مسیحی ریاست
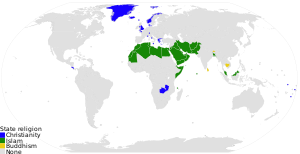
مسیحیت بطور سرکاری مذہب
مسیحی ریاست (انگریزی: Christian state) ایک ایسا ملک ہے جو مسیحیت کی کسی ایک شکل کو اپنے سرکاری مذہب کے طور پر تسلیم کرتا ہے اور اکثر اس کا اپنا ریاستی کلیسیا ہوتا ہے، [1] جو ملک کا غالب مسیحی فرقہ ہوتا ہے جسے حکومت کی حمایت حاصل ہوتی ہے۔ [2]
تاریخی طور پر آرمینیا [3]، حبشہ (ایتھوپیا) [4]، جارجیا [5] اور ان کے علاوہ رومی سلطنت اور بازنطینی سلطنت بھی خود کو مسیحی ریاست [6][7] قرار دے چکی ہیں۔
آج کئی قومیں باضابطہ طور پر خود کو مسیحی ریاست کے طور شناخت کرواتی ہیں یا ان کا اپنا ریاستی کلیسیا ہے، ان میں ارجنٹائن،[8] کوسٹاریکا،[9] ڈنمارک،[10] انگلستان،[11] جزائر فارو،[12] یونان،[13] گرین لینڈ،[14] آئس لینڈ،[15] لیختینستائن،[16] مالٹا،[17] موناکو،[18] سامووا،[19] ٹونگا،[20] تووالو،[21] ویٹیکن سٹی،[22] اور زیمبیا [23] شامل ہیں۔
ریاستی کلیسیا یا سابقہ ریاستی کلیسیا
| ملک | کلیسیا | مذہبی فرقہ | تحلیل |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anhalt | Evangelical State Church of Anhalt | united Protestant | 1918 |
| آرمینیا | آرمینیائی رسولی کلیسیا | اورینٹل راسخ الاعتقادی | 1921 |
| آسٹریا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1918 |
| Baden | کاتھولک کلیسیا and the United Evangelical Protestant State Church of Baden | کاتھولک کلیسیا and united Protestant | 1918 |
| مملکت بویریا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1918 |
| بولیویا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 2009 |
| برازیل[note 1] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1890 |
| Brunswick | Evangelical Lutheran State Church in Brunswick | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| بلغاریہ | بلغاری راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1946 |
| چلی | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1925 |
| کولمبیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1936[24] |
| Connecticut Colony | Congregational Church | کالوینیت | 1818 |
| کیوبا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1902 |
| قبرص | کلیسیائے قبرص | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1977 with the death of the Ethnarch مکاریوس سوم |
| چیکو سلوواکیہ | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1920 |
| ڈنمارک | Church of Denmark | لوتھریت | Current |
| East Florida | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1783 |
| انگلستان | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | Current |
| سلطنت ایتھوپیا | حبشی راسخ الاعتقاد توحیدی کلیسیا | اورینٹل راسخ الاعتقادی | 1974 |
| جزائر فارو | Church of the Faroe Islands | لوتھریت | Current; elevated from a diocese of the Church of Denmark in 2007 (the two remain in close cooperation) |
| فن لینڈ | Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland | لوتھریت | 1869 |
| Finnish Orthodox Church | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1917 | |
| فرانس[note 2] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1905 |
| جارجیا | جارجیائی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1921 |
| یونان | کلیسیائے یونان | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا[25] | The کلیسیائے یونان is recognized by the Greek Constitution as the "prevailing religion" in Greece.[25] However, this provision does not give official status to the Church of Greece, while all other religions are recognized as equal and may be practiced freely.[26] |
| گرین لینڈ | Church of Denmark | لوتھریت | Current; under discussion to be elevated from The Diocese of Greenland in the Church of Denmark to a state church for Greenland, along‐the‐lines the Faroese Church took in 2007 |
| گواتیمالا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1871 |
| ہیٹی | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1987 |
| ہوائی | Church of Hawaii | انگلیکانیت | 1893 |
| Hesse | Evangelical Church in Hesse | united Protestant | 1918 |
| مجارستان[note 3] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1946 |
| آئس لینڈ | Lutheran Evangelical Church | لوتھریت | Current |
| مملکت آئرلینڈ[note 4] | کلیسیائے آئرلینڈ | انگلیکانیت | 1871 |
| جمہوریہ آئرلینڈ[note 5] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1973 |
| اطالیہ | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1985 |
| لیختینستائن | کاتھولک کلیسیا[33] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | Current |
| Lippe | Church of Lippe | کالوینیت | 1918 |
| لتھووینیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1940 |
| Lübeck | Evangelical Lutheran Church in the State of Lübeck | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| لکسمبرگ | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | Current |
| شمالی مقدونیہ | Macedonian Orthodox Church | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1921 |
| مالٹا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | Current |
