List of historic states of Italy
| History of Italy |
|---|
 |
|
|
Italy, up until its unification in 1861, was a conglomeration of city-states, republics, and other independent entities. The following is a list of the various Italian states during that period. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the arrival of the Middle Ages (in particular from the 11th century), the Italian Peninsula was divided into numerous states. Many of these states consolidated into major political units that balanced the power on the Italian Peninsula: the Papal States, the Venetian Republic, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Milan, the Kingdom of Naples and the Kingdom of Sicily. Unlike all the other Italian states, the republics of Venice and Genoa, thanks to their maritime powers, went beyond territorial conquests within the Italian Peninsula, conquering various regions across the Mediterranean and Black Seas.[1][2]
Ancient Italy

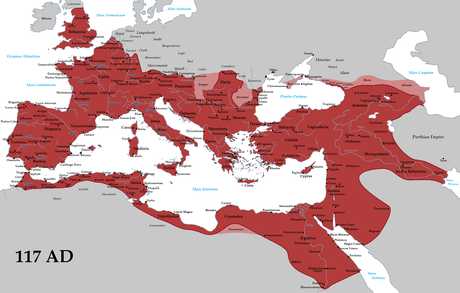
The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as Italic peoples, although in modern linguistics this term is used to define only the speakers of the Italic languages, namely the Latino-Faliscans and the Osco-Umbrians. They include:
- Etruscans
- Italic peoples in the strict sense:
- Latino-Faliscans:
- Osco-Umbrians, also called Sabellians:
- Ligures
- Sardinians
- Greek colonies in Magna Graecia
- Phoenician settlements in insular Italy
- Carthaginian settlements in insular Italy
- Cisalpine Gauls
Early Middle Ages
- Kingdom of Italy
- Ostrogothic Kingdom[3]
- Lombard Kingdom
- Duchy of Rome (under the Byzantine Empire)
- Exarchate of Ravenna (under the Byzantine Empire)
- Exarchate of Carthage (under the Byzantine Empire)
- Thema of Sicily (under the Byzantine Empire)
- Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire)
 Duchy of Benevento
Duchy of Benevento Duchy of Spoleto
Duchy of Spoleto- Duchy of Naples
- Papal States
- Republic of Venice
High Middle Ages

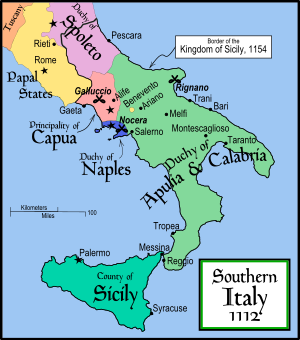
States in Central and Northern Italy
- Papal States
 Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa Republic of Pisa
Republic of Pisa Republic of Florence
Republic of Florence Republic of Lucca
Republic of Lucca Republic of Siena
Republic of Siena Republic of Ancona
Republic of Ancona Republic of Noli
Republic of Noli Republic of Ragusa
Republic of Ragusa- Republic of San Marino
States in Southern Italy
 Principality of Benevento
Principality of Benevento Principality of Salerno
Principality of Salerno- Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire)
- Principality of Capua
 Duchy of Gaeta
Duchy of Gaeta- Duchy of Naples
 Duchy of Amalfi
Duchy of Amalfi Duchy of Sorrento
Duchy of Sorrento Emirate of Sicily (under the Fatimid Caliphate)
Emirate of Sicily (under the Fatimid Caliphate) County of Sicily
County of Sicily County of Apulia
County of Apulia Duchy of Apulia
Duchy of Apulia Duchy of Calabria
Duchy of Calabria Duchy of Apulia and Calabria
Duchy of Apulia and Calabria Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
States of the Holy Roman Empire
 Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy Commune of Milan
Commune of Milan March of Tuscany
March of Tuscany March of Verona
March of Verona- March of Treviso
- March of Ivrea
- March of Turin
 March of Montferrat
March of Montferrat- March of Genoa
 Patriarchate of Aquileia (including March of Friuli and March of Istria)
Patriarchate of Aquileia (including March of Friuli and March of Istria) Duchy of Spoleto
Duchy of Spoleto Bishopric of Brixen
Bishopric of Brixen Bishopric of Trent
Bishopric of Trent County of Savoy
County of Savoy County of Gorizia
County of Gorizia Marquisate of Saluzzo
Marquisate of Saluzzo Marquisate of Ceva
Marquisate of Ceva Marquisate of Incisa
Marquisate of Incisa Marquisate of Finale
Marquisate of Finale
Late Middle Ages

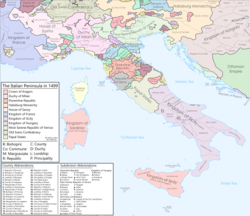
Major states
 Papal States
Papal States Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice Republic of Florence
Republic of Florence Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa
