กลุ่มอาการโชเกรน
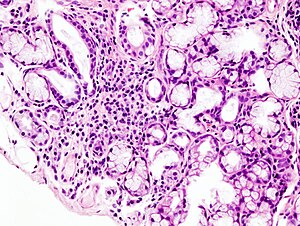
กลุ่มอาการโชเกรน ชื่ออื่น Sjögren's syndrome, sicca syndrome ภาพจากกล้องจุลทรรศน์ แสดงการแทรกซึมของลิมฟอยด์ เฉพาะจุดในต่อมน้ำลายน้อย ซึ่งเกี่ยวข้องกับกลุ่มอาการโชเกรน การออกเสียง , [ 1] ภาษาสวีเดน: [ˈɧø̂ːɡreːn] สาขาวิชา วิทยาภูมิคุ้มกัน , วิทยารูมาติก อาการ ปากแห้ง, ตาแห้ง, ภาวะแห้งในอวัยวะอื่น[ 2] ภาวะแทรกซ้อน มะเร็งต่อมน้ำเหลือง [ 2] การตั้งต้น วัยกลางคน[ 2] [ 3] ระยะดำเนินโรค ระยะยาว[ 4] สาเหตุ โรคภูมิต้านตนเอง (ไม่ทราบสาเหตุ)[ 4] วิธีวินิจฉัย การตัดเนื้อออกตรวจ , การตรวจเลือด [ 2] โรคอื่นที่คล้ายกัน ผลเคียงข้างจากยา, ความวิตกกังวล , โรคซาร์คอยด์, โรคแอมิลอยด์ [ 5] การรักษา น้ำตาเทียม, ยาแก้อักเสบ, การผ่าตัด[ 4] พยากรณ์โรค การคาดหมายคงชีพ ปกติ[ 6] ความชุก ~0.7%[ 7]
กลุ่มอาการโชเกรน (อังกฤษ : Sjögren syndrome, Sjögren's syndrome ; ย่อ SjS, SS) เป็นโรคภูมิต้านตนเอง ระยะยาวที่ส่งผลต่ออวัยวะผลิตของเหลวในร่างกายอย่างต่อมน้ำตาและต่อมน้ำลาย [ 4] [ 8] [ 2] ล้า [ 9] ต่อมไทรอยด์ทำงานผิดปกติ [ 4] มะเร็งต่อมน้ำเหลือง มากขึ้น 15%[ 2] [ 7]
ยังไม่ทราบสาเหตุแน่ชัดของกลุ่มอาการโชเกรน แต่คาดว่าเป็นกรรมพันธุ์ ร่วมกับสิ่งกระตุ้นทางสิ่งแวดล้อมอย่างการติดเชื้อไวรัส และแบคทีเรีย [ 4] [ 3] ข้ออักเสบรูมาตอยด์ (RA) ลูปัส อีริทีมาโตซัส ทั่วร่าง (SLE) และโรคหนังแข็งทั่วร่าง การวินิจฉัยใช้การเก็บตัวอย่างต่อมน้ำลาย เพื่อหาลิมโฟไซต์ และการตรวจเลือด เพื่อหาสารภูมิต้านทาน [ 2]
แม้กลุ่มอาการโชเกรนจะเป็นหนึ่งในโรคภูมิต้านตนเองที่พบได้ทั่วไป แต่ยังไม่มีการตรวจวินิจฉัยโรคแบบไม่ล่วงล้ำที่เฉพาะเจาะจง การรักษาเป็นการจัดการกับอาการผู้ป่วย[ 4] [ 4] หมากฝรั่ง (โดยเฉพาะชนิดไม่มีน้ำตาล) การจิบน้ำหรือใช้สารทดแทนน้ำลายในการบรรเทาอาการปากแห้ง[ 4] สารต้านฮิสตามีน ซึ่งก่อให้เกิดภาวะแห้ง[ 4]
เฮนริก โชเกรน จักษุแพทย์ชาวสวีเดนอธิบายโรคนี้ในปี ค.ศ. 1933 อย่างไรก็ตามยัน มิคุลิช-ราเดกคี ศัลยแพทย์ชาวเยอรมัน–โปแลนด์บรรยายถึงอาการผู้ป่วยก่อนหน้านี้ในปี ค.ศ. 1892[ 10] [ 11] [ 7] [ 3] [ 2] [ 3] การคาดหมายคงชีพ ปกติ[ 6]
↑ Elsevier , Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Brito-Zerón, Pilar; Baldini, Chiara; Bootsma, Hendrika; Bowman, Simon J.; Jonsson, Roland; Mariette, Xavier; Sivils, Kathy; Theander, Elke; Tzioufas, Athanasios; Ramos-Casals, Manuel (7 July 2016). "Sjögren syndrome". Nature Reviews Disease Primers . 2 (1): 16047. doi :10.1038/nrdp.2016.47 . hdl:11568/809074 PMID 27383445 . S2CID 4049076 . ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ng, Wan-Fai (2016). Sjögren's Syndrome ISBN 9780198736950 เก็บ จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 15 August 2016. ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 "What Is Sjögren's Syndrome? Fast Facts" . NIAMS . November 2014. เก็บ จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 4 July 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 15 July 2016 .↑ Ferri, Fred F. (2010). Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby. p. Chapter S. ISBN 978-0323076999 ↑ 6.0 6.1 Singh, AG; Singh, S; Matteson, EL (March 2016). "Rate, risk factors and causes of mortality in patients with Sjögren's syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies" . Rheumatology . 55 (3): 450–60. doi :10.1093/rheumatology/kev354 . PMC 5009445 PMID 26412810 . ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 John H., Klippel (2008). Primer on the rheumatic diseases ISBN 9780387685663 เก็บ จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 15 August 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 15 July 2016 . ↑ Holdgate, Nicholas; St. Clair, E. Wiliam (17 June 2016). "Recent advances in primary Sjogren's syndrome" . F1000Research . 