| Mecklenburg-Schwerin | Evangelical Lutheran State Church of Mecklenburg-Schwerin | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| Mecklenburg-Strelitz | Mecklenburg-Strelitz State Church | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| میکسیکو | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1857 (reestablished between 1864 and 1867) |
| موناکو | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | Current |
| نیدرلینڈز | ولندیزی اصلاح شدہ کلیسیا | کالوینیت | 1795 |
| نیو برنزویک | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | |
| ناروے | Church of Norway | لوتھریت | 2017[34][35] |
| نووا سکوشیا | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1850 |
| Oldenburg | Evangelical Lutheran Church of Oldenburg | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| پاناما | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1904 |
| پیراگوئے | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1992[36] |
| فلپائن[note 6] | Roman Catholic Church | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1898 |
| پولینڈ[note 7] | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1947 |
| پرتگال | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1910, 1976 (reestablished between 1933 and 1974) |
| پرنس ایڈورڈ آئی لینڈ | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | |
| Province of Georgia, برطانوی امریکہ | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1789 |
| صوبہ میری لینڈ | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1776 |
| Province of Massachusetts Bay | خودمختار کلیسیا | کالوینیت | 1834 |
| Province of New Hampshire | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1877 |
| Province of North Carolina | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1776 |
| Province of South Carolina | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1790 |
| مملکت پروشیا pre 1866 provinces |
Evangelical State Church of Prussia's older Provinces with nine ecclesiastical provinces | united Protestant | 1918 |
| Prussia Province of Hanover |
Evangelical Reformed State Church of the Province of Hanover | Reformed | 1918 |
| Prussia Province of Hanover |
Evangelical Lutheran State Church of Hanover | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| Prussia Province of Hesse-Nassau (partially) |
Evangelical State Church of Frankfurt upon Main | united Protestant | 1918 |
| Prussia Province of Hesse-Nassau (partially) |
Evangelical Church of Electoral Hesse | united Protestant | 1918 |
| Prussia Province of Hesse-Nassau (partially) |
Evangelical State Church in Nassau | united Protestant | 1918 |
| Prussia Prov. of Schleswig-Holstein |
Evangelical Lutheran Church of Schleswig-Holstein | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| کیوبیک | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1960 |
| رومانیہ | رومانیائی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1947 |
| روس | روسی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1917 |
| تورینگن | church bodies in principalities which merged in Thuringia in 1920 | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| Saxony | Evangelical Lutheran State Church of Saxony | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| Schaumburg-Lippe | Evangelical State Church of Schaumburg-Lippe | لوتھریت | 1918 |
| اسکاٹ لینڈ[37] | کلیسیائے اسکاٹ لینڈ | پریسبیٹیرین کلیسیا | State control disclaimed since 1638. Formally recognised as not an established church in 1921 |
| سربیا | سربیائی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا | 1920 |
| ہسپانیہ | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1978 |
| سویڈن | کلیسیائے سویڈن | لوتھریت | 2000 |
| سویٹذرلینڈ | separate Cantonal Churches («Landeskirchen») | Zwinglianism & کالوینیت or کاتھولک کلیسیا | during the 20th century |
| تووالو | Church of Tuvalu | کالوینیت | Current |
| United Province of Canada | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1854 |
| یوراگوئے | کاتھولک کلیسیا | کاتھولک کلیسیا | 1918 (into effect in 1919) |
| Virginia | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1786 |
| Waldeck | Evangelical State Church of Waldeck and Pyrmont | united Protestants | 1918 |
| ویلز[note 8] | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1920 |
| West Florida | کلیسیائے انگلستان | انگلیکانیت | 1783 |
| مملکت وورٹمبرگ | Evangelical State Church in Württemberg | لوتھریت | 1918 |
مزید دیکھیے
حوالہ جات
- ↑ Stephen Backhouse (7 جولائی 2011)۔ Kierkegaard's Critique of Christian Nationalism۔ اوکسفرڈ یونیورسٹی پریس۔ ص 60۔ ISBN:978-0-19-960472-2۔
۔۔۔it is only as an established institution that the Church can fully preserve and promote Christian tradition to the nation. One cannot have a Christian state without a state Church.
