbaik pada jam 21:00 (9:00 malam) ketika bulan Januari. | |
| sunting | |
Lembu Jantan, Kerbau Jantan, Lembu, Jantan, Saur (Arab: الثور al-Ṯawr), Wrisaba (Sanskrit: वृषभ Vṛṣabhá), atau Taurus (Tau; Lambang: ![]() , Unicode: ♉) ialah salah sebuah buruj zodiak, iaitu buruj ini disilangi oleh satah ekliptik. Taurus ialah buruj besar dan prominen di langit musim sejuk hemisfera utara. Buruj ini merupakan salah sebuah buruj paling lama, bertarikh kembali sekurang-kurang ke Zaman Gangsa Awal apabila Taurus menandakan lokasi Matahari semasa ekuinoks musim bunga. Kepentingannya kepada takwim pertanian mempengaruhi beberapa figura lembu dalam mitologi-mitologi Sumer Purba, Akkad, Assyria, Babilon, Mesir, Yunani, dan Rom.
, Unicode: ♉) ialah salah sebuah buruj zodiak, iaitu buruj ini disilangi oleh satah ekliptik. Taurus ialah buruj besar dan prominen di langit musim sejuk hemisfera utara. Buruj ini merupakan salah sebuah buruj paling lama, bertarikh kembali sekurang-kurang ke Zaman Gangsa Awal apabila Taurus menandakan lokasi Matahari semasa ekuinoks musim bunga. Kepentingannya kepada takwim pertanian mempengaruhi beberapa figura lembu dalam mitologi-mitologi Sumer Purba, Akkad, Assyria, Babilon, Mesir, Yunani, dan Rom.
Lihat juga
- Lembu Jantan (astronomi Cina)
- Pleiades dalam cerita rakyat dan sastera
Catatan
Rujukan
- ^ Sharp, Damian (2005). Learning astrology: an astrology book for beginners. Weiser. m/s. 17. ISBN 978-1-57863-298-5.
- ^ White, Gavin (2008). Babylonian Star-lore: An illustrated guide to the star-lore and constellations of ancient Babylonia. Solaria. m/s. 65. ISBN 978-0-9559037-0-0.
- ^ "T Tauri in NGC 1555". Balai Cerap Astronomi Optik Kebangsaan. Diarkibkan daripada yang asal pada 2019-10-09. Dicapai pada 16 Ogos 2009.
- ^ Schulz, Norbert S. (2005). From dust to stars: studies of the formation and early evolution of stars. Springer Praxis Books, Astrophysics and Astronomy Series. m/s. 231. ISBN 978-3-540-23711-2.
- ^ Babu, Gutti Jogesh; Feigelson, Eric D. (1996). Astrostatistics. CRC Press. m/s. 26. ISBN 978-0-412-98391-7.
- ^ Templat:Petik arXiv
- ^ Templat:Petik news
- ^ Brown, Cynthia Stokes (2008). Big history: from the Big Bang to the present. The New Press. m/s. 64. ISBN 978-1-59558-558-5.
- ^ Rogers, John H. (1998). "Origins of the ancient contellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions". Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 108: 9–28. Bibcode:1998JBAA..108....9R.
- ^ Wilson, Robert (1997). Astronomy through the ages: the story of the human attempt to understand the universe. CRC Press. m/s. 13. ISBN 978-0-7484-0748-4.
- ^ Hines, Derrek (2002). Gilgamesh. Random House Digital, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4000-7733-5.
- ^ Fekel, F. C., Jr.; Tomkin, J. (1 Disember 1982). "Secondaries of eclipsing binaries. IV – The triple system Lambda Tauri". Astrophysical Journal, Part 1. 263: 289–301. Bibcode:1982ApJ...263..289F. doi:10.1086/160503.
- ^ Ridpath, Ian (24 Disember 1988). "Private lives of the stars". New Scientist. 120 (1644): 36.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- ^ Rogers, J. H. (1998). "Origins of the ancient constellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions". Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 108 (1): 9–28. Bibcode:1998JBAA..108....9R.
- ^ Ridpath, Ian (1989). Star tales. James Clarke & Co. m/s. 18–20. ISBN 978-0-7188-2695-6.
- ^ Ptak, Roger (1998). Sky stories: ancient and modern. Nova Publishers. m/s. 22. ISBN 978-1-56072-507-7.
- ^ Palaephatus; Stern, Jacob (1996). On unbelievable tales. Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers. m/s. 47. ISBN 978-0-86516-320-1.
- ^ Noonan, George C. (2005). Classical scientific astrology. American Federation of Astr. m/s. 66–67. ISBN 978-0-86690-049-2.
- ^ Grünwedel, Albert (1901). Burgess, James (penyunting). Buddhist art in India. Agnes C. Gibson. B. Quaritch. m/s. 131.
- ^ Comins, Neil F.; Kaufmann, William J. (2008). Discovering the Universe: from the stars to the planets. Macmillan. m/s. 20. ISBN 978-1-4292-3042-1.
- ^ Bertout, Claude (1989). "T Tauri stars – wild as dust". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 27 (1): 351–395. Bibcode:1989ARA&A..27..351B. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.27.090189.002031.