Minor states
 Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica
Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily Duchy of Ferrara
Duchy of Ferrara Lordship of Milan (before being raised to Duchy in 1395)
Lordship of Milan (before being raised to Duchy in 1395) Duchy of Modena and Reggio
Duchy of Modena and Reggio Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
Prince-Bishopric of Brixen Prince-Bishopric of Trent
Prince-Bishopric of Trent Marquisate of Bastia
Marquisate of Bastia Marquisate of Ceva
Marquisate of Ceva Marquisate of Finale
Marquisate of Finale Marquisate of Fosdinovo
Marquisate of Fosdinovo Marquisate of Incisa
Marquisate of Incisa Marquisate of Mantua
Marquisate of Mantua Marquisate of Massa
Marquisate of Massa Marquisate of Saluzzo
Marquisate of Saluzzo Marquisate of Montferrat
Marquisate of Montferrat County of Asti
County of Asti County of Correggio
County of Correggio County of Gorizia
County of Gorizia County of Guastalla
County of Guastalla County of Masserano
County of Masserano County of Mirandola
County of Mirandola County of Montechiarugolo
County of Montechiarugolo County of Novellara
County of Novellara County of Pitigliano
County of Pitigliano County of Santa Fiora
County of Santa Fiora County of Savoy (raised to Duchy of Savoy in 1416)
County of Savoy (raised to Duchy of Savoy in 1416)
 County of Nice (in personal union with Savoy)
County of Nice (in personal union with Savoy)
- County of Scandiano
 County of Sovana
County of Sovana County of Tende
County of Tende County of Urbino (raised to Duchy of Urbino in 1443)
County of Urbino (raised to Duchy of Urbino in 1443) Golden Ambrosian Republic
Golden Ambrosian Republic Republic of Ancona
Republic of Ancona Republic of Cospaia
Republic of Cospaia Republic of Lucca
Republic of Lucca Republic of Noli
Republic of Noli Republic of Ragusa
Republic of Ragusa- Republic of San Marino
 Republic of Siena
Republic of Siena- Rebel city-states in Papal States
After the Italian Wars

The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended the Italian Wars in 1559. The kingdoms of Sicily, Sardinia, Naples (inclusive of the State of Presidi) and the Duchy of Milan were left under the control of Spanish Habsburgs. France was in control of several fortresses and in particular of the Marquisate of Saluzzo. All the other Italian states remained independent, with the most powerful being the Venetian Republic, the Medici's Duchy of Tuscany, the Savoyard state, the Republic of Genoa, and the Papal States. The Gonzaga in Mantua, the Este in Modena and Ferrara and the Farnese in Parma and Piacenza continued to be important dynasties. Parts of the north of Italy remained a part of the Holy Roman Empire.[4][5][6]
Major states
 Papal States
Papal States Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice Grand Duchy of Tuscany
Grand Duchy of Tuscany Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
Minor states
 Kingdom of Sardinia (under Spanish rule)
Kingdom of Sardinia (under Spanish rule) Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
Prince-Bishopric of Brixen Prince-Bishopric of Trent
Prince-Bishopric of Trent Principality of Piombino
Principality of Piombino Principality of Monaco
Principality of Monaco Duchy of Mantua
Duchy of Mantua Duchy of Ferrara
Duchy of Ferrara
 Duchy of Modena and Reggio (In personal union with Ferrara)
Duchy of Modena and Reggio (In personal union with Ferrara)
 Duchy of Parma and Piacenza
Duchy of Parma and Piacenza
 Duchy of Castro (in personal union with Parma)
Duchy of Castro (in personal union with Parma)
 Duchy of Urbino
Duchy of Urbino Marquisate of Bastia
Marquisate of Bastia- Marquisate of Castiglione (raised to Principality of Castiglione in 1609)
 Marquisate of Finale
Marquisate of Finale Marquisate of Fosdinovo
Marquisate of Fosdinovo Marquisate of Massa (raised to Principality of Massa in 1568)
Marquisate of Massa (raised to Principality of Massa in 1568)
- Marquisate of Carrara (in personal union with Massa)
 Marquisate of Masserano (raised to Principality of Masserano in 1598)