- ↑ Edward J. Eberle (28 فروری 2013)۔ Church and State in Western Society: Established Church, Cooperation and Separation۔ Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.۔ ص 6۔ ISBN:978-1-4094-9780-6۔
Under the established church approach, the government will assist the state church and likewise the church will assist the government. Religious education is mandated by law to be taught in all schools, public or private.
- ↑ Henry Hart Milman؛ James Murdock (1887)۔ The History of Christianity۔ A. C. Armstrong & Son۔ ص 258۔
But while Persia fiercely repelled Christianity from its frontier, upon that frontier arose a Christian state. Armenia was the first country which embraced Christianity as the religion of the King, the nobles, and the people.
{حوالہ کتاب}: الوسيط|accessdateبحاجة لـ|مسار=(معاونت) - ↑ Francis D. K. Ching؛ Mark M. Jarzombek؛ Vikramaditya Prakash (13 دسمبر 2010)۔ A Global History of Architecture۔ John Wiley & Sons۔ ص 213۔ ISBN:978-0-470-40257-3۔
In the 4th century, King Ezana converted to Christianity and declared Aksum a Christian state—the first Christian state in the history of the world.
- ↑ James Stuart Olson؛ Lee Brigance Pappas؛ Nicholas Charles Pappas (1 جنوری 1994)۔ An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires۔ Greenwood Publishing Group۔ ص 242۔ ISBN:978-0-313-27497-8۔
Kartli became a Christian state under King Mirian in 337.
- ↑ Warren Ashby (4 جولائی 2010)۔ A Comprehensive History Of Western Ethics۔ Prometheus Books۔ ص 152۔ ISBN:978-1-61592-694-7۔
In the Edict of Thessalonica (380) he expressed the imperial "desire" that all Roman citizens should become Christians, the emperor adjudging all other madmen and ordering them to be designated as heretics,۔.۔condemned as such.۔.to suffer divine punishment, and, therewith, the vengeance of that power, which we, by celestial authority, have assumed. There was thus created the "Christian State."
- ↑ Richard C. Frucht (2004)۔ Eastern Europe۔ ABC-CLIO۔ ص 627۔ ISBN:978-1-57607-800-6۔
In contrast, the emperor Justinian (527-565) refashioned the eastern part of the Roman Empire into a strong and dynamic Byzantine Empire, which claimed Bosnia-Hercegovina, among other provinces. The Byzantine Empire became the world's predominant Christian state, based on Roman law, Greek culture, and the Greek language.
- ↑ "Argentina"۔ Encyclopædia Britannica۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2008-05-11
- ↑ Alexander Yakobson؛ Amnon Rubinstein (2009)۔ Israel and the Family of Nations: The Jewish Nation-state and Human Rights۔ Taylor & Francis۔ ص 215۔ ISBN:978-0-415-46441-3۔
Thus the Constitution of Costa Rica, which is considered a model of stable democracy in Latin America, states in Article 75: The Roman Catholic and Apostolic Religion is the religion of the State, which contributes to its maintenance, without preventing the free exercise in the Republic of other forms of worship that are not opposed to universal morality or good customs.