- ^ Wilkins, Jamie; Dunn, Robert (2006). 300 Astronomical Objects: A visual reference to the Universe (ed. 1st). Buffalo, New York: Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1-55407-175-3.
- ^ Crossen, Craig; Rhemann, Gerald (2004). Sky vistas: astronomy for binoculars and richest-field telescopes. Springer. m/s. 133. ISBN 978-3-211-00851-5.
- ^ Seeds, Michael A. (2007). Foundations of Astronomy (ed. 10th). Cengage Learning. m/s. 19. ISBN 978-0-495-38724-4.
- ^ "Taurus, constellation boundary". The Constellations. Kesatuan Astronomi Antarabangsa. Dicapai pada 2 Januari 2012.
- ^ Lewis, John S. (1997). Rain of iron and ice: the very real threat of comet and asteroid bombardment. Basic Books. m/s. 48–49. ISBN 978-0-201-15494-8.
- ^ Burnham, Robert (1978). Burnham's celestial handbook: an observer's guide to the Universe beyond the Solar System. Three (ed. revised). Courier Dover Publications. m/s. 1807–1830. ISBN 978-0-486-23673-5.
- ^ "Taurus, the bull". Allthesky.com. Dicapai pada 16 Mei 2012.
- ^ Encyclopedia of observances, holidays and celebrations from MobileReference. MobileReference. 2007. m/s. 505. ISBN 978-1-60501-177-6.
- ^ Covington, Michael A. (2002). Celestial objects for modern telescopes. Akhbar Universiti Cambridge. m/s. 240. ISBN 978-0-521-52419-3.
- ^ Kaler, James B. "Theta-1 Tauri". Stars. Universiti Illinois. Dicapai pada 22 Mei 2012.
- ^ "NGC objects in Taurus". The Night Sky Atlas. Dicapai pada 23 April 2012.
- ^ Schaaf, Fred (2008). The brightest stars: discovering the Universe through the sky's most brilliant stars. John Wiley and Sons. m/s. 197. ISBN 978-0-471-70410-2.
- ^ Olcott, William Tyler (1907). A field book of the stars. New York and London: G.P. Putnam's sons. m/s. 96. ISBN 978-1-4179-0283-5. Dicapai pada 30 Jun 2009.
- ^ Inglis, Michael D. (2004). The Observer's guide to the northern Milky Way. Springer. m/s. 184. ISBN 978-1-85233-709-4.
- ^ Sasaki, Chris; Boddy, Joe (2003). Constellations: the stars and stories. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. m/s. 106. ISBN 978-1-4027-0800-8.
- ^ Marx, Siegfried; Pfau, Werner; Lamble, P. (1992). Astrophotography with the Schmidt telescope. Akhbar Universiti Cambridge. m/s. 80. ISBN 978-0-521-39549-6.
- ^ Hawkins, Gerald S. (2002). Mindsteps to the cosmos. World Scientific. m/s. 231. ISBN 978-981-238-123-1.
- ^ Garfinkle, Robert A. (1997). Star-hopping: your visa to viewing the Universe. Akhbar Universiti Cambridge. m/s. 77. ISBN 978-0-521-59889-7. Ralat petik: Tag
<ref>tidak sah, nama "Garfinkle 1997" digunakan secara berulang dengan kandungan yang berbeza - ^ a b c d "The constellations". Kesatuan Astronomi Antarabangsa. Dicapai pada 9 Februari 2010.
- ^ Russell, Henry Norris (1922). "The new international symbols for the constellations". Popular Astronomy. 30: 469. Bibcode:1922PA.....30..469R.
- ^ "Taurus". Merriam-Webster Online. Dicapai pada 9 Februari 2010.
- ^ a b Schaefer, Bradley E. (November 2002). "The latitude and epoch for the formation of the southern Greek constellations". Journal for the History of Astronomy. 33 (113): 313–350. Bibcode:2002JHA....33..313S.
Rujukan buku
- Allen, Richard Hinckley (1963) [1899]. Star names: their lore and meaning (ed. dibetulkan). Dover Publications. m/s. 383. ISBN 978-0-486-21079-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Levy, David H. (2005). Deep Sky Objects. Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-1-59102-361-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- O'Meara, Stephen James (2011). Deep-sky companions: the secret deep. Akhbar Universiti Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-19876-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2003). Monthly sky guide (ed. 6th). Akhbar Universiti Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-53306-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2007). Stars and planets guide. London, United Kingdom: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-725120-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Pautan luar
- The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Taurus (Inggeris)
- BBC article on the possibility of Taurus being represented in Lascaux (Inggeris)
- Star Tales – Taurus (Inggeris)
- Buruj Taurus di Constellation Guide (Inggeris)
Zodiak
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astronomi | Jenis-jenis buruj | ||||||||||||
| Aries | Taurus | Gemini | Cancer | Leo | Virgo | Libra | Scorpius | Ophiuchus | Sagittarius | Capricornus | Aquarius | Pisces |
| Astrologi | Tanda-tanda astrologi | ||||||||||||
| Aries | Taurus | Gemini | Cancer | Leo | Virgo | Libra | Scorpio | Serpentarius | Sagittarius | Capricorn | Aquarius | Pisces |