Marquisate of Masserano (raised to Principality of Masserano in 1598) Marquisate of Montferrat (raised to Duchy of Montferrat in 1574; in personal union with Mantua)
Marquisate of Montferrat (raised to Duchy of Montferrat in 1574; in personal union with Mantua) Marquisate of Sabbioneta (raised to Duchy of Sabbioneta in 1577)
Marquisate of Sabbioneta (raised to Duchy of Sabbioneta in 1577) Marquisate of Torriglia
Marquisate of Torriglia County of Correggio (raised to Principality of Correggio in 1616)
County of Correggio (raised to Principality of Correggio in 1616) County of Guastalla
County of Guastalla County of Pitigliano
County of Pitigliano County of Mirandola
County of Mirandola County of Montechiarugolo
County of Montechiarugolo County of Novellara
County of Novellara County of Santa Fiora
County of Santa Fiora County of Tende
County of Tende Monastic State of the Order of Malta
Monastic State of the Order of Malta Republic of Ancona
Republic of Ancona Republic of Cospaia
Republic of Cospaia Republic of Lucca
Republic of Lucca Republic of Noli
Republic of Noli Republic of Ragusa
Republic of Ragusa- Republic of San Marino
After the Wars of Succession of the 18th century
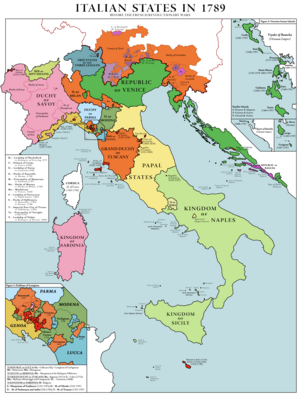
During the war of the Spanish succession (1700-1714), Savoy acquired Sicily, while the remaining Spanish dominions in Italy (Naples, Sardinia, and Milan) were taken over by the Austrian Habsburgs. In 1720, Savoy exchanged Sicily for Sardinia. Following the extinction of the House of Medici, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany was ruled by the Habsburg-Lorraine. Later on, Southern Italy passed to a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon, known as House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies. Other states such as Genoa, Venice, Modena, the Papal States and Lucca remained with their governments unchanged.
Major states
- Papal States
- Kingdom of Naples (under the Habsburg monarchy from 1714 to 1735; in personal union with Sicily under the Bourbon-Two Sicilies thereafter)
 Grand Duchy of Tuscany (under Habsburg-Lorraine after 1737)
Grand Duchy of Tuscany (under Habsburg-Lorraine after 1737) Duchy of Milan (under Habsburg Monarchy)
Duchy of Milan (under Habsburg Monarchy) Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
Minor states
 Kingdom of Sardinia (under Austrian monarchy from 1714 to 1720; in personal union with Savoy thereafter)
Kingdom of Sardinia (under Austrian monarchy from 1714 to 1720; in personal union with Savoy thereafter) Kingdom of Sicily (under Savoy from 1713 to 1720; under Austrian monarchy from 1720 to 1734; in personal union with Naples under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies thereafter)
Kingdom of Sicily (under Savoy from 1713 to 1720; under Austrian monarchy from 1720 to 1734; in personal union with Naples under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies thereafter) Duchy of Mantua (under House of Gonzaga until 1708, Austrian Monarchy thereafter)
Duchy of Mantua (under House of Gonzaga until 1708, Austrian Monarchy thereafter) Duchy of Parma and Piacenza (under Habsburg Monarchy from 1734 to 1748, under House of Bourbon-Parma thereafter)
Duchy of Parma and Piacenza (under Habsburg Monarchy from 1734 to 1748, under House of Bourbon-Parma thereafter) Duchy of Guastalla (in personal union with Parma from 1748)
Duchy of Guastalla (in personal union with Parma from 1748) Duchy of Modena and Reggio
Duchy of Modena and Reggio 
Political map of Italy in the year 1796  Duchy of Massa and Carrara (in personal union with Modena from 1731)
Duchy of Massa and Carrara (in personal union with Modena from 1731) Duchy of Mirandola (in personal union with Modena from 1710)
Duchy of Mirandola (in personal union with Modena from 1710) Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
Prince-Bishopric of Brixen Prince-Bishopric of Trent
Prince-Bishopric of Trent Principality of Masserano
Principality of Masserano Principality of Torriglia
Principality of Torriglia Principality of Piombino
Principality of Piombino Principality of Monaco
Principality of Monaco Duchy of Montferrat, to House of Savoy from 1708
