ප්රදාහ
Physical effects resulting from activation of the immune systemසැකිල්ල:SHORTDESC:Physical effects resulting from activation of the immune system
| ප්රදාහ |
|---|
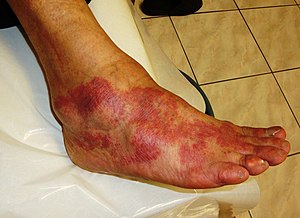 |
| ප්රදාහයක ප්රමුඛ සලකුණු වන්නේ උණුසුම, වේදනාව, රතු වීම, ඉදිමීම, සහ ක්රියා නොකිරීම වෙයි. අසාත්මික ප්රතිචාරයක් හේතුකොට ගෙන ඉන් සමහරක් මෙහි දී දැකිය හැකිය. |
| විශේෂතාව | Immunology, rheumatology |
|---|
| රෝග ලක්ෂණ | Heat, pain, redness, swelling |
|---|
| සංකුලතා | Asthma, pneumonia, autoimmune diseases |
|---|
| කාලපරාසය | Acute: few days
Chronic: up to many months, or years |
|---|
| හේතු | Infection, physical injury, autoimmune disorder |
|---|
ප්රදාහ (ලතින්: inflammatio වෙතින් ආ වදනක් වන ඉංග්රීසි: Inflammation) යනු, ප්රතිශක්තිකරණ පද්ධතිය සක්රීය වීම භෞතිකව පෙන්නුම් කිරීමක් වෙයි. මේවා ව්යාධිජනක, හානි වූ සෛල, හෝ උද්දීපක වැනි හානිකර උත්තේජක කෙරෙහි දේහ පටක දක්වන ජෛවවේදාත්මක ප්රතිචාරයක කොටසක් වෙයි.[1][2] මේවායේ ප්රමුඛ සලකුණු පහ වන්නේ උණුසුම, වේදනාව, රතු වීම, ඉදිමීම, සහ ක්රියා නොකිරීම (ලතින් බසින් calor, dolor, rubor, tumor, සහ functio laesa ලෙස හැඳින්වෙයි) වෙයි.
අමහර අවධානයට
- Anaphylatoxin
- Anti-inflammatories
- Essential fatty acid interactions
- සුවවීම
- Inflammaging
- Inflammatory cytokine
- Inflammatory reflex
- Interleukin
- Lipoxin
- Neurogenic inflammation
- Substance P
- Stress (biology)
- Endothelial Cell Tropism
සටහන්
මූලාශ්ර
- ^ Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE (February 2007). "Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 147 (2): 227–235. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03261.x. PMC 1810472. PMID 17223962.
- ^ Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, et al. (January 2018). "Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs". Oncotarget. 9 (6). Impact Journals, LLC: 7204–7218. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.23208. PMC 5805548. PMID 29467962. S2CID 3571245.
භාහිර සබැඳි
ප්රදාහ හා සබැඳි මාධ්ය විකිමාධ්ය කොමන්ස් හි ඇත.
- Inflammation at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
|
|---|
| Symptoms |
- Flushing (Rubor)
- Fever (Calor)
- Swelling (Tumor)
- Pain (Dolor)
- Loss of function (Functio laesa)
|
|---|
| Mechanism | | Acute | | Plasma-derived mediators |
- Bradykinin
- complement
- coagulation
- Factor XII
- Plasmin
- Thrombin
|
|---|
| Cell-derived mediators | | preformed |
- Lysosome granules
- biogenic amines
|
|---|
| synthesized on demand |
- cytokines
- eicosanoids
- Leukotriene B4
- Prostaglandins
- Nitric oxide
- Kinins
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Chronic |
- Macrophage
- Epithelioid cell
- Giant cell
- Granuloma
|
|---|
| Other |
- Acute-phase reaction
- Vasodilation
- Increased vascular permeability
- Exudate
- Leukocyte extravasation
- Chemotaxis
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Tests |
- Full blood count
- C-reactive protein
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
|
|---|
| General |
- Lymphadenopathy
- List of inflammatory disorders
|
|---|
Lymphocytic adaptive immune system and complement |
|---|
| Lymphoid | | Antigens |
- Antigen
- Superantigen
- Allergen
- Antigenic variation
- Hapten
- Antigen presentation/professional APCs: Dendritic cell
- Macrophage
- B cell
- Immunogen
|
|---|
| Antibodies |
- Antibody
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Polyclonal antibodies
- Autoantibody
- Microantibody
- Polyclonal B cell response
- Allotype
- Isotype
- Idiotype
|
|---|
Immunity vs.
tolerance |
- Inaction: Tolerance
- Central
- Peripheral
- Clonal anergy
- Clonal deletion
- Tolerance in pregnancy
- Immunodeficiency
- Immune privilege
|
|---|
| Immunogenetics |
- Affinity maturation
- Somatic hypermutation
- Clonal selection
- V(D)J recombination
- Junctional diversity
- Immunoglobulin class switching
- MHC/HLA
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Lymphocytes | |
|---|
| Substances |
- Cytokines
- Opsonin
- Cytolysin
|
|---|
Pathology |
|---|
| Principles of pathology |
- Cellular adaptation
- Atrophy
- Hypertrophy
- Hyperplasia
- Dysplasia
- Metaplasia
- Squamous
- Glandular
- Cell death
- Necrosis
- Coagulative necrosis
- Liquefactive necrosis
- Gangrenous necrosis
- Caseous necrosis
- Fat necrosis
- Fibrinoid necrosis
- Myocytolysis
- Programmed cell death
- Apoptosis
- Pyknosis
- Karyorrhexis
- Karyolysis
- Accumulations
- pigment
- Hemosiderin
- Lipochrome/Lipofuscin
- Melanin
- Steatosis
|
|---|
| Anatomical pathology |
- Surgical pathology
- Cytopathology
- Autopsy
- Molecular pathology
- Forensic pathology
- Oral and maxillofacial pathology
- Gross processing
- Histopathology
- Immunohistochemistry
- Electron microscopy
- Immunofluorescence
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization
|
|---|
| Clinical pathology |
- Clinical chemistry
- Hematopathology
- Transfusion medicine
- Medical microbiology
- Diagnostic immunology
- Immunopathology
- Enzyme assay
- Mass spectrometry
- Chromatography
- Flow cytometry
- Blood bank
- Microbiological culture
- Serology
|
|---|