5 : 1412. doi :10.12688/f1000research.8352.1 . PMC 4916986 PMID 27347394 . ↑ Cornec, Divi; Devauchelle-Pensec, Valérie; Mariette, Xavier; Jousse-Joulin, Sandrine; Berthelot, Jean-Marie; Perdriger, Aleth; Puéchal, Xavier; Le Guern, Véronique; Sibilia, Jean; Gottenberg, Jacques-Eric; Chiche, Laurent; Hachulla, Eric; Yves Hatron, Pierre; Goeb, Vincent; Hayem, Gilles; Morel, Jacques; Zarnitsky, Charles; Dubost, Jean Jacques; Saliou, Philippe; Pers, Jacques Olivier; Seror, Raphaèle; Saraux, Alain (April 2017). "Severe Health-Related Quality of Life Impairment in Active Primary Sjögren's Syndrome and Patient-Reported Outcomes: Data From a Large Therapeutic Trial" . Arthritis Care & Research . 69 (4): 528–535. doi :10.1002/acr.22974 PMID 27390310 . S2CID 22904103 . ↑ Fox R. I. (2005). "Sjögren's syndrome". Lancet . 366 (9482): 321–331. doi :10.1016/s0140-6736(05)66990-5 . PMID 16039337 . S2CID 16426363 . ↑ Parke AL, Buchanan WW (1998). "Sjögren's syndrome: History, clinical and pathological features". Inflammopharmacology . 6 (4): 271–87. doi :10.1007/s10787-998-0012-6 . PMID 17657625 . S2CID 12580734 .
Type I/allergy /atopy
จากภายนอก จากภูมิต้านตนเอง
Type II/ADCCIgM , IgG )
จากภายนอก จากภูมิต้านตนเอง
Cytotoxic
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
Bullous pemphigoid
Pemphigus vulgaris
ไข้รูมาติก Goodpasture's syndrome "Type 5 "/receptor
Type III
จากภายนอก จากภูมิต้านตนเอง
Type IV/cell-mediated
จากภายนอก
Allergic contact dermatitis
Mantoux test จากภูมิต้านตนเอง โรคกราฟท์ต่อกรกับโฮสต์
Transfusion-associated graft versus host disease
Unknown/
จากภายนอก
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Transplant rejection
Latex allergy (I+IV) จากภูมิต้านตนเอง
กลุ่มอาการโชเกรน Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome
Autoimmune adrenalitis
Systemic autoimmune disease
Oral and maxillofacial pathology (K00–K06, K11–K14, 520–525, 527–529)
Lips
Cheilitis
Actinic
Angular
Plasma cell
Cleft lip Congenital lip pit
Eclabium
Herpes labialis
Macrocheilia
Microcheilia
Nasolabial cyst
Sun poisoning
Trumpeter's wart
Tongue
Ankyloglossia
Black hairy tongue
Caviar tongue
Crenated tongue
Cunnilingus tongue
Fissured tongue
Foliate papillitis
Glossitis
Glossoptosis
Hypoglossia
Lingual thyroid
Macroglossia
Microglossia
Rhabdomyoma
Palate
Bednar's aphthae
Cleft palate High-arched palate
Palatal cysts of the newborn
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
Stomatitis nicotina
Torus palatinus
Oral mucosa – Lining of mouth
Amalgam tattoo
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
Behçet's disease
Bohn's nodules
Burning mouth syndrome
Candidiasis
Condyloma acuminatum
Darier's disease
Epulis fissuratum
Erythema multiforme Erythroplakia
Fibroma
Focal epithelial hyperplasia
Fordyce spots
Hairy leukoplakia
Hand, foot and mouth disease Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
Herpangina Herpes zoster Intraoral dental sinus
Leukoedema
Leukoplakia
Lichen planus
Linea alba
Lupus erythematosus Melanocytic nevus
Melanocytic oral lesion
Molluscum contagiosum Morsicatio buccarum
Oral cancer
Benign: Squamous cell papillomaKeratoacanthoma
Malignant: Adenosquamous carcinomaBasaloid squamous carcinoma
Mucosal melanoma
Spindle cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Verrucous carcinoma
Oral florid papillomatosis
Oral melanosis
Pemphigoid
Pemphigus Plasmoacanthoma
Stomatitis
Aphthous
Denture-related
Herpetic
Smokeless tobacco keratosis
Submucous fibrosis
Ulceration
Verruca vulgaris
Verruciform xanthoma
White sponge nevus
Teeth (pulp, dentin, enamel)
Amelogenesis imperfecta
Ankylosis
Anodontia
Caries
Concrescence
Failure of eruption of teeth
Dens evaginatus
Dentin dysplasia
Dentin hypersensitivity
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dilaceration
Discoloration
Ectopic enamel
Enamel hypocalcification
Enamel hypoplasia
Enamel pearl
Fluorosis
Fusion
Gemination
Hyperdontia
Hypodontia
Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis
Impaction
Macrodontia
Meth mouth
Microdontia
Odontogenic tumors
Keratocystic odontogenic tumour