- ↑ W. A. R. Shadid (1 جنوری 1995)۔ Religious Freedom and the Position of Islam in Western Europe۔ Peeters Publishers۔ ص 11۔ ISBN:9789039000656۔
Denmark has declared the Evangelical Lutheran church to be that national church (par. 4 of the Constitution)، which corresponds the fact that 91.5% of the population are registered members of this church. This declaration implies that the Danish State does not take a neutral stand in religious matters. Nevertheless, freedom of religion has been incorporated in the Constitution. Nielsen (1992, 77) gives a short description of the position of the minority religious communities in comparison to that of the State Church: The Lutheran established church is a department of the state. Church affairs are government by a central government ministry, and clergy are government employees. The registration of births, deaths and marriages falls under this ministry of church affairs, and normally speaking the local Lutheran pastor is also the official registrar. The other small religious communities, viz. Roman Catholics, Methodists, Baptists and Jews, have the constitutional status of 'recognised communities of faith'۔ … Contrary to the minority religious communities, the Lutheran Church is fully financed by the Danish State.
- ↑ Christian Joppke (3 مئی 2013)۔ Veil۔ John Wiley & Sons۔ ص 1۔ ISBN:978-0-7456-5857-5
- ↑ Faroe Islands in figures 2015 Statistics Faroe Island
- ↑ Qing Jiang (2012)۔ A Confucian Constitutional Order۔ Princeton University Press۔ ص 221۔ ISBN:978-0-691-15460-2۔
The features of the state affect the essence of the state, but the key term is that of historical identity, hence this chapter concentrates on historical identity as the essence of the state, though at times some of the other features will also be referred to. For instance, ancient Greece has now become an Orthodox Christian state. Ancient Persia (Iran) has now become a Muslim state, and the ancient Buddhist states of the Silk Route have also become Islamic states.
- ↑ "Constitution of Denmark" (PDF)
- ↑ J. Gordon Melton (1 جنوری 2005)۔ Encyclopedia of Protestantism۔ Infobase Publishing۔ ص 283۔ ISBN:978-0-8160-6983-5
- ↑ Jonathan Fox (19 مئی 2008)۔ A World Survey of Religion and the State۔ Cambridge University Press۔ ص 119۔ ISBN:978-1-139-47259-3۔
Liechtenstein's constitution designates the Catholic Church as the state Church and guarantees religious freedom. Article 38 provides protection for the property rights of all religious institutions and states that "the administration of church property in the parishes shall be regulated by a specific law; the agreement of church authorities shall be sought before the law is enacted." Article 16 states that religious instruction in public schools "shall be given by church authorities."
- ↑ "Chapter 1 – The Republic of Malta"۔ Legal-Malta۔ 2011-08-27 کو اصل سے آرکائیو کیا گیا۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2011-09-04
{حوالہ ویب}: الوسيط غير المعروف|deadurl=تم تجاهله (معاونت) - ↑ CONSTITUTION DE LA PRINCIPAUTE بذریعہ وے بیک مشین (آرکائیو شدہ ستمبر 27, 2011) (French): Art. 9.، Principaute De Monaco: Ministère d'Etat (archived from the original on 27 ستمبر 2011)۔
- ↑ Grant Wyeth (16 جون 2017)۔ "Samoa Officially Becomes a Christian State"۔ The Diplomat۔ 2017-06-16 کو اصل سے آرکائیو کیا گیا۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2017-06-16
{حوالہ خبر}: استعمال الخط المائل أو الغليظ غير مسموح:|publisher=(معاونت) - ↑ Fodor's (12 فروری 1986)۔ Fodor's South Pacific۔ Fodor's۔ ISBN:978-0-679-01307-5۔
As King George I of Tonga, Tupou created the "modern" Christian state with the Cross dominating its flag, and with the rigorous constitutional clause regulating observation of the Sabbath.
