Template:Infobox carbon
 Graphite (left) an diamont (richt), twa allotropes o caurbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | clear (diamond) & black (graphite) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(C) | [12.0096, 12.0116] conventional: 12.011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
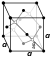
| Carbon in the periodic cairt | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic nummer (Z) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 14 (caurbon group) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | Reactive nonmetal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron confeeguration | [He] 2s2 2p2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pheesical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation pynt | 3915 K (3642 °C, 6588 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | amorphous:[1] 1.8–2.1 g/cm3 diamond: 3.515 g/cm3 graphite: 2.267 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treeple pynt | 4600 K, 10800[2][3] kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat o fusion | 117 (graphite) kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 6.155 (diamond) 8.517 (graphite) J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −4, −3, −2, −1, 0, +1,[4] +2, +3,[5] +4[6] (a mildly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionisation energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 77(sp³), 73(sp²), 69(sp) pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 170 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ither properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naitural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creestal structur | diamond cubic (diamond, clear) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed o soond thin rod | 18350 (diamond) m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 0.8 (diamond)[7] µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 900-2300 (diamond) 119-165 (graphite) W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic orderin | diamagnetic[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 1050 (diamond)[7] GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 478 (diamond)[7] GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 442 (diamond)[7] GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.1 (diamond)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs haurdness | 10 (diamond) 1-2 (graphite) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Nummer | 7440-44-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diskivery | Egyptians an Sumerians[9] (3750 BC) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as an element bi | Antoine Lavoisier[10] (1789) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes o carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Check temperaturs C: na inpit for C, K, F.
Check temperaturs C: na inpit for C, K, F.
References
- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ Haaland, D (1976). "Graphite-liquid-vapor triple point pressure and the density of liquid carbon". Carbon. 14 (6): 357. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(76)90010-5.
- ↑ Savvatimskiy, A (2005). "Measurements of the melting point of graphite and the properties of liquid carbon (a review for 1963–2003)". Carbon. 43 (6): 1115. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2004.12.027.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the Electronic Transition of the Jet-Cooled CCI Free Radical" (PDF). Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the System of CP" (PDF). Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ↑ "Carbon: Binary compounds". Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ↑ a b c d e Properties of diamond, Ioffe Institute Database
- ↑ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition, CRC press.
- ↑ "History of Carbon and Carbon Materials - Center for Applied Energy Research - University of Kentucky". Caer.uky.edu. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ↑ Senese, Fred (200-09-09). "Who discovered carbon?". Frostburg State University. Retrieved 2007-11-24. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the System of CP" (PDF). Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the Electronic Transition of the Jet-Cooled CCI Free Radical" (PDF). Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ↑ "Carbon: Binary compounds". Retrieved 6 December 2007.