Odontoma
Open contact
Premature eruption
Pulp calcification
Pulp canal obliteration
Pulp necrosis
Pulp polyp
Pulpitis
Regional odontodysplasia
Resorption
Shovel-shaped incisors
Supernumerary root
Taurodontism
Trauma
Avulsion
Cracked tooth syndrome
Vertical root fracture
Occlusal
Tooth loss
Tooth wear
Abrasion
Abfraction
Acid erosion
Attrition
Periodontium (gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, alveolus) – Gums and tooth-supporting structures
Cementicle
Cementoblastoma
Cementoma
Eruption cyst
Epulis
Pyogenic granuloma
Congenital epulis
Gingival enlargement
Gingival cyst of the adult
Gingival cyst of the newborn
Gingivitis
Desquamative
Granulomatous
Plasma cell
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis
Hypercementosis
Hypocementosis
Linear gingival erythema
Necrotizing periodontal diseases
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Pericoronitis
Peri-implantitis
Periodontal abscess
Periodontal trauma
Periodontitis
Aggressive
As a manifestation of systemic disease
Chronic
Perio-endo lesion
Teething
Periapaical, mandibular and maxillary hard tissues – Bones of jaws
Agnathia
Alveolar osteitis
Buccal exostosis
Cherubism
Idiopathic osteosclerosis
Mandibular fracture
Microgenia
Micrognathia
Intraosseous cysts
Odontogenic: periapicalDentigerous
Buccal bifurcation
Lateral periodontal
Globulomaxillary
Calcifying odontogenic
Glandular odontogenic
Non-odontogenic: Nasopalatine ductMedian mandibular
Median palatal
Traumatic bone
Osteoma
Osteomyelitis
Osteonecrosis
Bisphosphonate-associated
Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis
Osteoporotic bone marrow defect
Paget's disease of bone
Periapical abscess
Periapical periodontitis
Stafne defect
Torus mandibularis
Temporomandibular joints, muscles of mastication and malocclusions – Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities
Bruxism
Condylar resorption
Mandibular dislocation
Malocclusion
Crossbite
Open bite
Overbite
Overeruption
Overjet
Prognathia
Retrognathia
Scissor bite
Maxillary hypoplasia
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Salivary glands
Benign lymphoepithelial lesion
Ectopic salivary gland tissue
Frey's syndrome
HIV salivary gland disease
Necrotizing sialometaplasia
Mucocele
Pneumoparotitis
Salivary duct stricture
Salivary gland aplasia
Salivary gland atresia
Salivary gland diverticulum
Salivary gland fistula
Salivary gland hyperplasia
Salivary gland hypoplasia
Salivary gland neoplasms
Benign: Basal cell adenomaCanalicular adenoma
Ductal papilloma
Monomorphic adenoma
Myoepithelioma
Oncocytoma
Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
Pleomorphic adenoma
Sebaceous adenoma
Malignant: Acinic cell carcinomaAdenocarcinoma Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
Lymphoma Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Sclerosing polycystic adenosis
Sialadenitis
Parotitis
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
Sialectasis
Sialocele
Sialodochitis
Sialosis
Sialolithiasis
กลุ่มอาการโชเกรน
Orofacial soft tissues – Soft tissues around the mouth
Actinomycosis
Angioedema
Basal cell carcinoma
Cutaneous sinus of dental origin
Cystic hygroma
Gnathophyma
Ludwig's angina Macrostomia
Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome
Microstomia
Noma
Oral Crohn's disease
Orofacial granulomatosis
Perioral dermatitis
Pyostomatitis vegetans
Other
Eagle syndrome
Hemifacial hypertrophy
Facial hemiatrophy
Oral manifestations of systemic disease
The article is a derivative under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License .
A link to the original article can be found here and attribution parties here
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use . Gpedia ® is a registered trademark of the Cyberajah Pty Ltd