- ↑ Jeroen Temperman (2010)۔ State-Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law۔ Brill Academic Publishers۔ ص 18۔ ISBN:9789004181489۔
The Constitution of Tuvalu in a similar vein constitutes Tuvalu as "an independent State based on Christian principles.۔.and Tuvaluan custom and tradition"; and also the Constitution of Vanuatu proclaims in its Preamble: "[we] HEREBY proclaim the establishment of the united and free Republic of Vanuatu founded on traditional Melanesian values, faith in God, and Christian principles.۔."
- ↑ Jeroen Temperman (2010)۔ State-Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law۔ Brill Academic Publishers۔ ص 18۔ ISBN:9789004181489۔
The Roman Catholic State of Vatican City is, of course, the best contemporary example of a Christian state. The State of Vatican City, originally established by the Lateran Pacts of 1929, approximates most faithfully the ideal-typical conception of theocratic Roman Catholic state. The Pope is ex officio simultaneously leader of the Roman Catholic Church as well as Head of State and Head of the Government of the State of the Vatican City; he also possesses (de jure) absolute authority over the legislative, executive and judicial branches. Practically all acts and policies of the Vatican City revolve around the interests of the Holy See and, apart from the members of the Pontifical Swiss Guard, virtually all inhabitants of the Vatican City are members of the clergy.
- ↑ Philip Jenkins (11 اگست 2011)۔ The Next Christendom: The Coming of Global Christianity۔ Oxford University Press۔ ص 187۔ ISBN:978-0-19-991153-0
- ↑ John Gunter, Inside Latin America (1941), p. 166
- ^ ا ب [1] آرکائیو شدہ (Date missing) بذریعہ hri.org (Error: unknown archive URL) THE CONSTITUTION OF GREECE: SECTION II RELATIONS OF CHURCH AND STATE: Article 3, Hellenic Resources network آرکائیو شدہ (Date missing) بذریعہ hri.org (Error: unknown archive URL).
- ↑ [2] آرکائیو شدہ (Date missing) بذریعہ hri.org (Error: unknown archive URL) THE CONSTITUTION OF GREECE: PART TWO INDIVIDUAL AND SOCIAL RIGHTS: Article 13
- ↑ Constitution of the Republic of Hungary بذریعہ وے بیک مشین (آرکائیو شدہ 20 فروری 2008) (archived from the original on 2008-02-20)
- ↑ The right of thought, the freedom of conscience and religion –Hungary.hu بذریعہ وے بیک مشین (آرکائیو شدہ 23 مئی 2007) (archived from the original on 2007-05-23)
- ^ ا ب E. A. Livingstone؛ M. W. D. Sparks؛ R. W. Peacocke (12 ستمبر 2013)۔ "Ireland"۔ The Concise Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church۔ Oxford University Press۔ ص 286۔ ISBN:9780199659623۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2014-12-03
- ↑ "CONSTITUTION OF IRELAND"۔ Irish Statute Book۔ ص Article 44۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2014-12-03
- ↑ Dermot Keogh؛ Dr. Andrew McCarthy (1 جنوری 2007)۔ The Making of the Irish Constitution 1937: Bunreacht Na HÉireann۔ Mercier Press۔ ص 172۔ ISBN:9781856355612
- ↑ "Fifth Amendment of the Constitution Act, 1972."۔ Irish Statute Book۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2014-12-03
- ↑ Constitution Religion بذریعہ وے بیک مشین (آرکائیو شدہ 26 مارچ 2009) (archived from the original on 2009-03-26).
- ↑ "Norway's church and state to divorce after almost 500 years"۔ christiandaily.com۔ 2018-02-20 کو اصل سے آرکائیو کیا گیا۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2017-01-02
- ↑ "2017 - et kirkehistorisk merkeår"۔ Den norske kirke, Kirkerådet۔ 30 دسمبر 2017۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 2017-01-02
- ↑ Under the 1967 Constitution, Roman Catholicism was the state religion as stated in Article 6: "The Roman Catholic Apostolic religion is the state religion, without prejudice to religious freedom, which is guaranteed in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution. Official relations of the republic with the Holy See shall be governed by concordats or other bilateral agreements." The 1992 Constitution, which replaced the 1967 one, establishes Paraguay as a secular state, as mentioned in section (1) of Article 24: "Freedom of religion, worship, and ideology is recognized without any restrictions other than those established in this Constitution and the law. The State has no official religion."