Duchy of Montferrat, to House of Savoy from 1708 Marquisate of Fosdinovo
Marquisate of Fosdinovo Marquisate of Bastia
Marquisate of Bastia Republic of Lucca
Republic of Lucca- Republic of San Marino
 Republic of Ragusa
Republic of Ragusa Republic of Noli
Republic of Noli Republic of Cospaia
Republic of Cospaia City of Fiume and its District
City of Fiume and its District Monastic State of the Order of Malta
Monastic State of the Order of Malta
Their populations and other vital statistics stood as follows in the late 18th century:[7]
- Kingdom of Naples (including Sicily): 6,000,000 (400,000 in Naples), army of 60,000 to 80,000, 2 ships of the lines and some frigates
- Republic of Venice: 3,500,000 (140,000 in the city of Venice itself), standing army and navy of 30,000, 12-15 ships of at least 54 guns plus frigates and brigs
- Kingdom of Sardinia: 2,900,000 (2,400,000 on the mainland and 500,000 on the island), 12-15 fortified cities and towns (largest being Turin at 80,000), standing army of 25,000, which could be raised to 50,000 in a time of war and 100,000 with militia
- Papal States: 2,400,000 (140,000 in the city of Rome), standing army of 6,000 to 7,000
- Austrian Lombardy (Duchy of Milan, Duchy of Mantua, and minor territories): 1,100,000 (40,000 in the city of Milan itself)
- Grand Duchy of Tuscany: 1,000,000 (80,000 in Florence), standing army of 6,000, navy of 3 frigates
- Republic of Genoa: 500,000 (100,000 in the city of Genoa itself)
- Duchy of Parma: 500,000 (40,000 in the city of Parma itself), standing army of 2,500 to 3,000
- Duchy of Modena: 350,000 (20,000 in the city of Modena itself), standing army of 5,000 to 6,000
- Republic of Lucca: 100,000
Total: 18.3 million
During Napoleonic times (1792–1815)
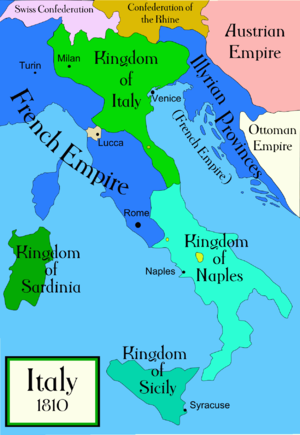
Sister republics of Revolutionary France
 Republic of Alba
Republic of Alba Anconine Republic
Anconine Republic Astese Republic
Astese Republic Republic of Bergamo
Republic of Bergamo- Bolognese Republic
 Republic of Brescia
Republic of Brescia Cisalpine Republic
Cisalpine Republic Cispadane Republic
Cispadane Republic Republic of Crema
Republic of Crema Italian Republic
Italian Republic Ligurian Republic
Ligurian Republic Jacobin State of Lucca
Jacobin State of Lucca Parthenopean Republic
Parthenopean Republic Republic of Pescara
Republic of Pescara- Piedmontese Republic
 Roman Republic
Roman Republic- Subalpine Republic
- Tiberina Republic
 Transpadane Republic
Transpadane Republic
Client states of the First French Empire
 Kingdom of Etruria
Kingdom of Etruria Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples Principality of Lucca and Piombino
Principality of Lucca and Piombino Principality of Benevento
Principality of Benevento Principality of Pontecorvo
Principality of Pontecorvo
Other states
 Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia- Kingdom of Sicily
 Principality of Elba (non-hereditary Monarchy under the exiled Emperor Napoleon)
Principality of Elba (non-hereditary Monarchy under the exiled Emperor Napoleon) Republic of Cospaia
Republic of Cospaia- Republic of San Marino
From the restoration to the unification

Following the defeat of Napoleon's France, the Congress of Vienna (1815) was convened to redraw the European continent. In Italy, the Congress restored the pre-Napoleonic patchwork of independent governments, either directly ruled or strongly influenced by the prevailing European powers, particularly Austria. The Congress also determined the end of two millenary republics: Genoa was annexed by the then Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia, and Venice was incorporated with Milan into a new kingdom of the Austrian Empire.
At the time, the struggle for Italian unification was perceived to be waged primarily against the Habsburgs, since they directly controlled the predominantly Italian-speaking northeastern part of present-day Italy and were the most powerful force against the Italian unification. The Austrian Empire vigorously repressed nationalist sentiment growing in its domains on the Italian Peninsula, as well as in the other parts of Habsburg domains.