- ↑ The modern Church of Scotland has always disclaimed recognition as an "established" church. The Church of Scotland Act 1921 formally recognised the Kirk's independence from the state.
حوالہ جات کی نمائش
- ↑ Brazilian Laws - the Federal Constitution - The Organization of State. V-brazil.com. Retrieved 5 May 2012. برازیل had کاتھولک کلیسیا as the state religion from the country's independence, in 1822, until the fall of the سلطنت برازیل. The new Republican government passed, in 1890, Decree 119-A "Decreto 119-A"۔
Prohibits federal and state authorities to intervene on religion, granting freedom of religion.
(still in force), instituting the separation of church and state for the first time in Brazilian law. مثبتیت thinker Demétrio Nunes Ribeiro urged the new government to adopt this stance. The 1891 Constitution, the first under the Republican system of government, abolished privileges for any specific religion, reaffirming the separation of church and state. This has been the case ever since – the 1988 Constitution of Brazil, currently in force, does so in its Nineteenth Article. The Preamble to the Constitution does refer to "God's protection" over the document's promulgation, but this is not legally taken as endorsement of belief in any deity. - ↑ In France the Concordat of 1801 made the Roman Catholic, کالوینیت and لوتھریت churches state-sponsored religions, as well as یہودیت.
- ↑ In Hungary the constitutional laws of 1848 declared five established churches on equal status: the کاتھولک کلیسیا, کالوینیت, لوتھریت, مشرقی راسخ الاعتقاد کلیسیا and توحید پرستی (مسیحیت) Church. In 1868 the law was ratified again after the Ausgleich. In 1895 یہودیت was also recognized as the sixth established church. In 1948 every distinction between the different denominations were abolished.[27][28]
- ↑ In the مملکت آئرلینڈ the کلیسیائے آئرلینڈ was established in the Reformation.[29] The Act of Union 1800 created the متحدہ مملکت برطانیہ عظمی و آئر لینڈ with the کلیسیائے انگلستان established outside Scotland. The Irish Church Act 1869 demerged and disestablished the Church of Ireland,[29] and the island was تقسیم آئرلینڈ.
- ↑ The Republic of Ireland's 1937 constitution prohibits an established religion.[30] Originally, it recognized the "special position" of the Roman Catholic Church "as the guardian of the Faith professed by the great majority of the citizens", and recognized "the کلیسیائے آئرلینڈ, the Presbyterian Church in Ireland, the Methodist Church in Ireland, the کوئکر in Ireland, as well as the Jewish Congregations and the other religious denominations existing in Ireland at the date of the coming into operation of this Constitution".[31] These provisions were deleted in 1973.[32]
- ↑ The Philippines was among several possessions ceded by ہسپانیہ to the United States in 1898; religious freedom was subsequently guaranteed in the archipelago. This was codified in the Philippine Organic Act (1902), section 5: "... That no law shall be made respecting an establishment of religion or prohibiting the free exercise thereof, and that the free exercise and enjoyment of religious profession and worship, without discrimination or preference, shall forever be allowed." A similarly-worded provision still exists in the present Constitution. Catholicism remains the predominant religion, wielding considerable political and cultural influence.
- ↑ Article 25 of the constitution states: "1. Churches and other religious organizations shall have equal rights. 2. Public authorities in the Republic of Poland shall be impartial in matters of personal conviction". Article 114 of the Polish March Constitution of 1921 declared the Roman Catholic Church to hold "the principal position among religious denominations equal before the law" (in reference to the idea of first among equals). The article was continued in force by article 81 of the April Constitution of 1935. The Soviet-backed PKWN Manifesto of 1944 reintroduced the March Constitution, which remained in force until it was replaced by the Small Constitution of 1947.
- ↑ The Church in Wales was split from the کلیسیائے انگلستان in 1920, by Welsh Church Act 1914; at the same time becoming disestablished.