 Papal States
Papal States Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia (under Austrian Empire)
Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia (under Austrian Empire) Kingdom of Illyria (under Austrian Empire)
Kingdom of Illyria (under Austrian Empire) Grand Duchy of Tuscany
Grand Duchy of Tuscany Duchy of Parma, Piacenza and Guastalla
Duchy of Parma, Piacenza and Guastalla Duchy of Modena and Reggio
Duchy of Modena and Reggio Duchy of Massa and Carrara
Duchy of Massa and Carrara Duchy of Lucca
Duchy of Lucca Principality of Monaco
Principality of Monaco Republic of San Marino
Republic of San Marino Republic of Cospaia
Republic of Cospaia Republic of San Marco
Republic of San Marco Roman Republic
Roman Republic United Provinces of Central Italy
United Provinces of Central Italy
Post-unification

 Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy Republic of San Marino
Republic of San Marino Italian Regency of Carnaro
Italian Regency of Carnaro Free State of Fiume
Free State of Fiume Italian Social Republic
Italian Social Republic Kingdom of the South
Kingdom of the South Free Territory of Trieste
Free Territory of Trieste
Italian Partisan Republics
The Italian Partisan Republics were the provisional state entities liberated by Italian partisans from the rule and occupation of Nazi Germany and the Italian Social Republic in 1944 during the Second World War. They were universally short-lived, with most of them being reconquered by the Wehrmacht within weeks of their formal establishments and re-incorporated into the Italian Social Republic.
 Republic of Alba (10 October - 2 November)
Republic of Alba (10 October - 2 November) Republic of Alto Monferrato (September - 2 December)
Republic of Alto Monferrato (September - 2 December) Republic of Alto Tortonese (September - December)
Republic of Alto Tortonese (September - December) Republic of Bobbio (7 July - 27 August)
Republic of Bobbio (7 July - 27 August) Republic of the Cansiglio (July - September)
Republic of the Cansiglio (July - September) Republic of Carnia (26 September - 10 October)
Republic of Carnia (26 September - 10 October) Republic of Carniola (2 February - March)
Republic of Carniola (2 February - March) Republic of Oriental Friuli (30 June - September)
Republic of Oriental Friuli (30 June - September) Republic of Pigna (IM) (18 September - 8 October)
Republic of Pigna (IM) (18 September - 8 October) Republic of the Langhe (September - November)
Republic of the Langhe (September - November) Republic of Montefiorino (17 June - 1 August)
Republic of Montefiorino (17 June - 1 August) Republic of Ossola (10 September - 23 October)
Republic of Ossola (10 September - 23 October) Republic of Torriglia (26 June - 27 November)
Republic of Torriglia (26 June - 27 November) Republic of the Ceno Valley (10 June - 11 July)
Republic of the Ceno Valley (10 June - 11 July) Republic of the Enza Valley and the Parma Valley (June - July)
Republic of the Enza Valley and the Parma Valley (June - July) Republic of the Maira Valley and the Varaita Valley (June - 21 August)
Republic of the Maira Valley and the Varaita Valley (June - 21 August) Republic of the Taro Valley (15 June - 24 July)
Republic of the Taro Valley (15 June - 24 July) Republic of the Lanzo Valley (25 June - September)
Republic of the Lanzo Valley (25 June - September) Republic of the Sesia Valley (11 June - 10 July)
Republic of the Sesia Valley (11 June - 10 July) Republic of Varzi (19/24 September - 29 November)
Republic of Varzi (19/24 September - 29 November)
Current states
See also
References
- ^ "End of Europe's Middle Ages - Italy's City-States". www.faculty.umb.edu. Retrieved 2021-09-10.
- ^ Bragadin, Marc'Antonio (2010). Storia delle repubbliche marinare (in Italian). Odoya. ISBN 978-8862880824.
- ^ Flavius Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator, Variae, Lib. II., XLI. Luduin regi Francorum Theodericus rex.
- ^ Burman, Edward (1989). Italian Dynasties: Great Families of Italy from the Renaissance to the Present Day. Equation; First Edition. ISBN 1853360058.
- ^ Christine Shaw, Michael Mallett. The Italian Wars 1494-1559: War, State and Society in Early Modern Europe. Routledge.
- ^ "Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis | European history". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2020-09-08.
- ^ Journal of the Private Life and Conversations of the Emperor, Vol. 3. Emmanuel-Auguste-Dieudonne comte de Las Cases. 1816.

